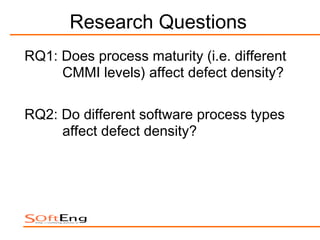
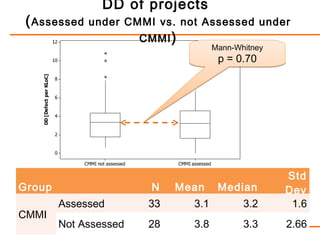
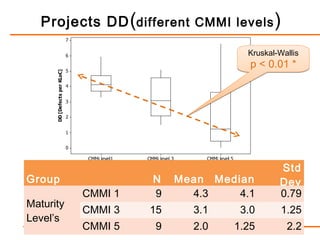
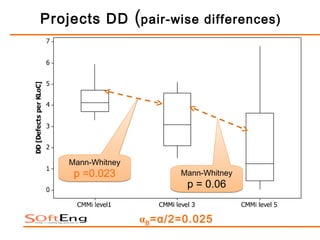
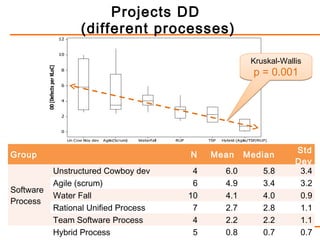
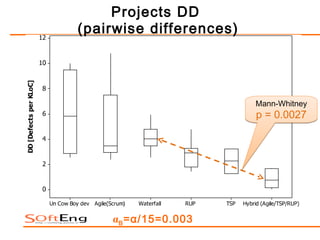
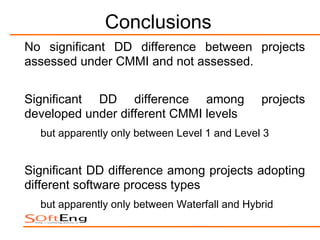
The study examines the relationship between software process maturity, as assessed by the CMMI model, and defect density across 61 software projects. It finds no significant difference in defect density between projects assessed under CMMI and those that are not, but significant differences exist among projects at different CMMI levels and types of software processes. Specifically, projects at CMMI level 1 display higher defect density compared to level 3, and significant differences are observed between waterfall and hybrid process types.