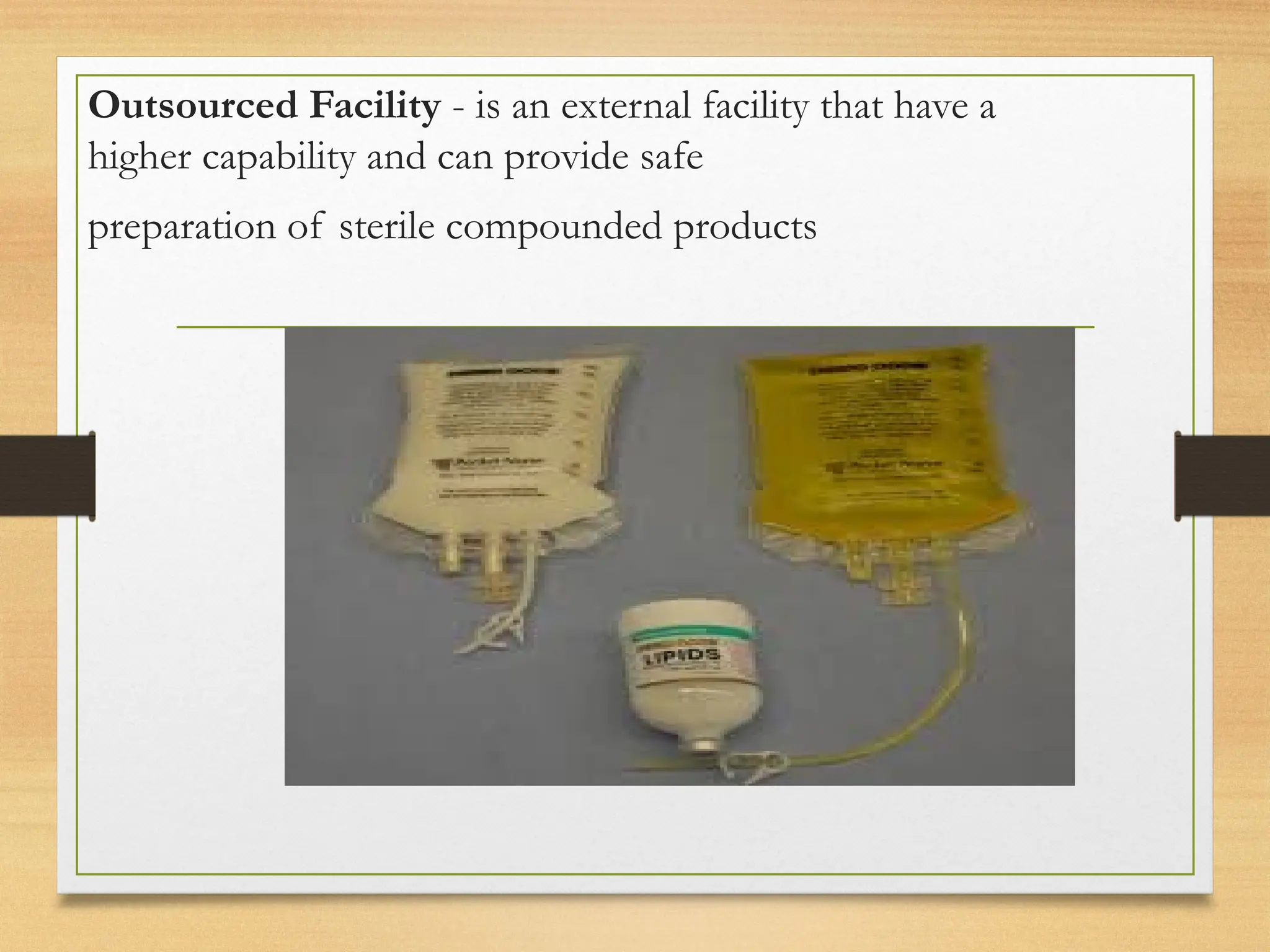
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) is an intravenous feeding method providing essential nutrients when oral intake is not possible. Proper protocols for prescribing, preparing, administering, and monitoring TPN are specified to prevent infections and ensure patient safety. Continuous monitoring and assessment of the patient's condition, including weight and laboratory tests, are crucial to evaluate nutritional status and manage potential complications.