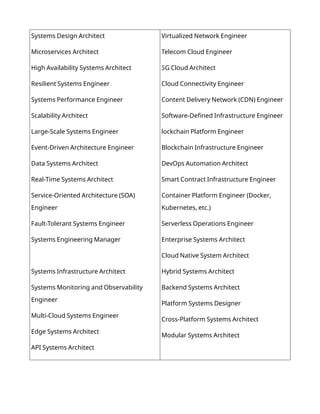
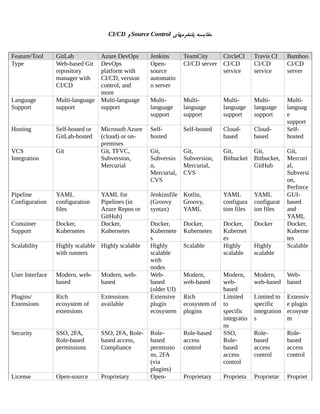
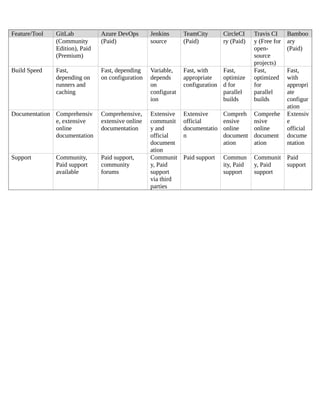
DevOps is a set of practices, principles, and cultural philosophies that aim to improve collaboration and communication between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) teams. The primary goal of DevOps is to shorten the software development lifecycle, increase the frequency of software releases, and improve the quality of software products. Here are some key aspects of DevOps and its goals:
Key Aspects of DevOps
Collaboration: DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams. This includes breaking down silos and fostering a culture of shared responsibility for the entire software delivery process.
Automation: Automation is a core principle of DevOps. It involves automating repetitive tasks such as code integration, testing, deployment, and infrastructure provisioning. This helps reduce manual errors and speeds up the delivery process.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): CI/CD practices are central to DevOps. Continuous Integration involves regularly merging code changes into a shared repository, where automated tests are run to ensure code quality. Continuous Deployment extends this by automatically deploying code changes to production after passing tests.
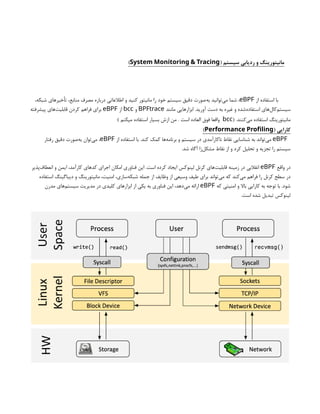
Monitoring and Feedback: DevOps encourages continuous monitoring of applications and infrastructure in production. This helps teams gather feedback on performance, user experience, and potential issues, allowing for rapid response and improvement.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): IaC is a practice where infrastructure is managed and provisioned using code and automation tools. This allows for consistent and repeatable infrastructure deployments, making it easier to manage and scale environments.
Cultural Change: DevOps is not just about tools and processes; it also involves a cultural shift within organizations. This includes fostering a mindset of collaboration, experimentation, and learning from failures.
Goals of DevOps
Faster Time to Market: One of the primary goals of DevOps is to accelerate the delivery of software to customers. By streamlining processes and automating tasks, organizations can release new features and updates more quickly.
Improved Quality: DevOps aims to enhance the quality of software by integrating testing and quality assurance into the development process. Continuous testing helps identify and fix issues early, reducing the likelihood of defects in production.
Increased Deployment Frequency: DevOps encourages frequent and smaller releases rather than large, infrequent ones. This reduces the risk associated with deployments and allows for quicker feedback from users.
Enhanced Collaboration: By fostering collaboration between development and operations teams, DevOps aims to create a more cohesive and efficient workflow. This leads to better communication, shared goals, and a more unified approach to software delivery.







































































































































