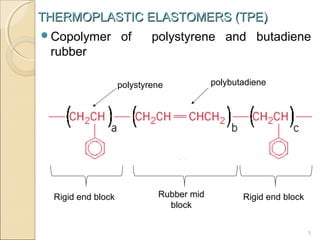
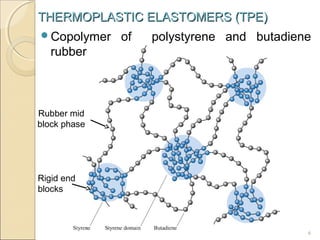
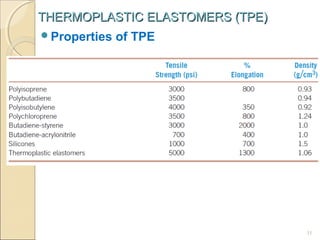
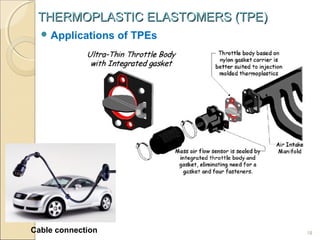
This document discusses thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs). TPEs have both thermoplastic and elastomeric properties. They can be melt-processed like thermoplastics but are flexible and elastic like vulcanized rubbers. The most common TPE is a styrene-butadiene block copolymer, which has rigid polystyrene end blocks and soft polybutadiene mid blocks. This structure allows it to behave like a rubber at low temperatures but melt and flow like a thermoplastic at higher temperatures. Common applications of TPEs include automotive parts, medical devices, shoes, and cables due to advantages like recyclability and simpler processing compared to thermoset rubbers