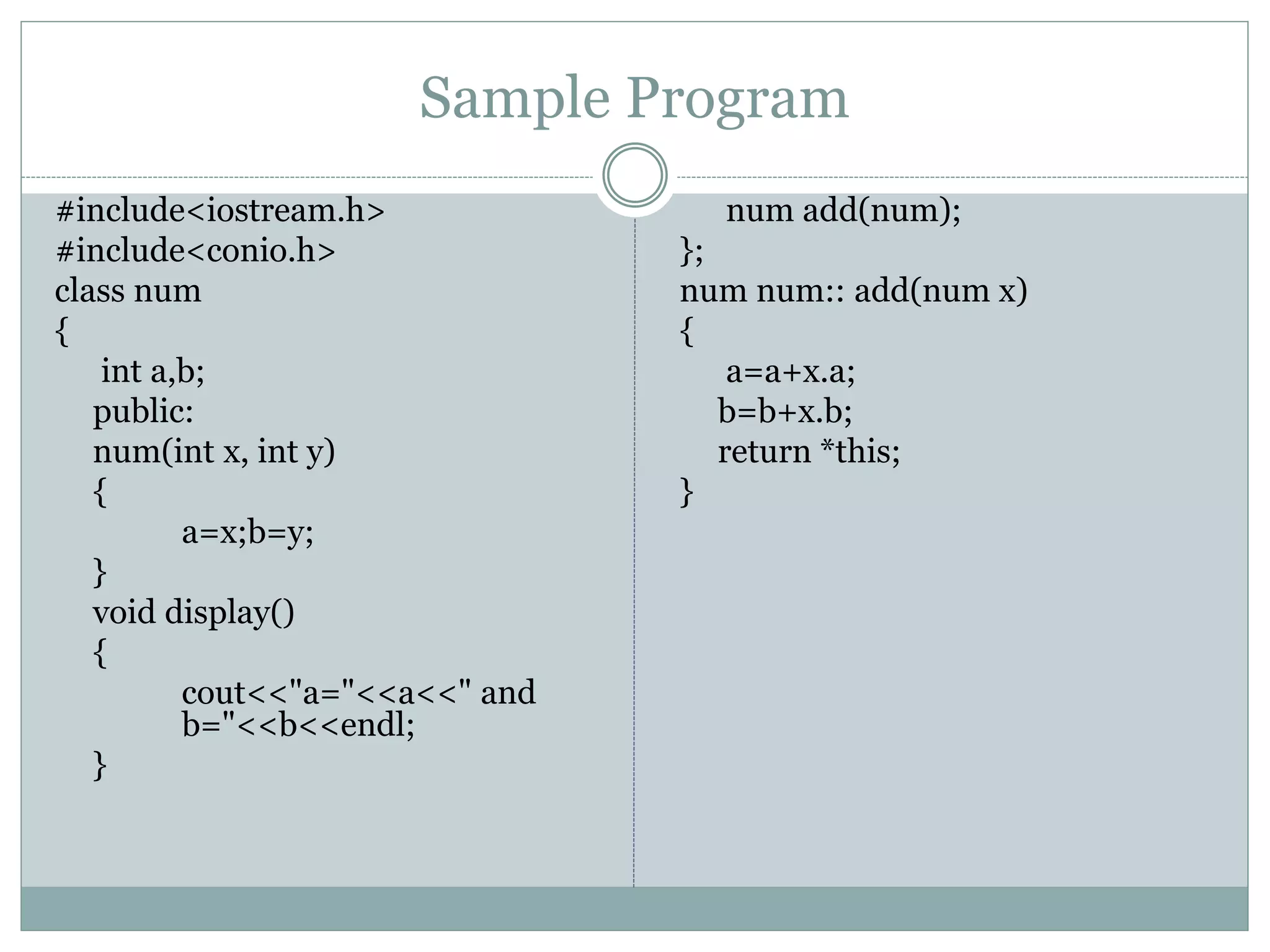
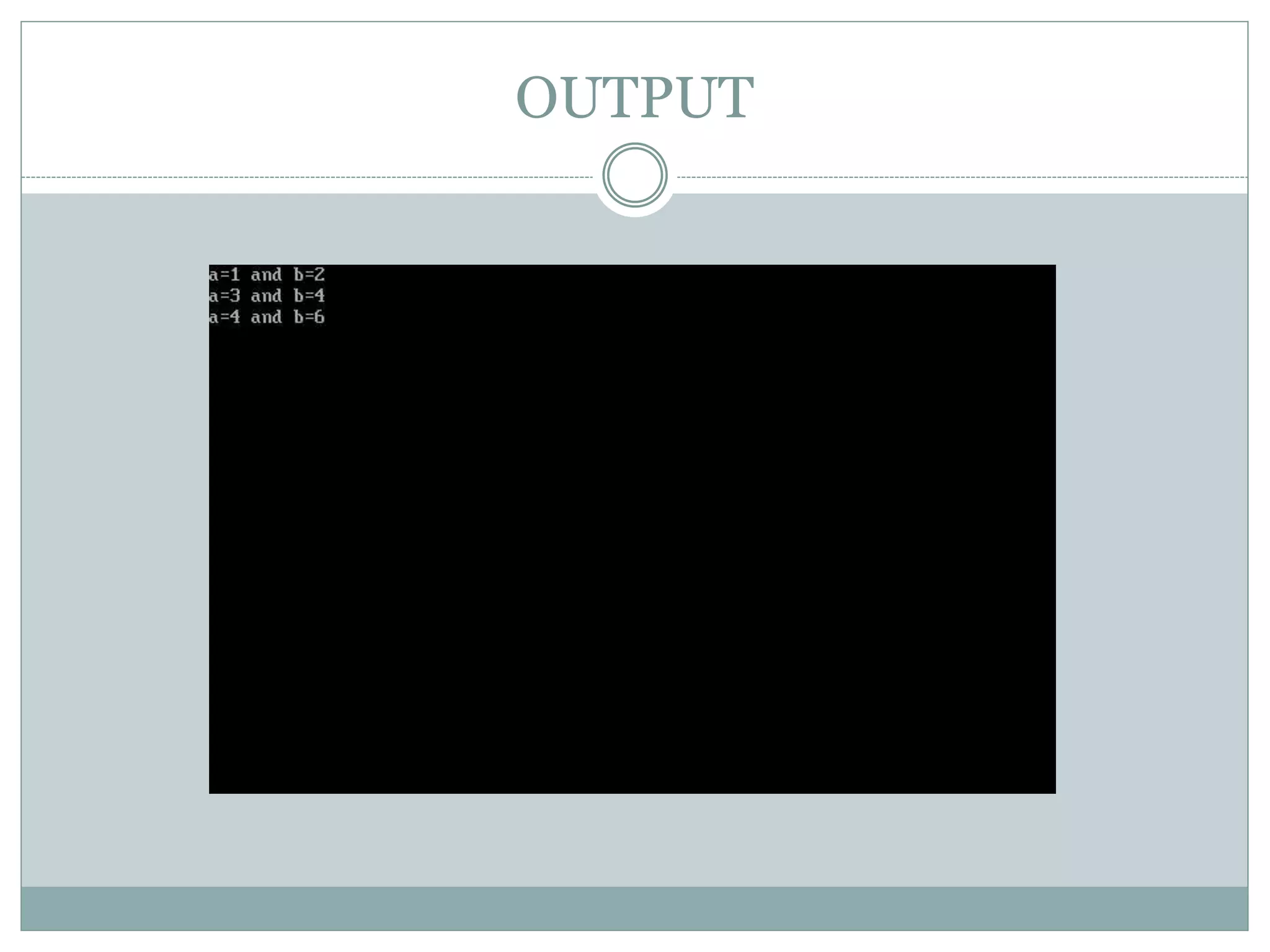
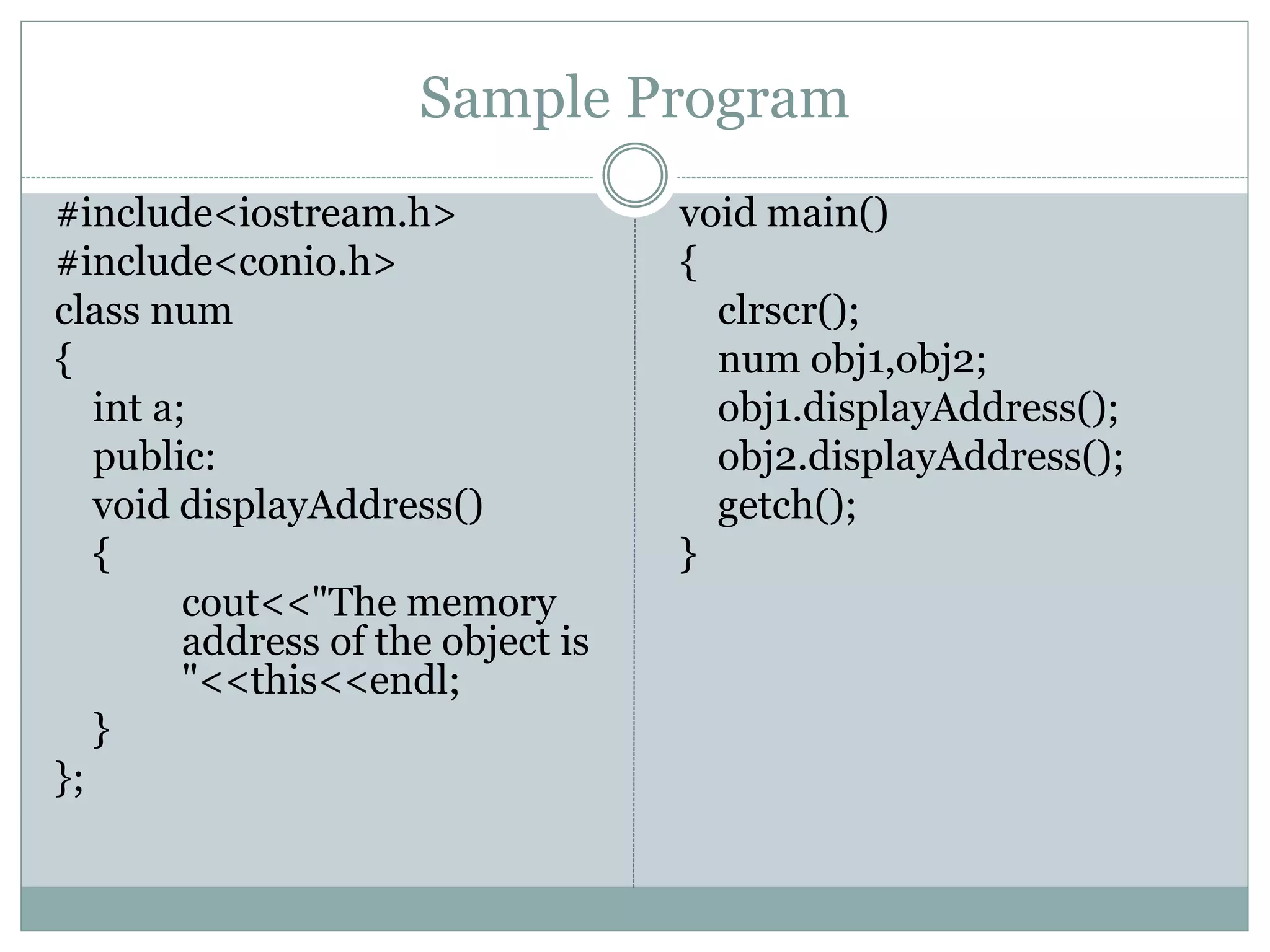
