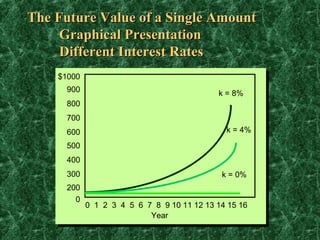
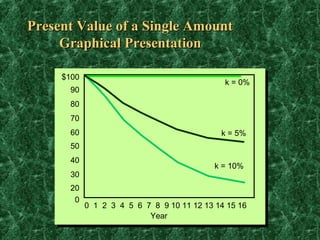
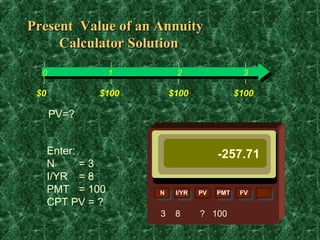
Let k = annual rate of return
FV = PV(1+k)n
230 = 200(1+k)2
1.15 = (1+k)2
1.075 = 1+k
.075 = k
k = 7.5% annual return
Therefore, the annual return on this investment is 7.5%
�Solving for k
Example: You invest $1,000 today and want it to grow to
$1,500 in 5 years. What rate of return is needed?
0 1 2
$1,000 $1,500