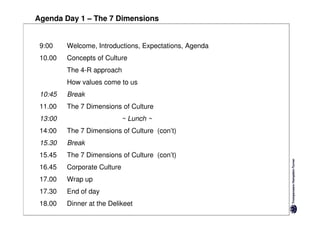
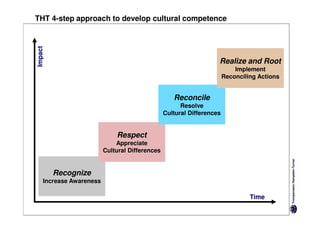
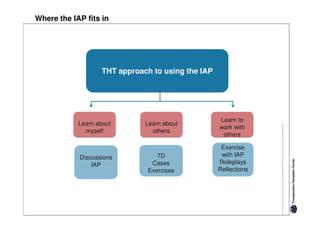
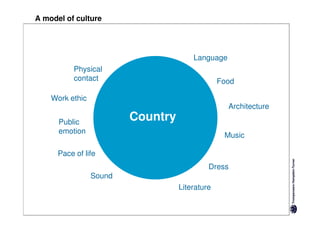
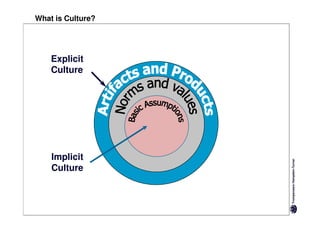
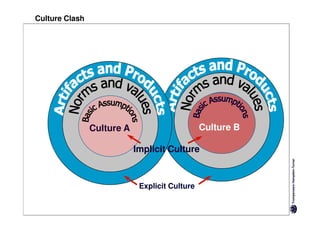
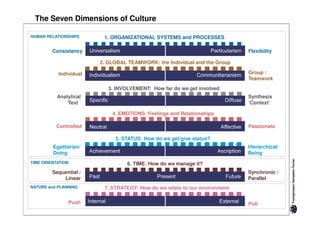
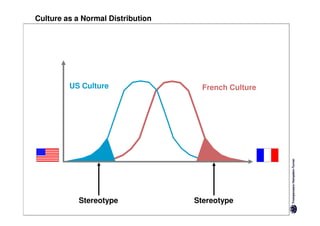
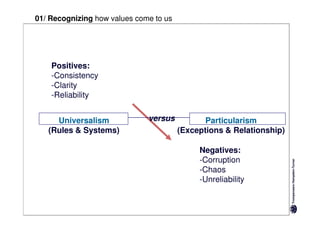
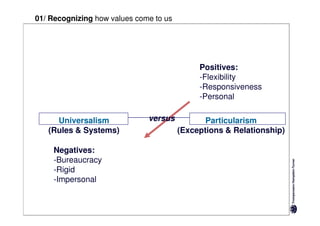
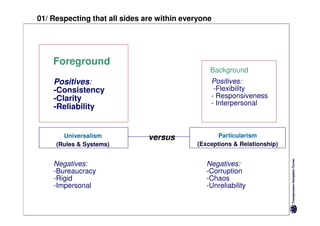
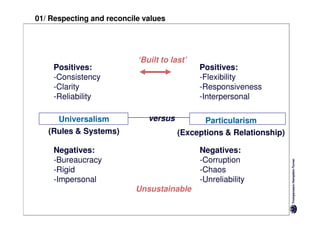
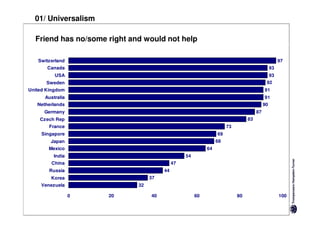
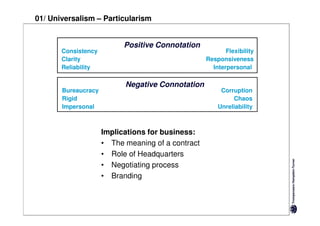
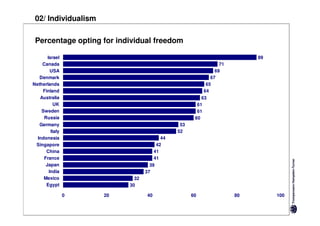
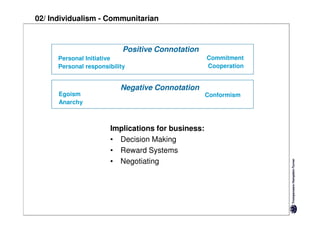
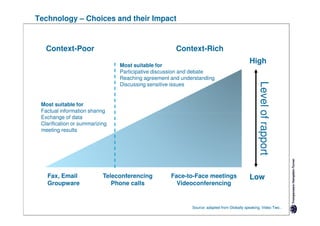
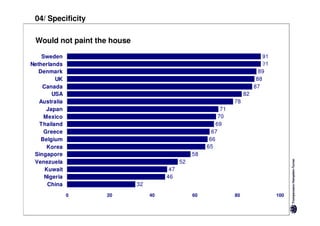
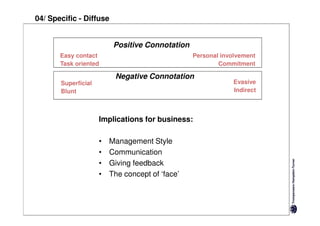
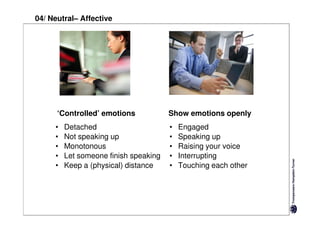
