This document discusses various thermodynamic power cycles including:
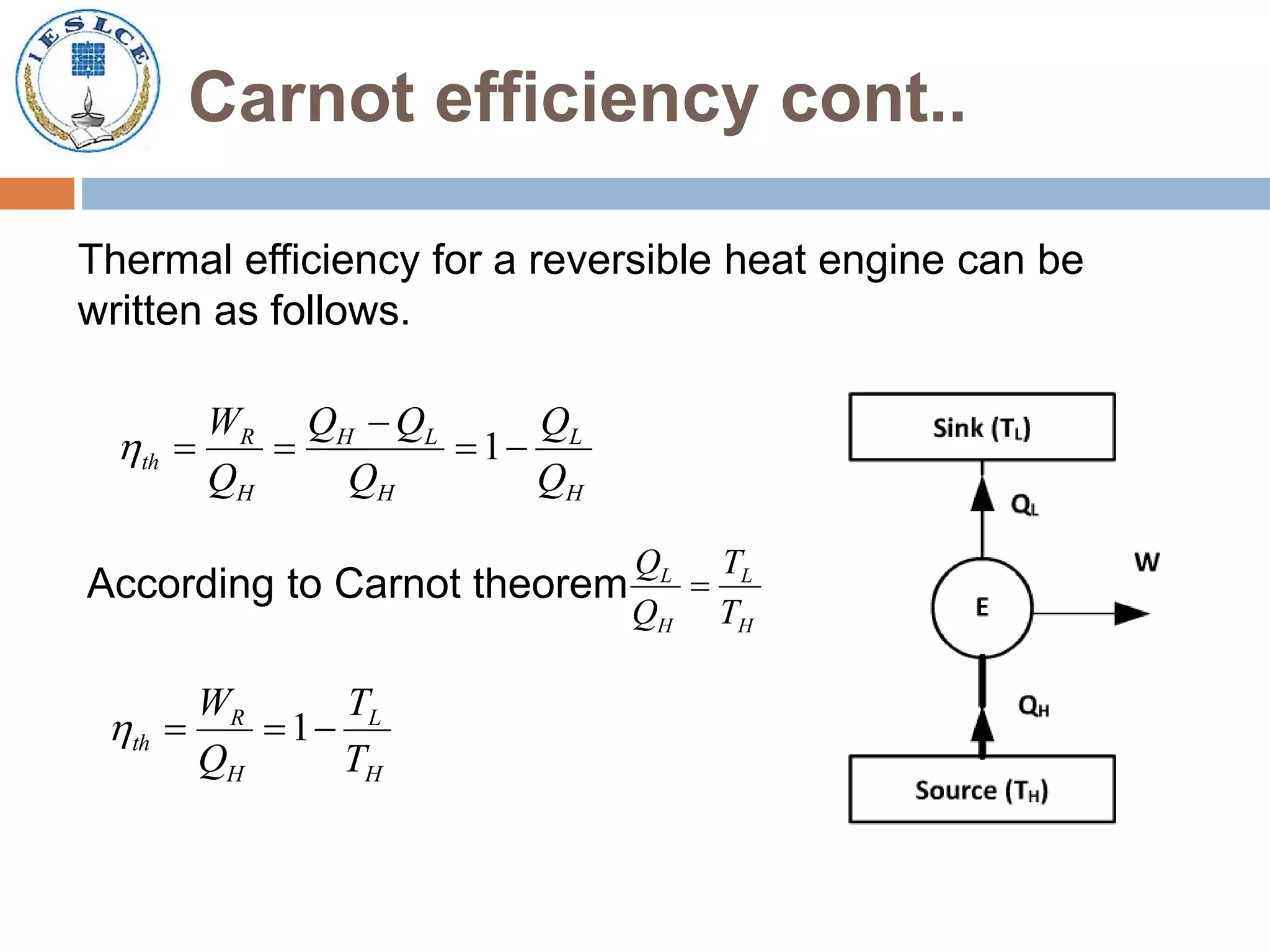
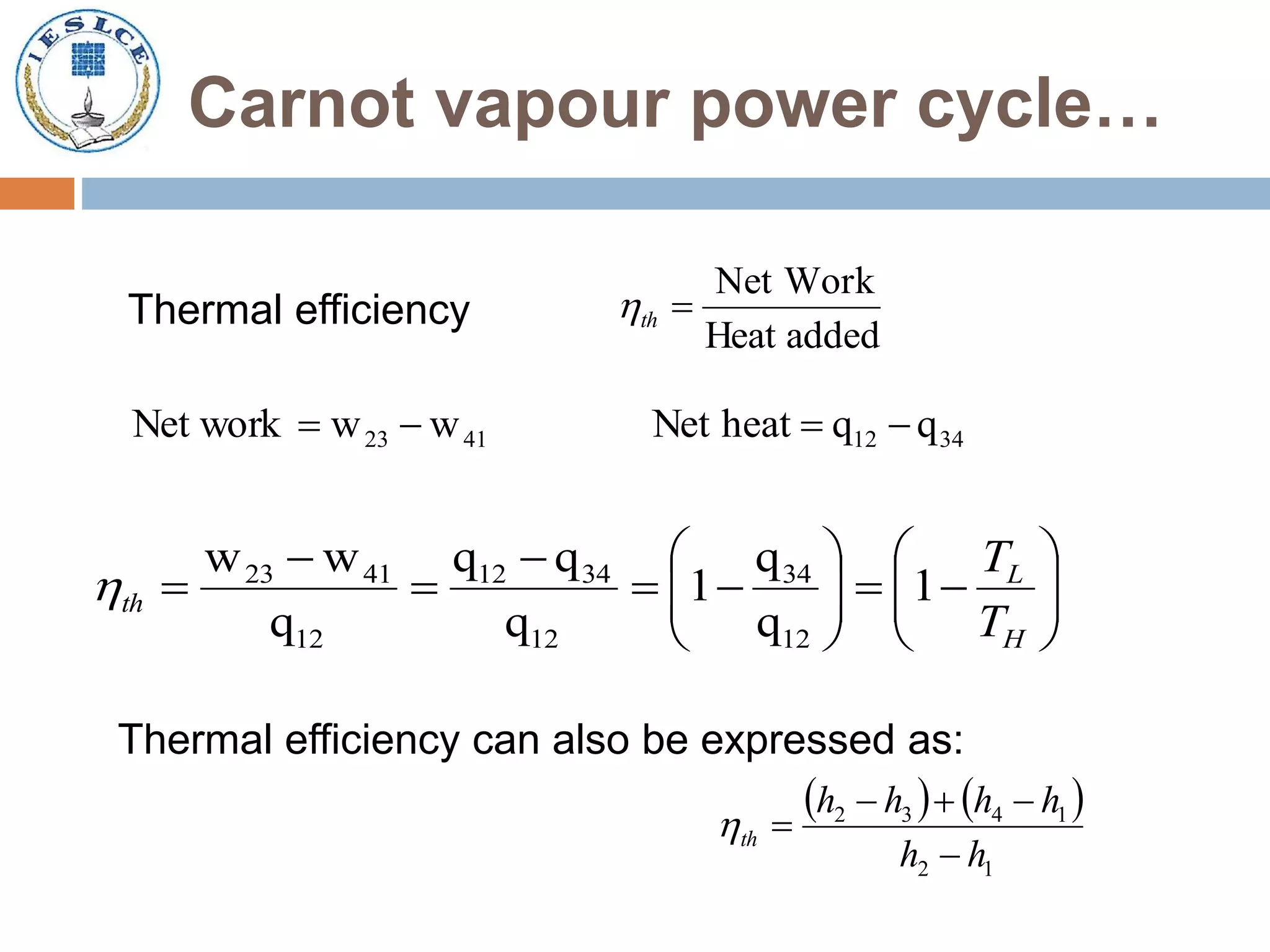
- The Carnot cycle, which is the most efficient but impractical cycle.
- Rankine cycles, which are more practical vapor power cycles that use steam as the working fluid.
- Simple Rankine cycles involve heating water to steam then expanding it in a turbine before condensing it back to water.
- Rankine cycles with superheated steam, which increase efficiency by heating steam above its saturation temperature.
- The efficiencies of different cycles are calculated and compared in examples. Superheated steam cycles have higher efficiencies than simple Rankine cycles due to higher average temperatures.