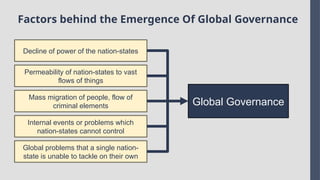
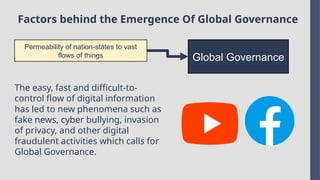
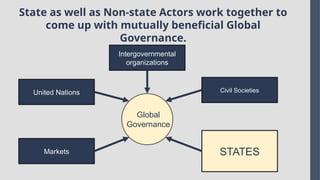
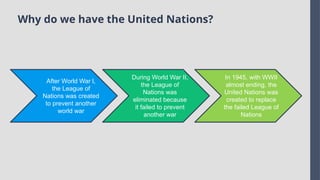
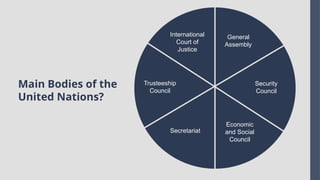
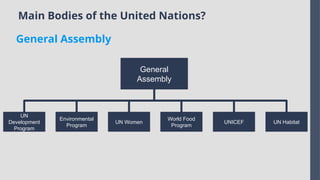
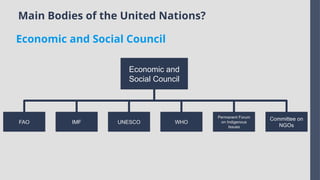
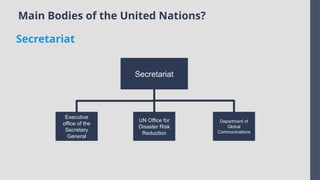
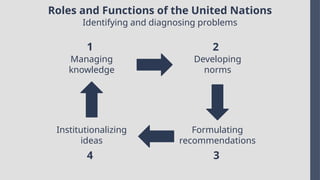
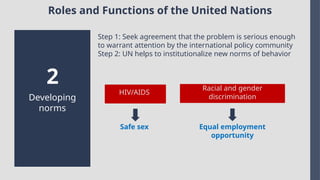
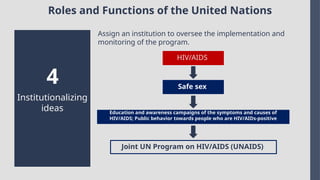
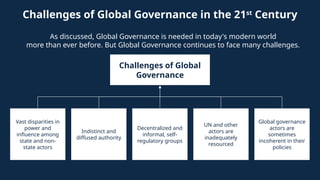
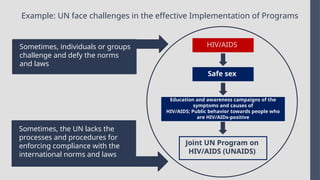
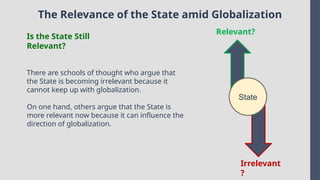
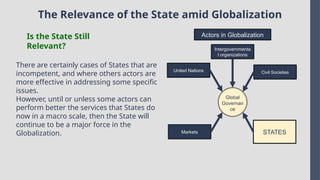
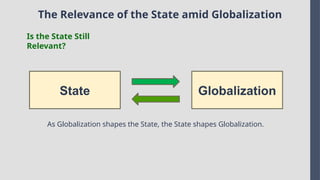
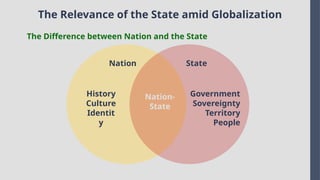
Explore the complexities and dynamics of contemporary global governance in this comprehensive PowerPoint presentation. Delve into the structures, challenges, and actors shaping the global order in the 21st century. From international organizations like the United Nations and World Bank to the role of non-state actors, multinational corporations, and grassroots movements, this presentation provides a nuanced understanding of how global policies are formulated and implemented. Examine key issues such as climate change, global security, human rights, and economic inequality, and discover how global governance mechanisms strive to address these pressing concerns. With a focus on collaboration, power dynamics, and the evolving nature of sovereignty, this presentation offers valuable insights into the opportunities and obstacles facing global governance today.