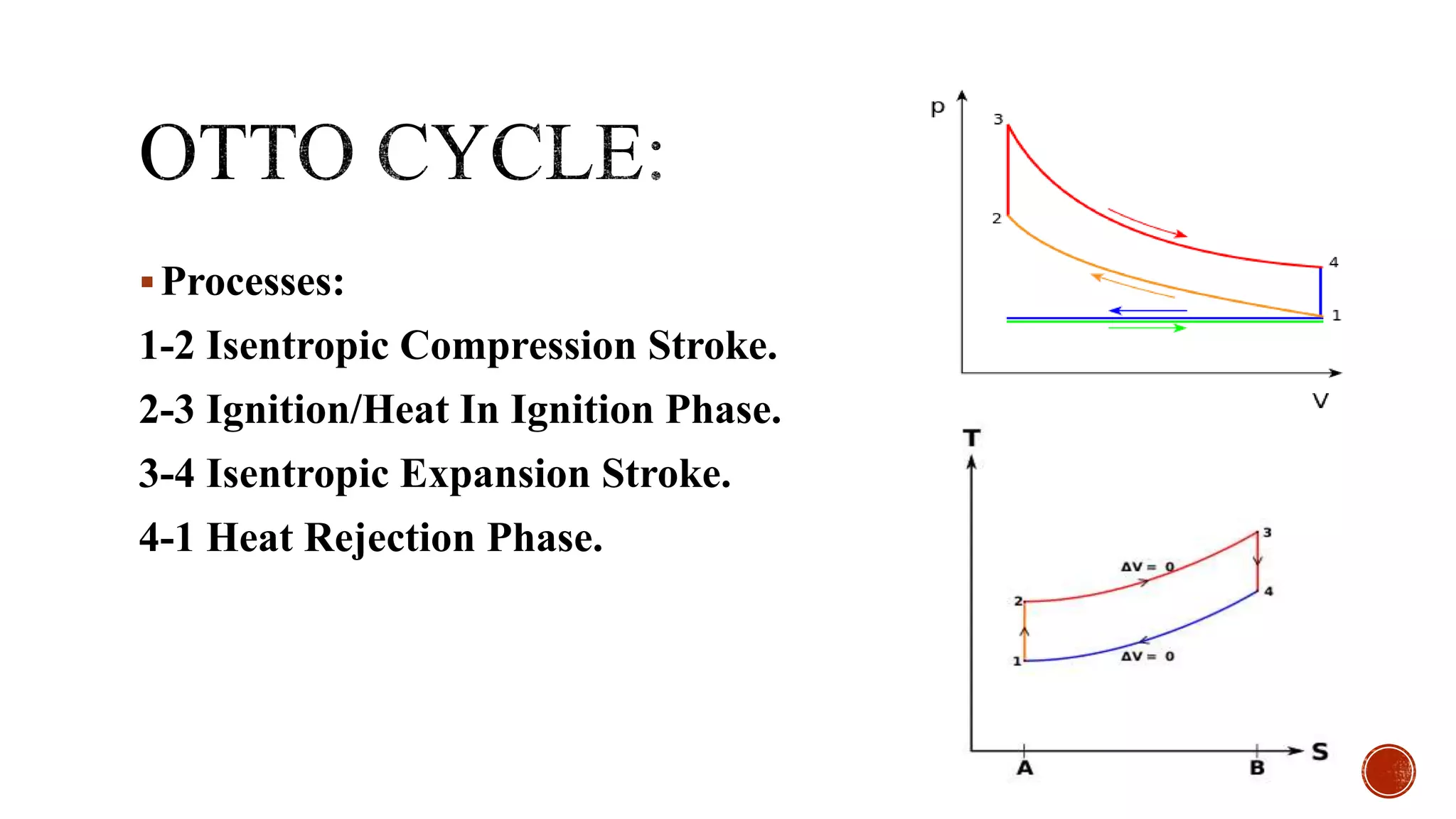
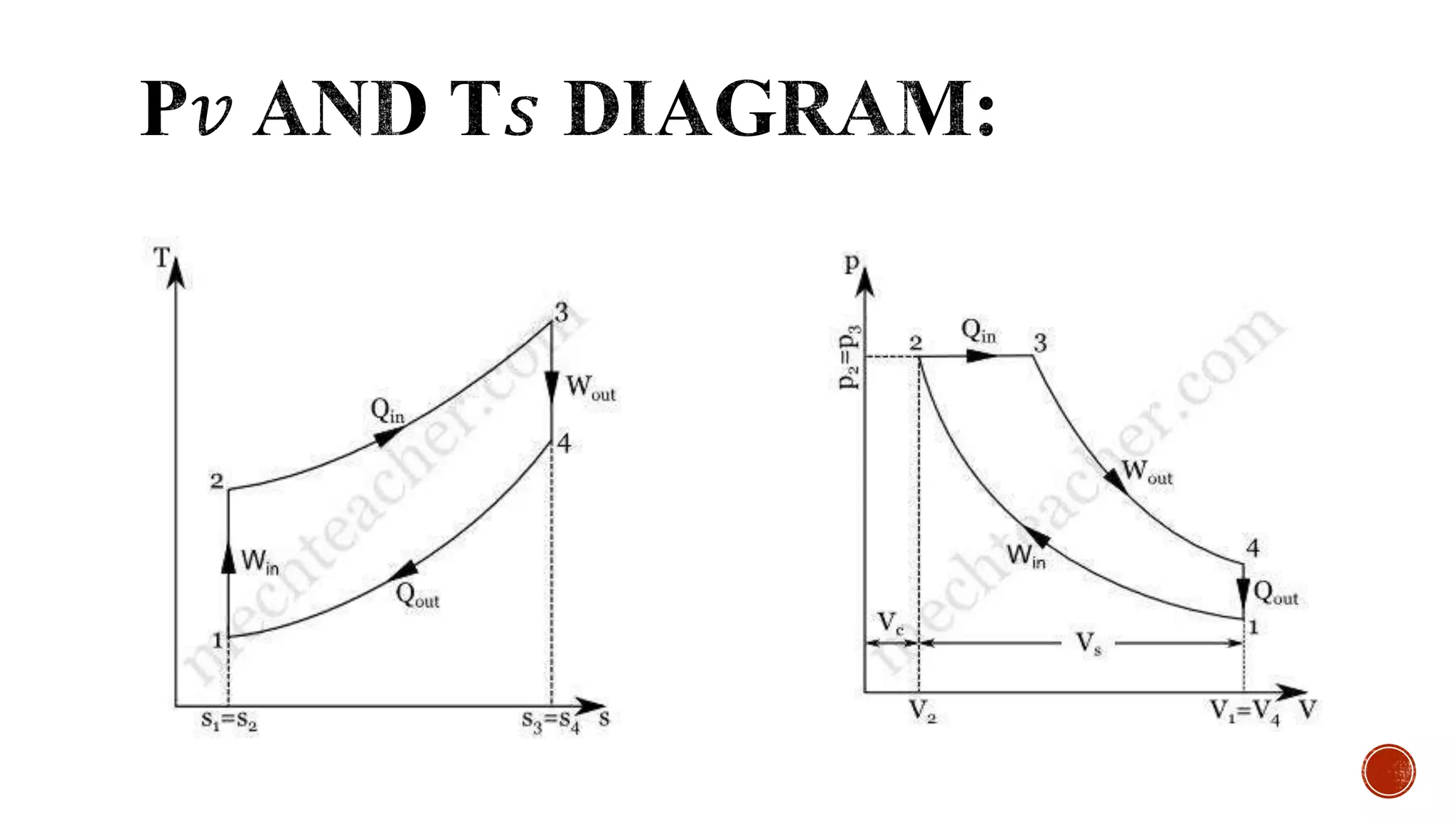
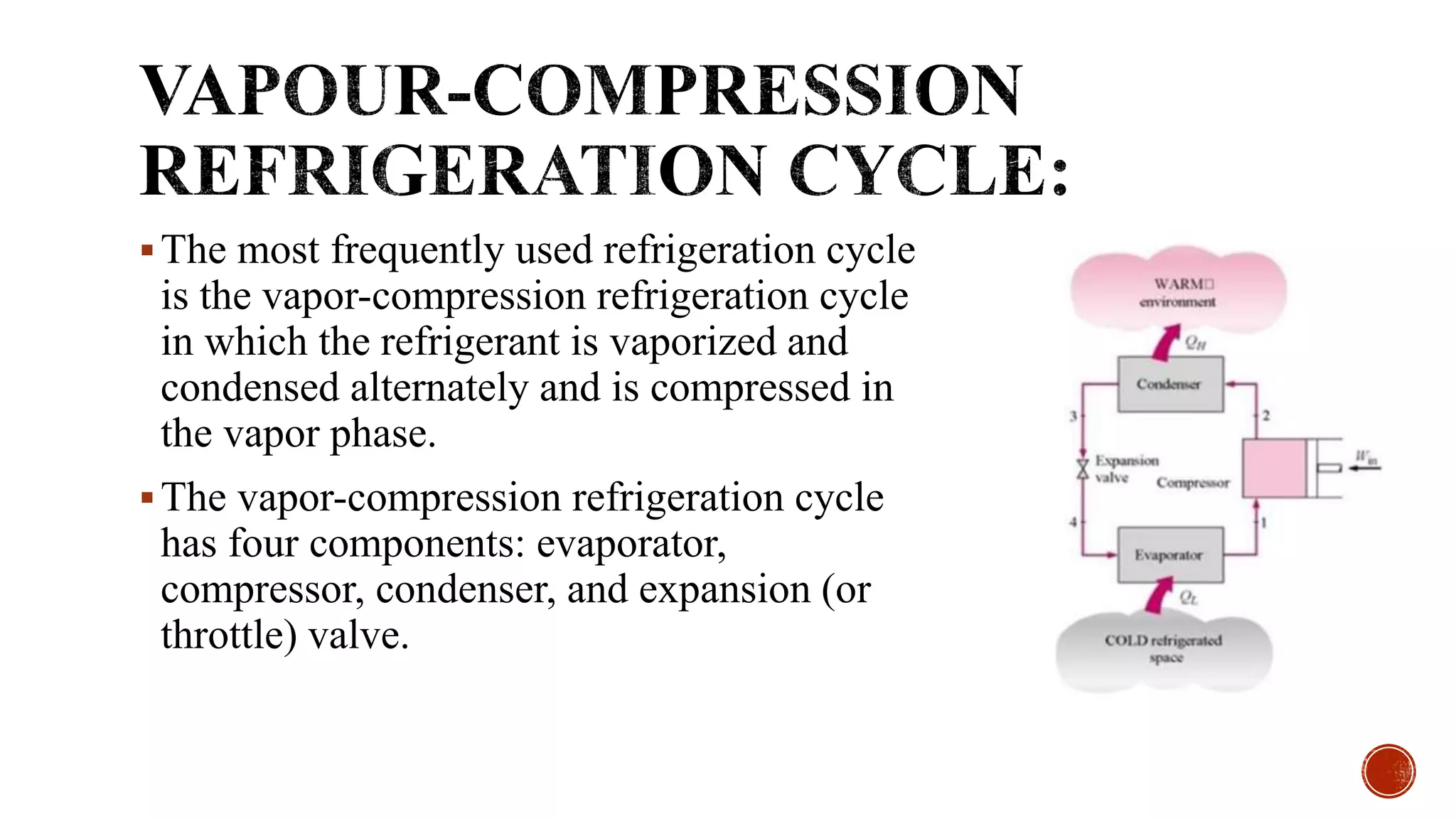
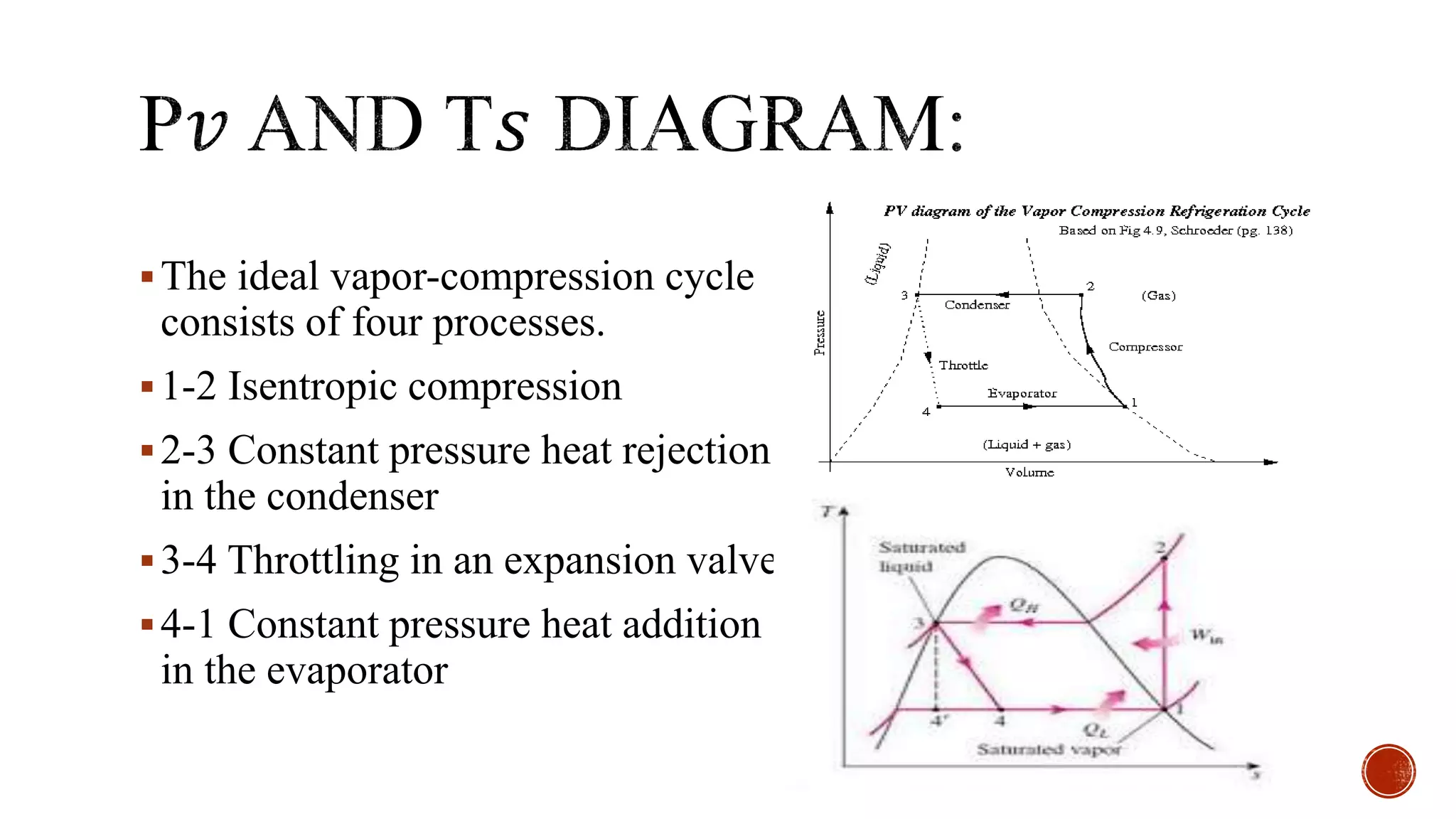
The document summarizes several thermodynamic cycles including the Otto, Diesel, Carnot, refrigeration, and Brayton cycles. For each cycle, it outlines the key processes and applications. The Otto cycle involves two isentropic and two constant volume processes and is used in spark ignition engines. The Diesel cycle uses constant pressure heat addition and has a higher efficiency than the Otto cycle. The Carnot cycle involves reversible, isothermal and adiabatic processes and sets the maximum possible efficiency. The refrigeration cycle uses vapor compression to transfer heat between regions. The Brayton cycle consists of adiabatic compression and expansion with isobaric heat transfer and is commonly used in gas turbine engines.