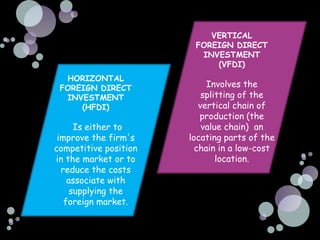
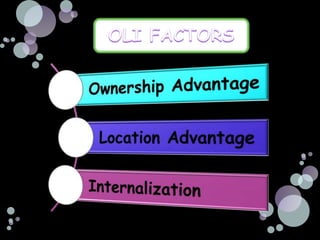
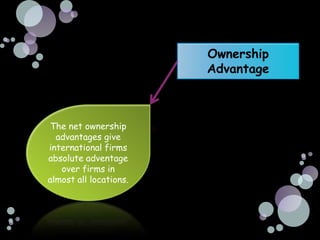
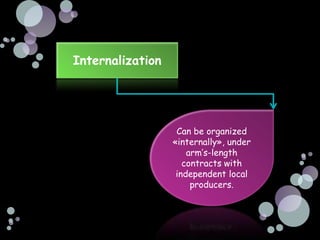
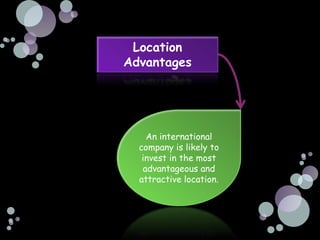
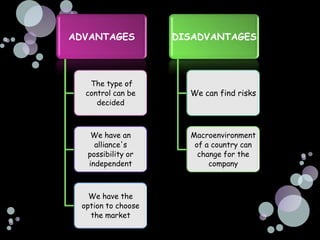
The document summarizes the main reasons firms engage in international investment through foreign direct investment, including horizontal foreign direct investment to serve local markets better and vertical foreign direct investment to access lower cost inputs. It discusses how the choice of entry mode is influenced by ownership advantages, internalization advantages, and location advantages, and notes that foreign direct investment allows firms to have more control but also carries some risks from changes in the macroenvironment of the host country.