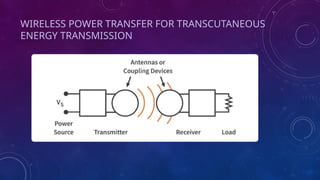
Transcutaneous energy transmission (TET) is a wireless power transfer technology that powers implanted medical devices without the need for percutaneous wires, enhancing patient comfort and reducing infection risk. It utilizes inductive coupling, wireless telemetry, and resonant circuits to ensure efficient energy transfer, and is applied in cardiac, neural, and orthopedic devices. Despite challenges such as tissue heating and alignment, TET is revolutionizing medical implants, improving patient outcomes and extending device lifespans.