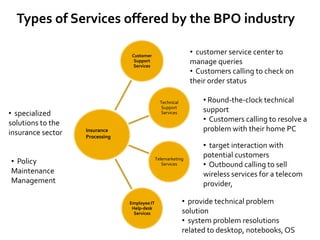
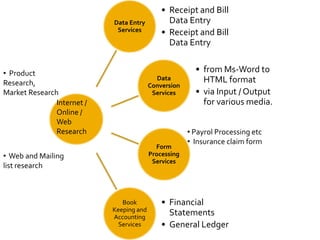
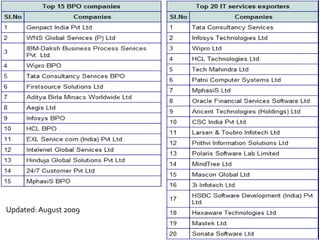
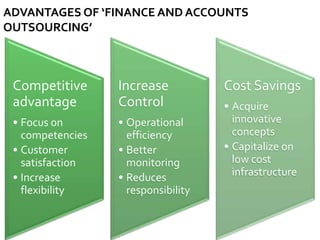
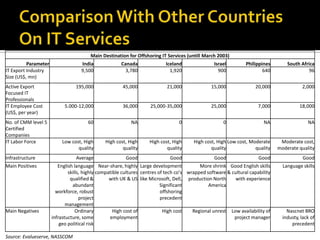
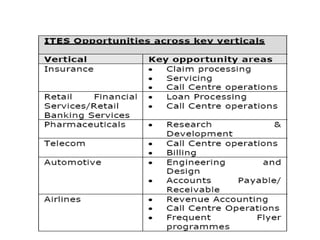
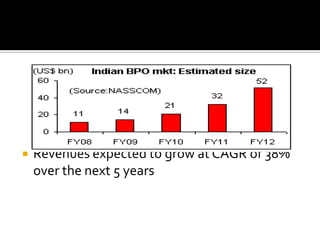
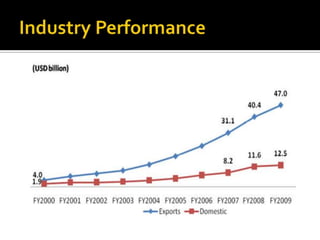
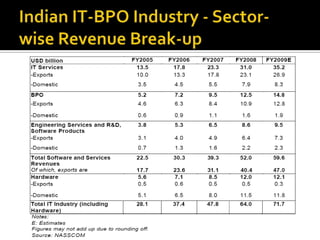
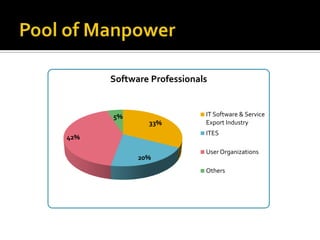
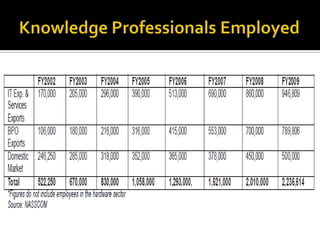
The document discusses the business process outsourcing (BPO) industry in India. It provides an overview of the types of BPO services offered, including customer support, technical support, telemarketing, and accounting. It also discusses the current size and growth potential of the Indian BPO industry. Some of the key challenges faced by the industry are also summarized, such as infrastructure issues and lack of skills. Overall, the Indian BPO industry has experienced significant growth and is well-positioned for continued expansion.