Thin capitalization refers to a situation where a company is financed through high levels of debt compared to equity, resulting in a thin capital structure. Section 94B of the Indian Income Tax Act governs thin capitalization by restricting the deduction of interest expenses in cases where debt is from an associated enterprise or guaranteed by an associated enterprise. Excess interest, defined as interest exceeding 30% of EBITDA or total interest paid to associated enterprises, whichever is lower, is not deductible and can be carried forward for up to 8 years. The provisions apply to both debt from non-resident associated enterprises and debt from Indian lenders that is guaranteed by a non-resident associated enterprise.



![Overview on thin capitalization
LIMITATION OF INTEREST DEDUCTION
The thin capitalisation provisions state that excess interest (i.e. interest amount that exceeds 30% of earnings before interest, tax, depreciation
and amortization [‘EBITDA’] or the total interest amount payable to Associated Enterprise, whichever is less) shall not be available for deduction.
However, such disallowed interest expenditure can be carried forward for eight assessment years, but deduction of the same cannot exceed the
excess interest.
The same is explained by way of few examples:
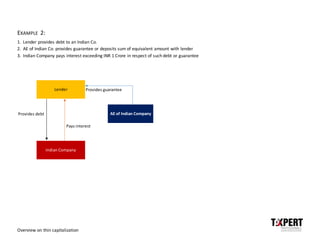
EXAMPLE 1:
1. Foreign AE provides debt to an Indian Co. or Permanent Establishment of a Foreign Co.
2. Indian Co. or PE of Foreign Co. pays interest exceeding INR 1 Crore in respect of such debt
Provides debt Outside India
India
Pays interest
Foreign AE
Indian Company or PE of
Foreign Company](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/190105thincapitalsiation-overview-190517103449/85/Thin-Capitalisation-4-320.jpg)