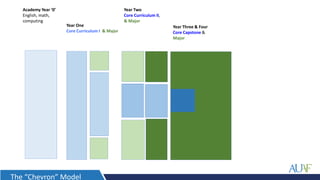
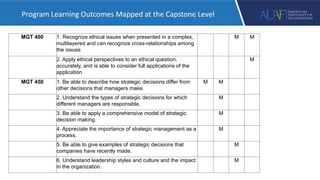
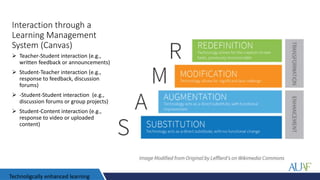
The document outlines AUAF's approach to education, which is informed by liberal arts and sciences traditions. It emphasizes interactive, experiential, and integrated teaching and learning. The curriculum focuses on developing general competencies through a core curriculum before specializing in majors. Learning outcomes are mapped from courses to programs to ensure integration. Teaching methods include discussion, group work, flipped classrooms, projects and case studies. Capstone courses integrate and assess prior learning through final projects.