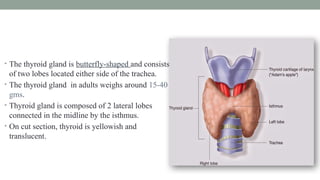
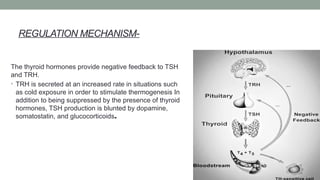
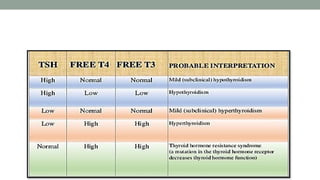
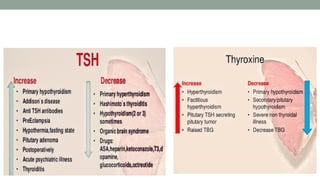
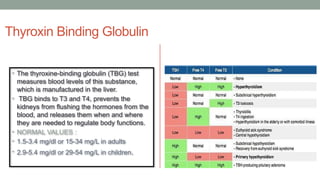
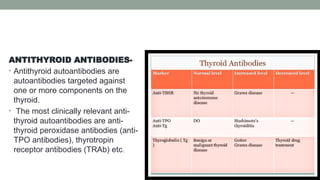
The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ, secretes hormones such as triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), with a role in regulating metabolism and calcium homeostasis. Thyroid function tests include TSH, T3, T4, TBG, T3RU, LATS, and tests for antithyroid antibodies to assess thyroid health. Normal thyroid hormone levels and regulatory mechanisms, including feedback systems involving TSH and TRH, are critical for maintaining homeostasis.