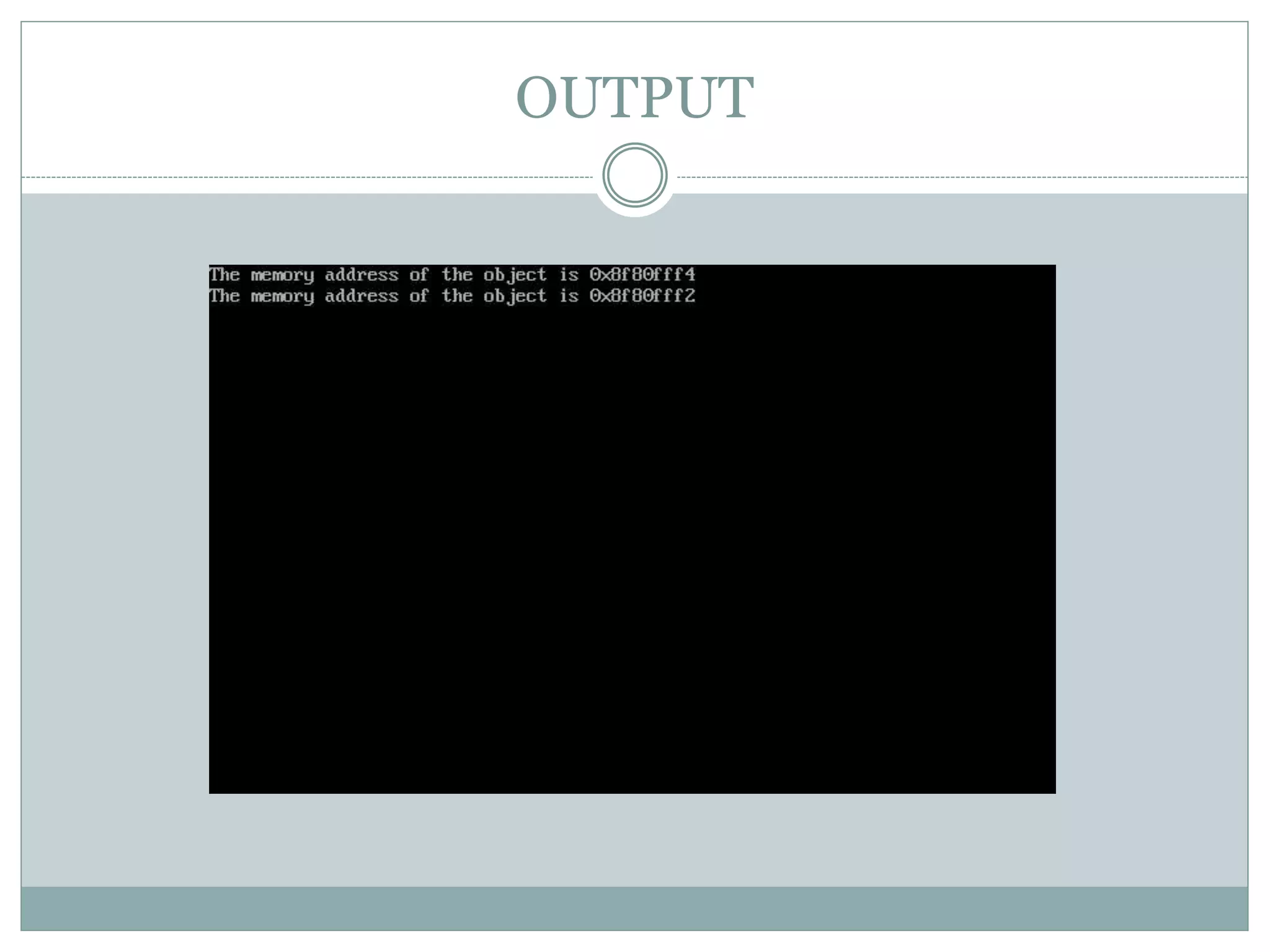
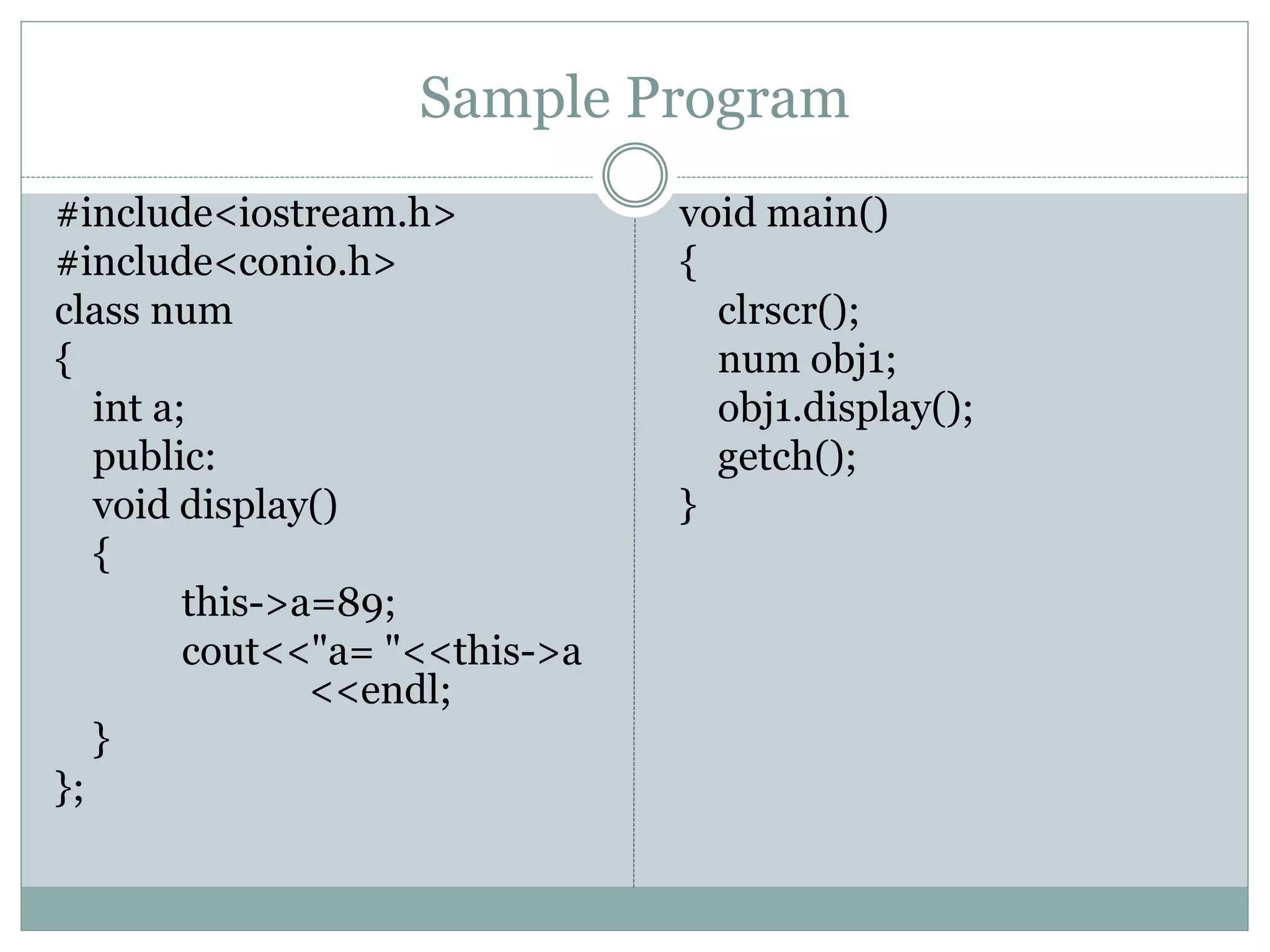
This document discusses different uses of the "this" pointer in C++ classes. This pointer points to the object whose member function is being called. It can be used to return the object from a member function, access the memory address of the object, and access data members within member functions. Sample programs are provided to demonstrate returning an object using this, displaying the memory address of an object using this, and accessing a data member within a member function using this->.