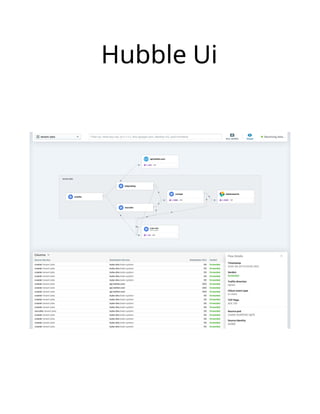


















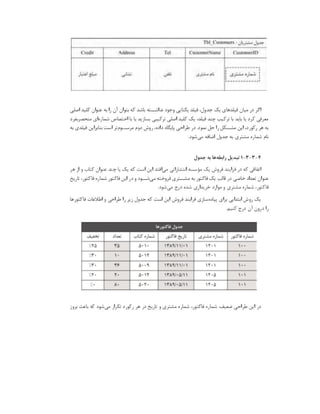

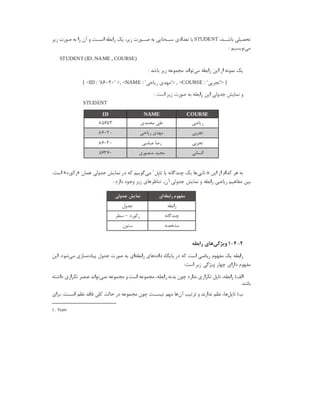








![# Example driver definitions
# Driver from the postgresql-odbc package
# Setup from the unixODBC package
[PostgreSQL]
Description = ODBC for PostgreSQL
Driver = /usr/lib/psqlodbcw.so
Setup = /usr/lib/libodbcpsqlS.so
Driver64 = /usr/lib64/psqlodbcw.so
Setup64 = /usr/lib64/libodbcpsqlS.so
FileUsage = 1
# Driver from the mysql-connector-odbc package
# Setup from the unixODBC package
[MySQL]
Description = ODBC for MySQL
Driver = /usr/lib/libmyodbc5.so
Setup = /usr/lib/libodbcmyS.so
Driver64 = /usr/lib64/libmyodbc5.so
Setup64 = /usr/lib64/libodbcmyS.so
FileUsage = 1
# Driver from the freetds-libs package
# Setup from the unixODBC package
[FreeTDS]
Description = Free Sybase & MS SQL Driver
Driver = /usr/lib/libtdsodbc.so
Setup = /usr/lib/libtdsS.so
Driver64 = /usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so
Setup64 = /usr/lib64/libtdsS.so
Port = 1433
# Driver from the mariadb-connector-odbc package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devops-250105143103-fb253e37/85/The-Refrence-Of-DevOps-The-0-5-release-193-320.jpg)
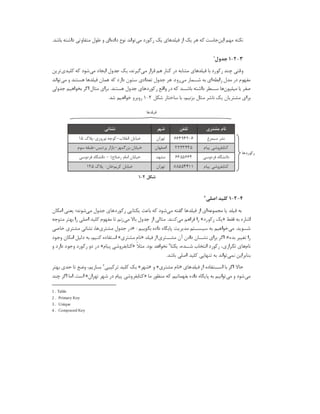
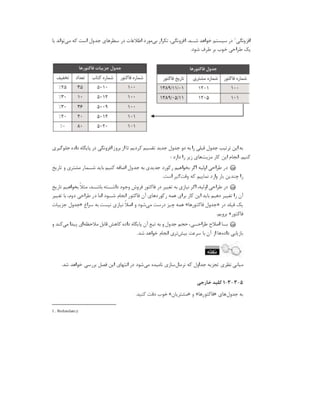
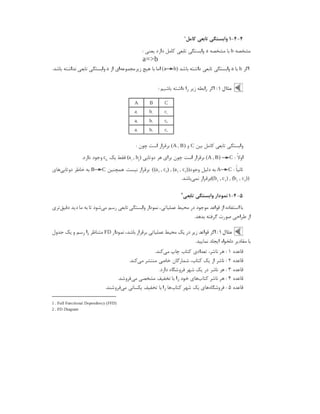
![# Setup from the unixODBC package
[MariaDB]
Description = ODBC for MariaDB
Driver = /usr/lib/libmaodbc.so
Setup = /usr/lib/libmaodbc.so
Driver64 = /usr/lib64/libmaodbc.so
Setup64 = /usr/lib64/libmaodbc.so
FileUsage = 1
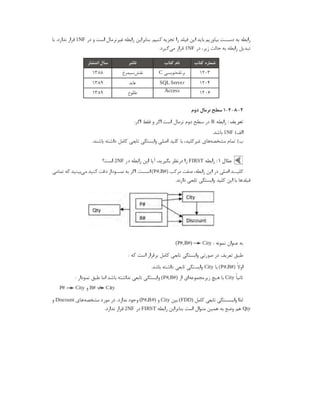
از غیر به ما : نکته
freetds
سایر
driver
. میکنیم اشاره نیز را ها
ایجاد نحوه
( )
Data Source Name DSN
:
توانیم می ما
dsn
/ مسیر در را
/ .
etc odbc ini
کنیم ایجاد کاربر هر خانگی پوشه مسیر در یا
/. .
~ odbc ini
: نمونه برای
[ODBC Data Sources]
MSSQLDEV = MSSQL Server
[MSSQLDEV]
