Embed presentation
Download to read offline



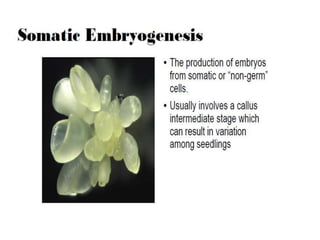

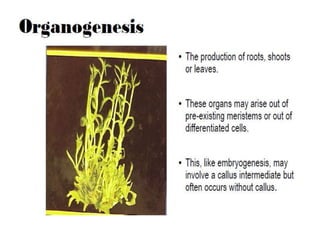

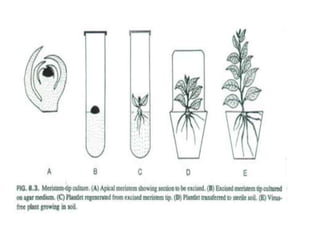


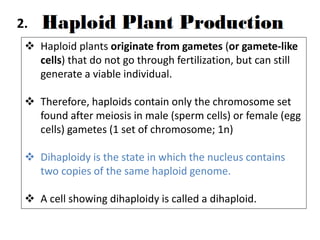
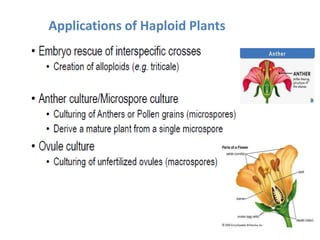
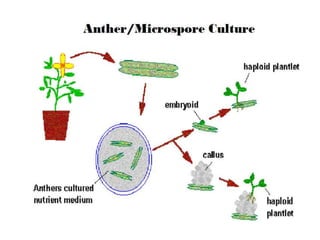
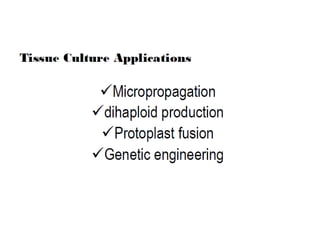


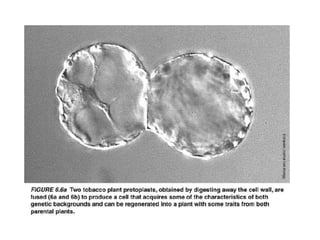
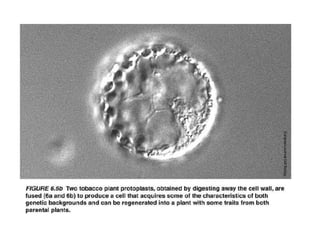
Micropropagation is the artificial process of producing plants through tissue or cell culture techniques. It involves taking plant cells or tissues and growing them in an artificial nutrient medium to produce multiple new plants. Methods include taking advantage of apical dominance to induce branching and producing haploid plants from gametes or gamete-like cells that did not undergo fertilization but can still generate a viable individual containing only one set of chromosomes. Haploid plants and dihaploid cells, which contain two copies of the same haploid genome, have applications in plant breeding and genetics.




















