The document explains the concept of inheritance in Java, which allows a child class to inherit properties and behaviors from a parent class, promoting code reusability. It outlines different types of inheritance, including single, multilevel, and hierarchical inheritance, along with their syntactical representations and examples. Additionally, it discusses method overriding and emphasizes that multiple inheritance is not supported in Java.




![Simple program
class super {
Public void display()
{
System.out.println(“I am parent class”);
}
}
class sub extends super {
public static void main(String args[])
{
sub message = new sub()
message.display();
}
}
Super
I am from parent class
sub
Parent class
Child classs
Output: I am parent class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/191-15-12994-201116144235/75/Inheritance-in-java-5-2048.jpg)


![SAMPLE PROGRAM OF SINGLE INHERITANCE :
class message_super {
Public void display()
{
System.out.println(“I am from superclass”);
}
}
class message_sub extends message_super {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Message_sub message = new message_sub()
Message.display();
}
}
Output: I am from superclass
message_super
I am from superclass
message_sub](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/191-15-12994-201116144235/75/Inheritance-in-java-8-2048.jpg)
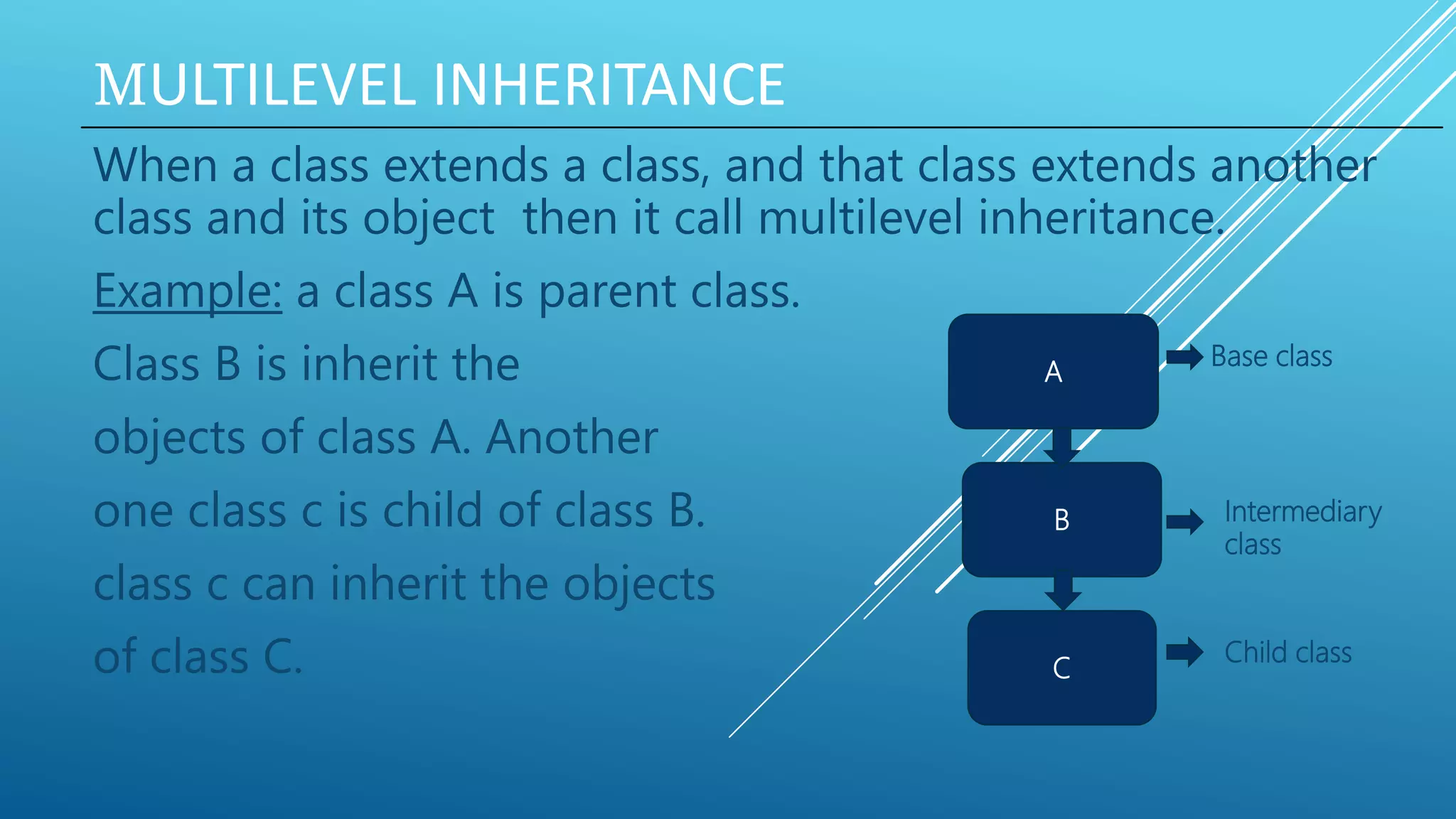
![SAMPLE PROGRAM OF MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE :
class a {
int data= 15; }
class b extends a {
}
class c extends b {
public void display() {
System.out.println(“number is:”+data);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
c num= new c()
num.display();
}
}
Output: number is: 15
a
Data=15
b
c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/191-15-12994-201116144235/75/Inheritance-in-java-10-2048.jpg)



![Sample program of method overriding:
class animal {
public void display() {
System.out.println(“I am animal”); }
}
class tiger extends animal {
public void display() {
System.out.println(“I am tiger”);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
tiger t = new tiger();
t.display(); }
}
Output: I am tiger](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/191-15-12994-201116144235/75/Inheritance-in-java-14-2048.jpg)
