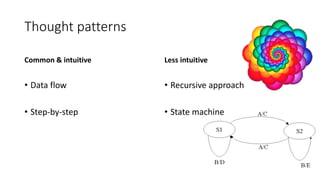
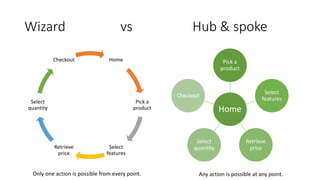
The document discusses software architecture's importance, drawing parallels to linguistic nuances, and introduces Kruchten's 4+1 view model to describe future systems effectively for various stakeholders. It covers architectural patterns, the differences between human and computer processing, and proposes approaches for designing user flows. Additionally, it emphasizes the continual review and iteration of system design to maintain a robust software architecture.


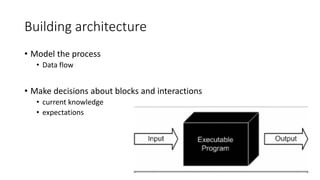

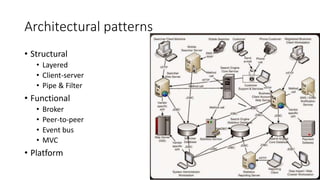
![For all of the architectural patterns:
Pros
• Well-understood
• [Some] Can be delivered piece-
meal
• Offer good support for original
purpose
Cons
• Complex
• [Some] Big bang delivery style
• Suitable in distinct situations
• Hard to expand beyond original
goals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarearchitecture-180506025004/85/Thoughts-on-building-software-architecture-7-320.jpg)