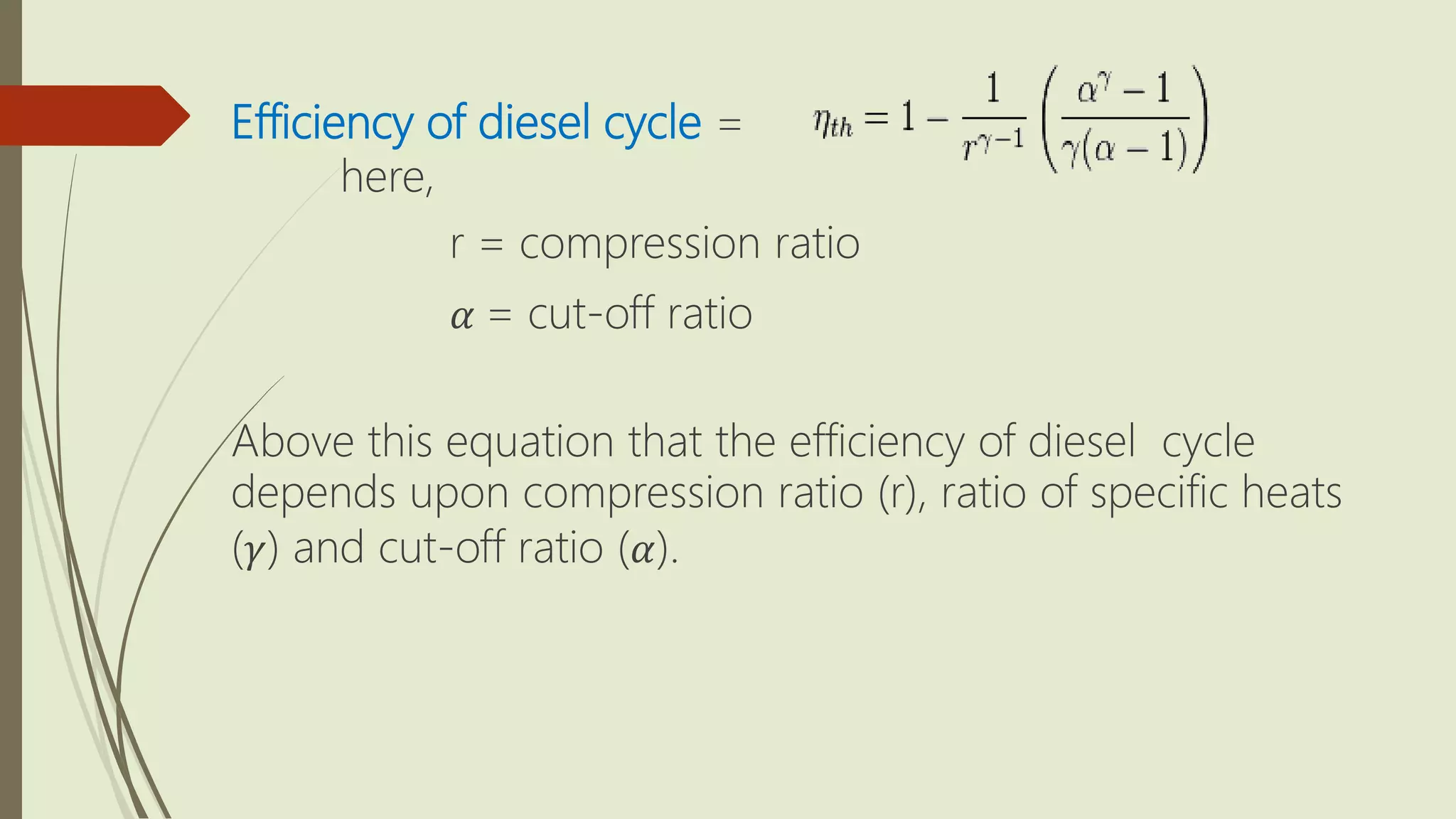
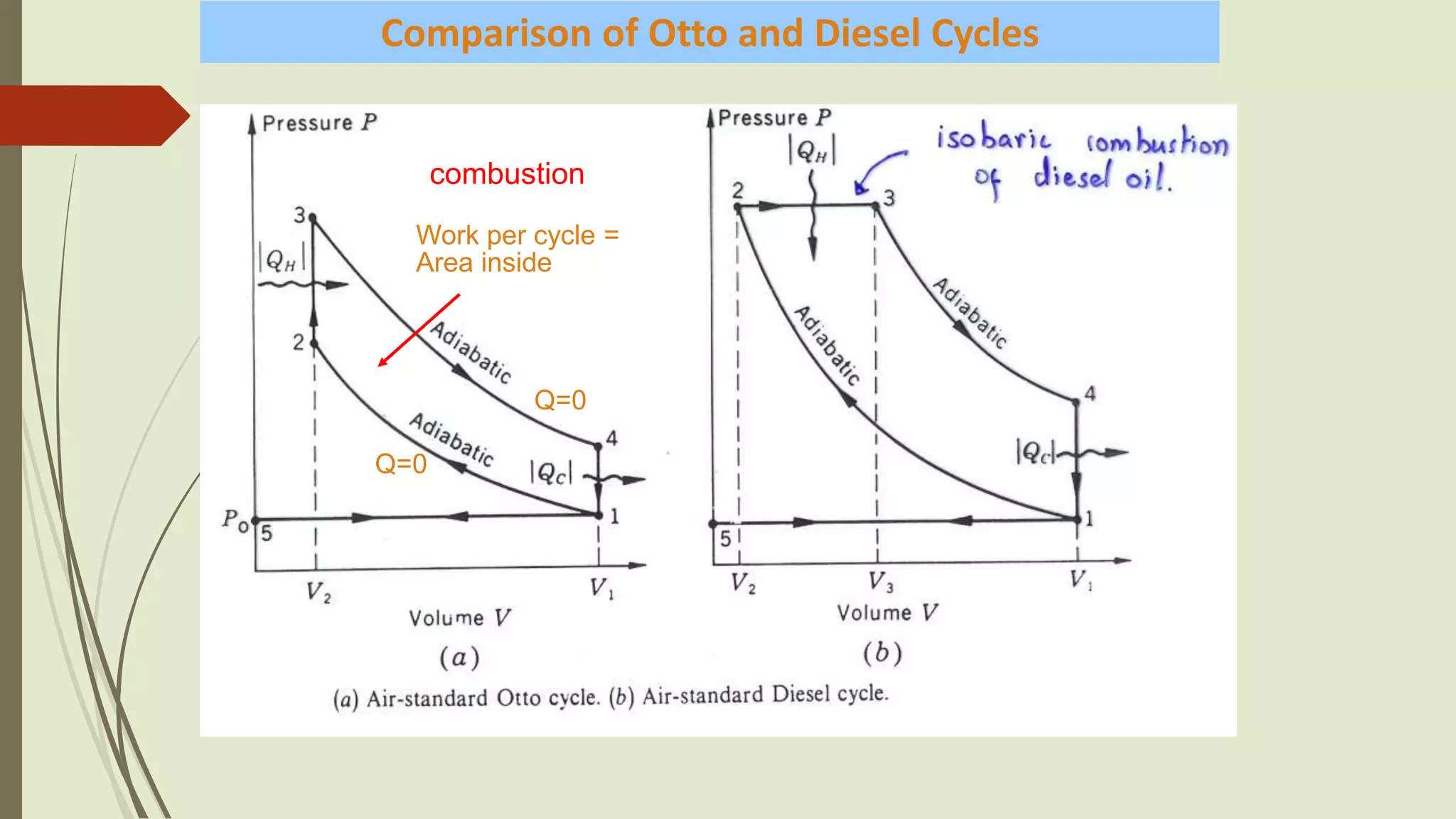
This document summarizes different types of heat engine cycles. It describes a heat engine as a device that absorbs heat (Q) and uses it to do useful work (W) when operating in a cycle. The document then discusses the Carnot, Rankine, Otto, and Diesel cycles - providing details on the processes involved in each cycle and equations for calculating their efficiencies. The Carnot cycle uses two reservoirs at fixed temperatures and is the most efficient possible. The Rankine cycle completely condenses vapor before pumping. The Otto and Diesel cycles differ in whether heat is supplied at constant volume or constant pressure.