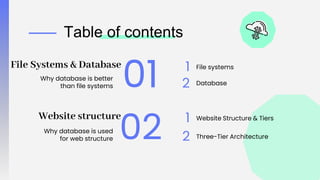
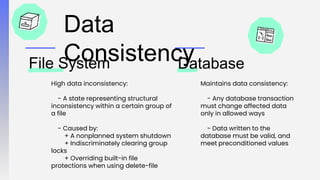
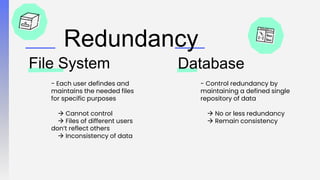
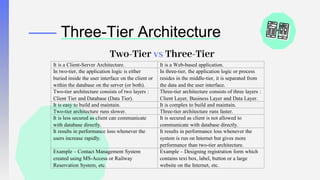
The document discusses three-tier architecture and why databases are better than file systems for websites. It describes three-tier architecture as a client-server architecture with three independent layers or tiers - the presentation tier, application tier, and data tier. This separates the user interface, business logic/processing, and data storage. This makes the architecture more efficient, secure, scalable, flexible, and higher performing compared to two-tier architectures that have the application logic embedded within the user interface or database tiers.