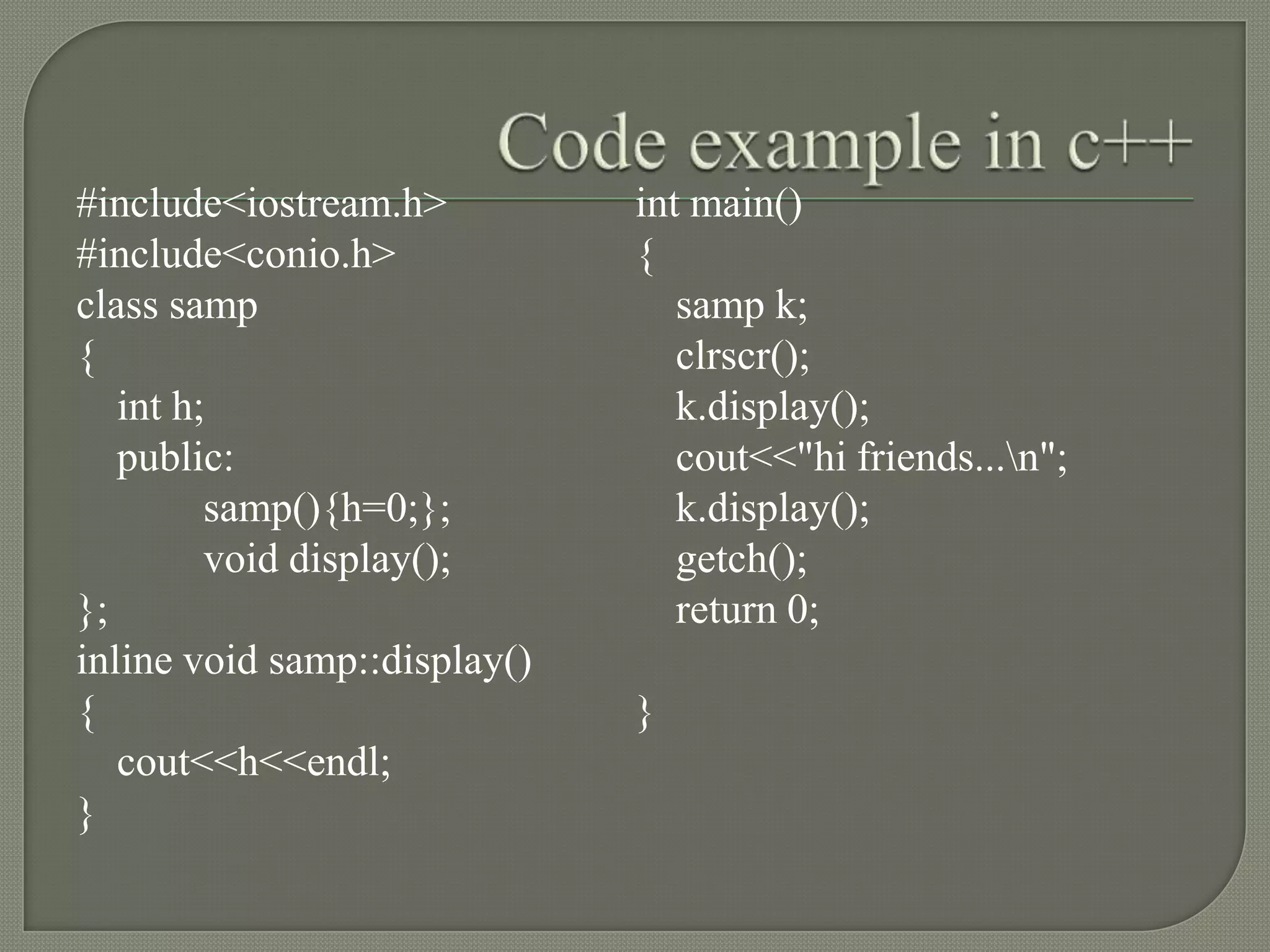
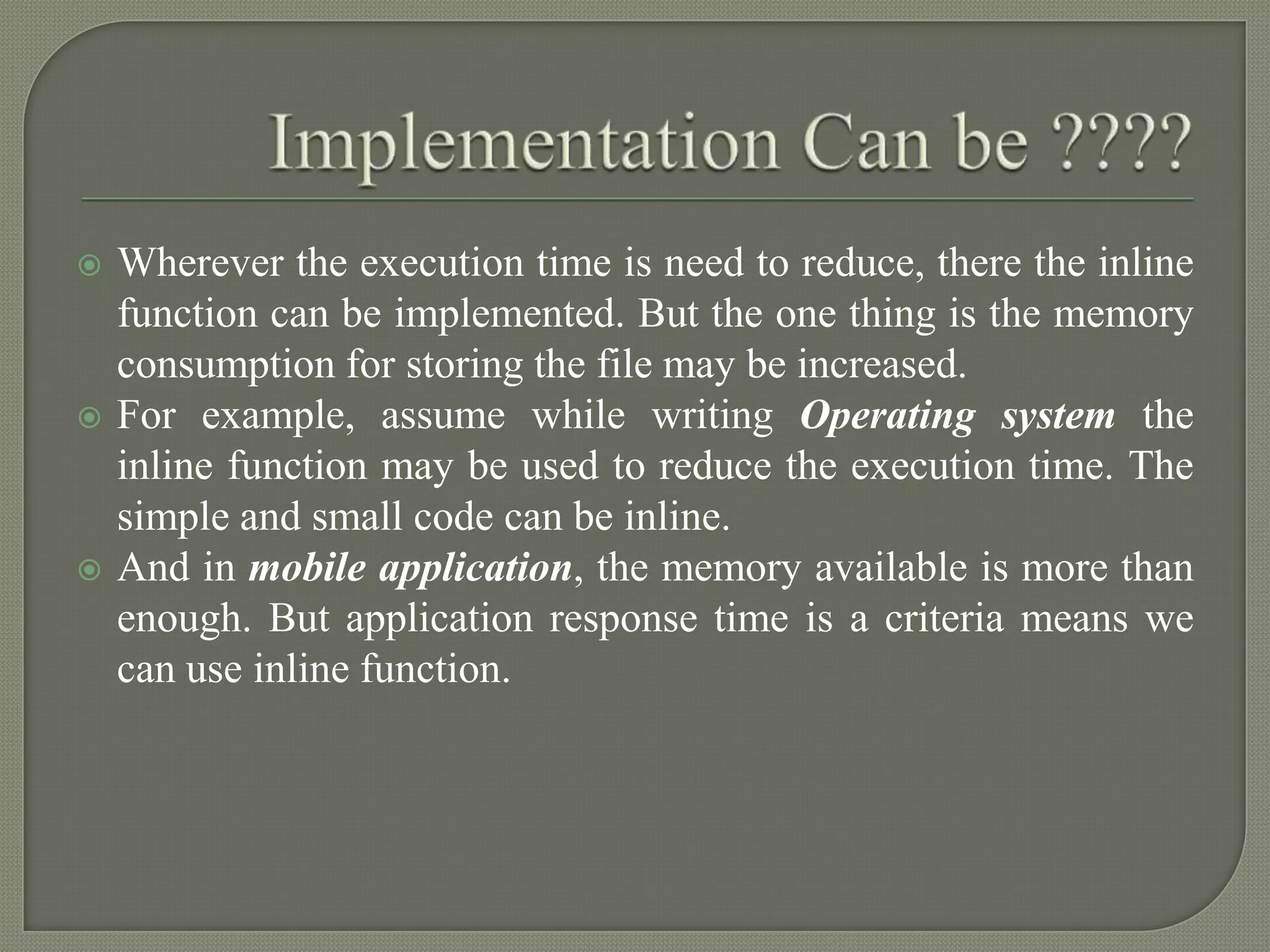
The document discusses inline functions in C++. Inline functions allow code from a function to be pasted directly into the call site rather than executing a function call. This avoids overhead from calling and returning from functions. Good candidates for inline are small, simple functions called frequently. The document provides an example of a function defined with the inline keyword and the optimizations a compiler may perform after inlining. It also compares inline functions to macros and discusses where inline functions are best used.