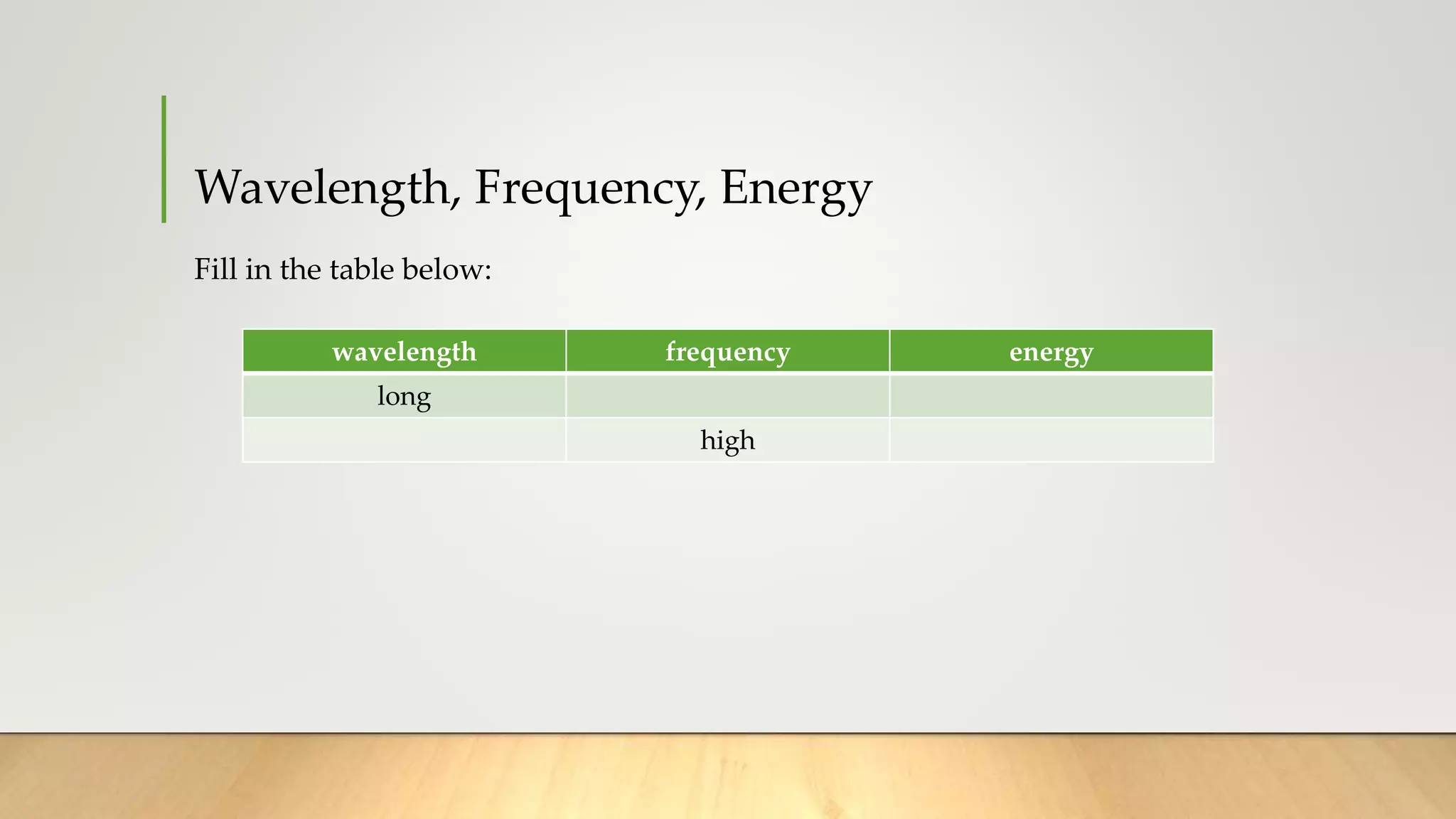
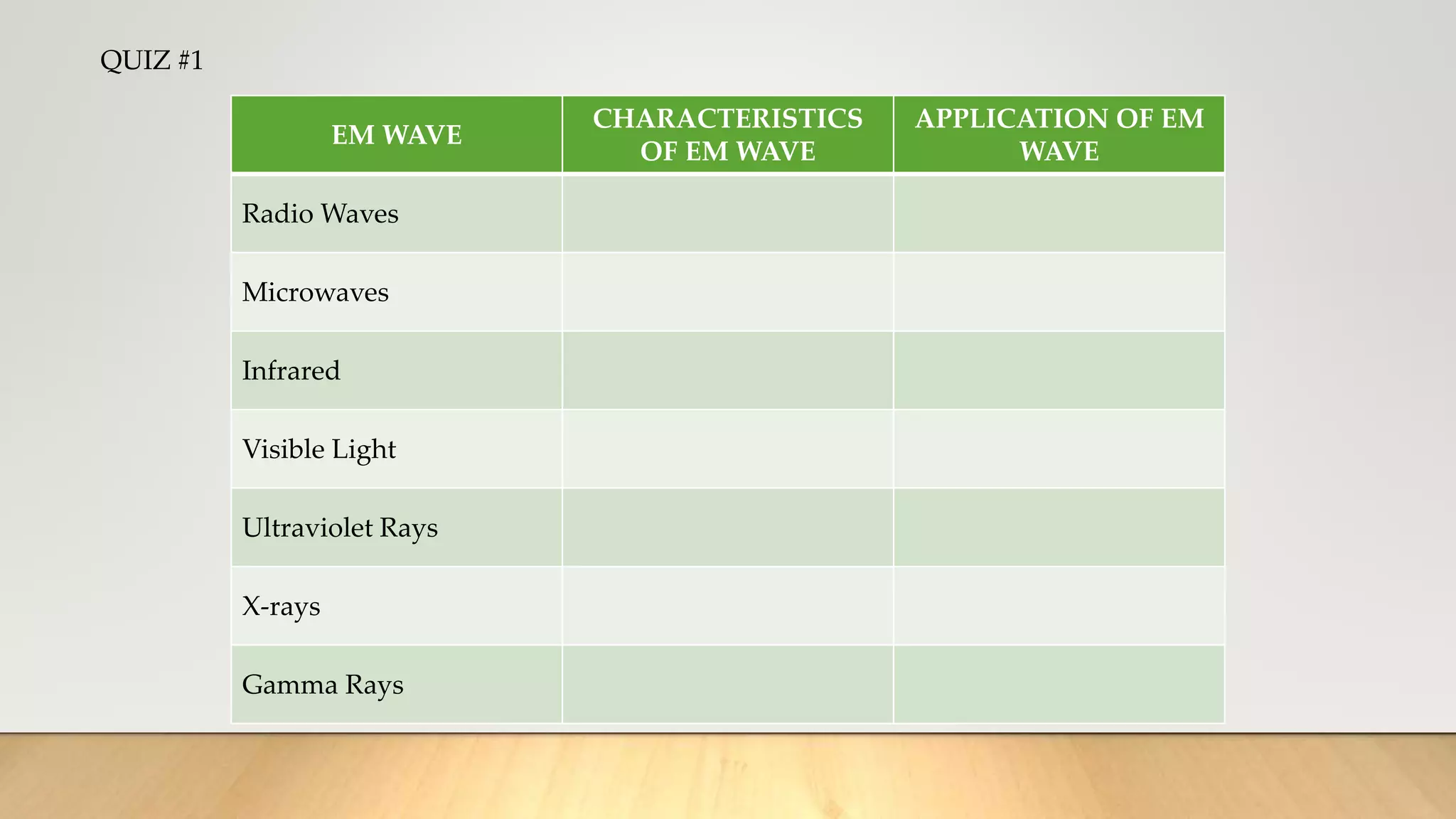
The electromagnetic spectrum consists of all types of electromagnetic waves, ranging from radio waves to gamma rays. The properties of electromagnetic waves include speed, frequency, and wavelength, with speed being equal to frequency multiplied by wavelength. Shorter wavelengths have higher frequencies and energies, while longer wavelengths have lower frequencies and energies. The electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays, which have various applications such as communication, heating, vision, sterilization, and medical imaging.