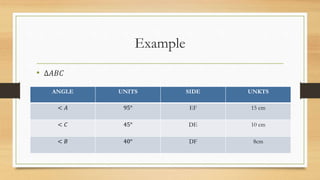
1) The triangle inequality theorem states that in any triangle, the largest side is opposite the largest angle and the smallest side is opposite the smallest angle.
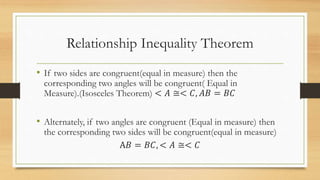
2) If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite those sides are also congruent. Similarly, if two angles are congruent, the sides opposite them are also congruent.
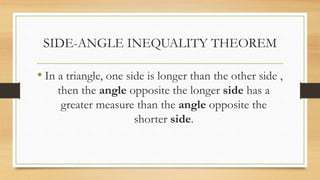
3) In a triangle, if one side is longer than the other, then the angle opposite the longer side has a greater measure than the angle opposite the shorter side.