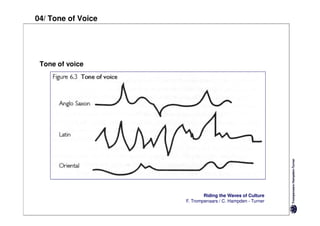
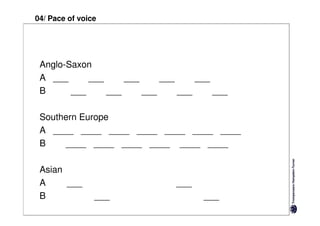
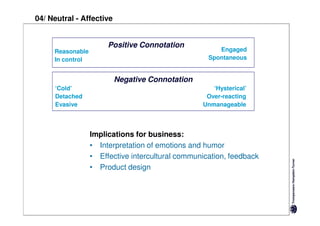
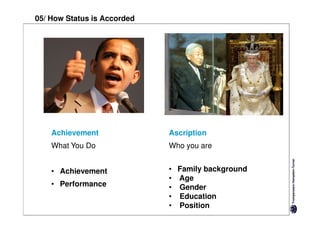
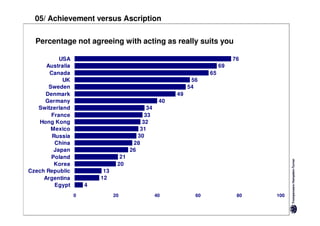
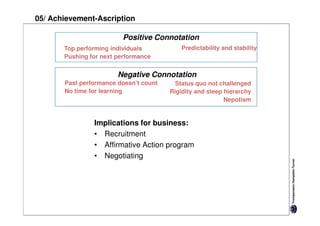
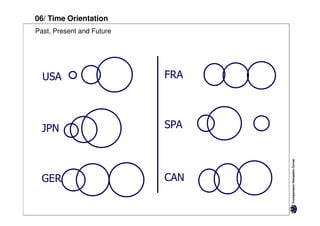
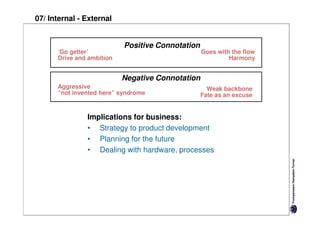
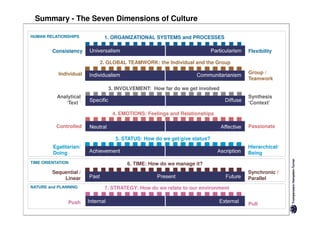
Here are the key differences between specific and diffuse cultures:
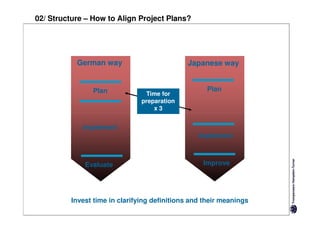
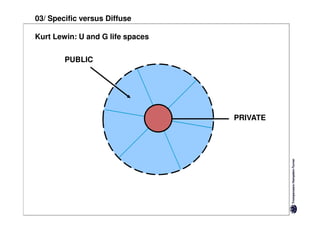
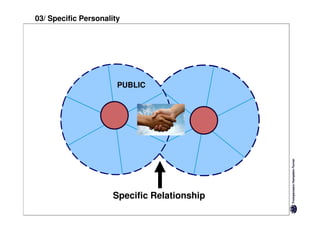
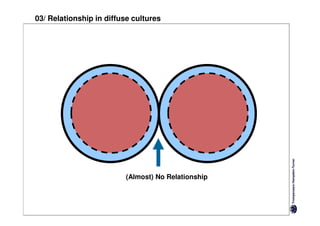
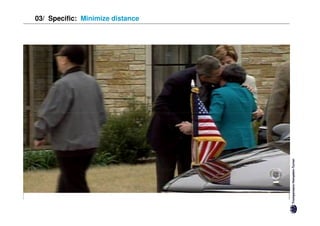
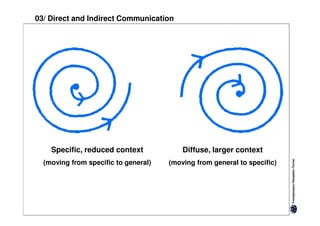
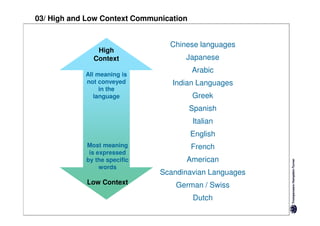
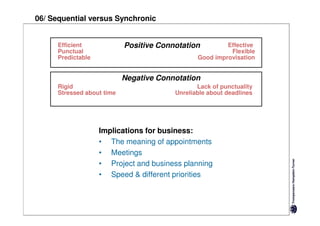
