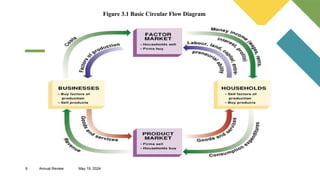
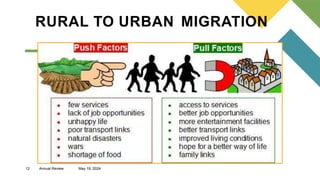
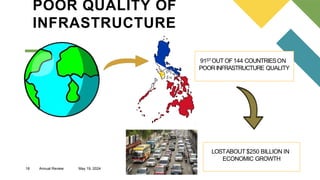
The document outlines the central economic problems related to resource allocation, including the factors of production: land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. It discusses three key economic questions—what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce—as well as contemporary issues such as unemployment, poverty, poor infrastructure, and income inequality in the Philippines, along with potential solutions. Strategies to improve economic conditions include enhancing education, revising labor policies, and fostering public-private partnerships.