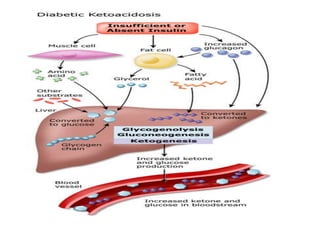
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) are life-threatening emergencies caused by lack of insulin. DKA is characterized by ketosis and acidosis, while HHS involves extreme hyperglycemia and hyperosmolality without significant ketosis. Both require intravenous fluids and insulin to rehydrate the patient and lower blood glucose levels. Complications can include hypoglycemia, cerebral edema, electrolyte imbalances, and death if not properly treated.