# Reference driver from the "/etc/odbcinst.ini" file.
# Driver = FreeTDS
# Or use a direct driver reference, rather than reference
# one in the "/etc/odbcinst.ini" file.
Driver=/usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so.0
Description = MSSQL Server
Trace = No
Server = 192.168.11.1
Database = dbtest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devops-250105143103-fb253e37/85/The-Refrence-Of-DevOps-The-0-5-release-194-320.jpg)
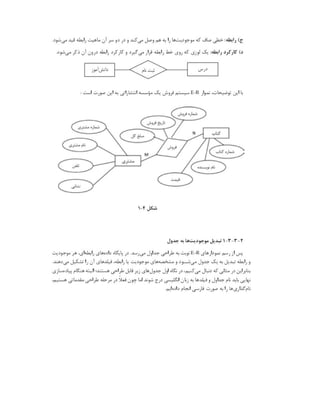
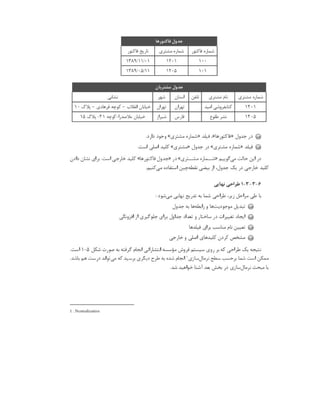
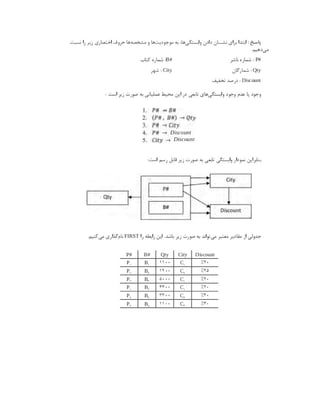
![Port = 1433
TDS_Version = 7.2
#QuotedId=YES
#AnsiNPW=YES
#VarMaxAsLong=YES
[Default]
Driver = /usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so.0
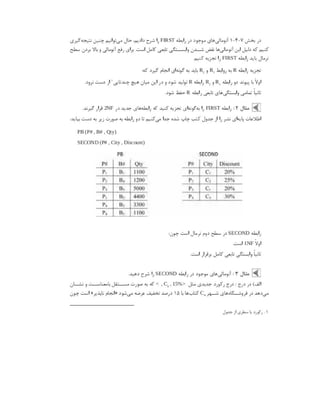
تست نحوه
( )
Data Source Name DSN
:
osql -S MSSQLDEV -U myuser -P mypassword
strings: '': No such file
trying /tmp/sql ... no
trying /tmp/sql ... no
trying /etc ... OK
checking odbc.ini files
reading /root/.odbc.ini
[MSSQLDEV] not found in /root/.odbc.ini
reading /etc/odbc.ini
[MSSQLDEV] found in /etc/odbc.ini
found this section:
[MSSQLDEV]
Driver = /usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so.0
Description = MSSQL Server
Trace = No
Server = 192.168.11.1
Database = dbtest
Port = 1433
TDS_Version = 7.1
looking for driver for DSN [MSSQLDEV] in /etc/odbc.ini
found driver line: " Driver = /usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so.0"
driver "/usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so.0" found for [MSSQLDEV] in odbc.ini
found driver named "/usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so.0"
/usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so.0 is an executable file
"Server" found, not using freetds.conf
Server is "my-sql-server.example.com"
Configuration looks OK. Connection details:
DSN: MSSQLDEV
odbc.ini: /etc/odbc.ini
Driver: /usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so.0
Server hostname: 192.168.11.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devops-250105143103-fb253e37/85/The-Refrence-Of-DevOps-The-0-5-release-195-320.jpg)
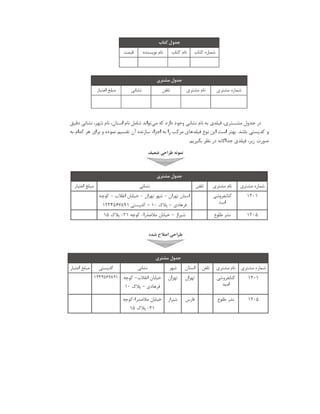
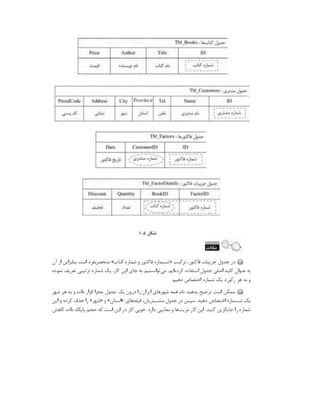
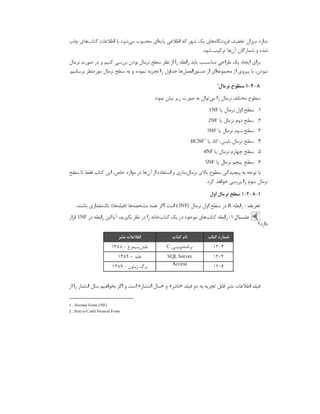
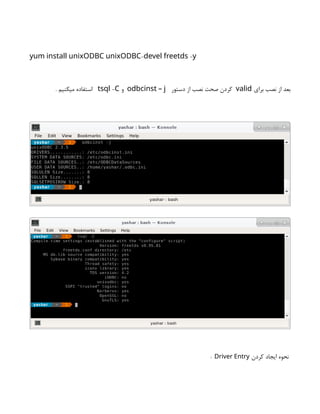
![Address: 192.168.11.1
Attempting connection as banner ...
+ isql MSSQLDEV myuser 'mypassword' -v
+---------------------------------------+
| Connected! |
| |
| sql-statement |
| help [tablename] |
| quit |
| |
+---------------------------------------+
SQL> quit
#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devops-250105143103-fb253e37/85/The-Refrence-Of-DevOps-The-0-5-release-196-320.jpg)