Specific cultures tend to focus more on tasks and have easier initial contact between people. Relationships tend to be more segmented and compartmentalized.
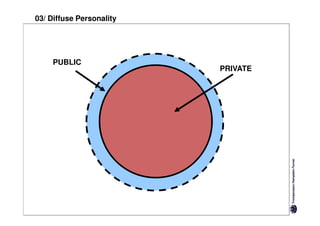
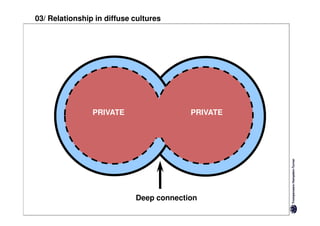
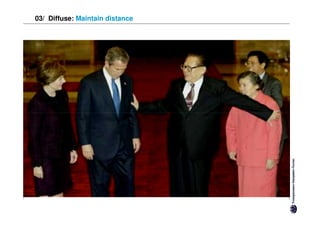
Diffuse cultures place more emphasis on personal involvement and commitment in relationships. Contact tends to develop more slowly as maintaining distance is important initially. Relationships span both personal and professional spheres.
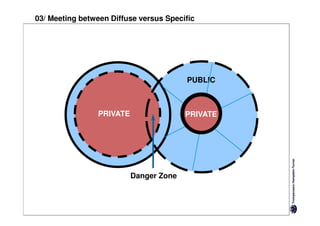
Both have positives and negatives. Specific cultures can come across as more superficial while diffuse cultures may seem less efficient in getting things done. Understanding these differences is important for effective cross-cultural communication and collaboration.