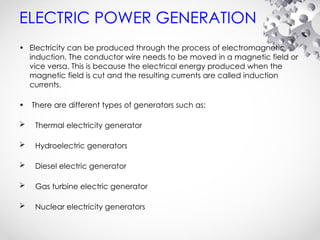
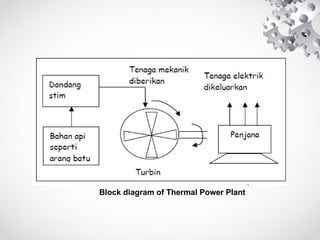
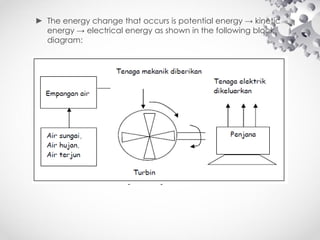
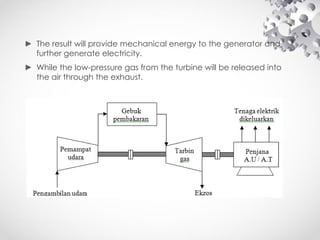
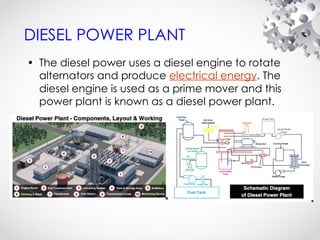
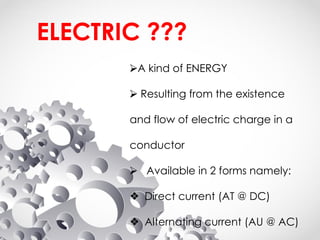
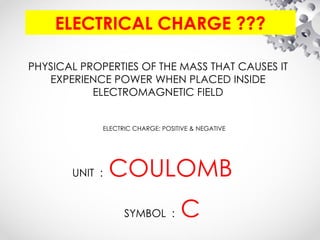
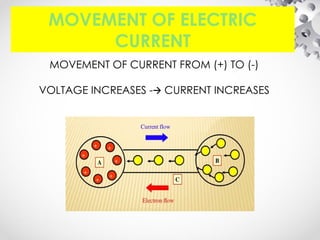
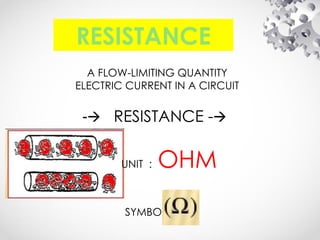
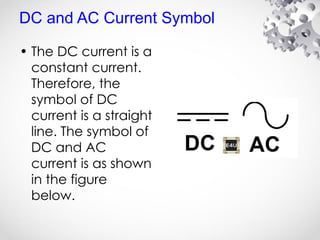
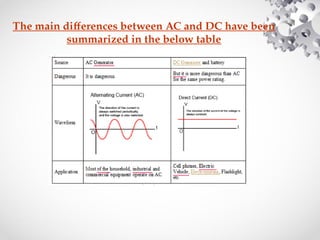
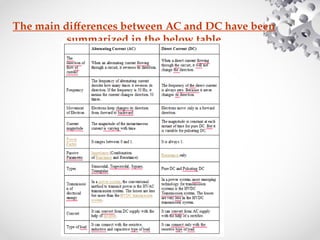
The document discusses the fundamentals of electrical energy, categorizing energy sources into renewable (e.g., solar, wind) and non-renewable (e.g., coal, nuclear). It outlines various methods of electricity generation including thermal, hydroelectric, gas, diesel, and nuclear power plants, explaining their operational principles. Additionally, it explains the concepts of electric charge, current types (DC and AC), and the characteristics of resistance and power in electrical circuits.