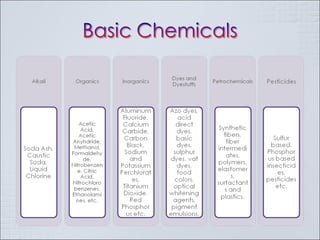
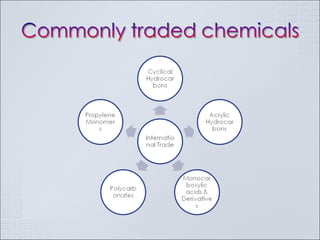
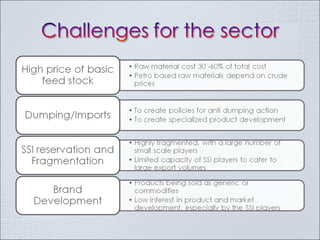
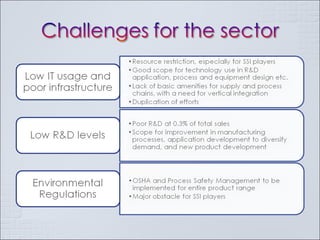
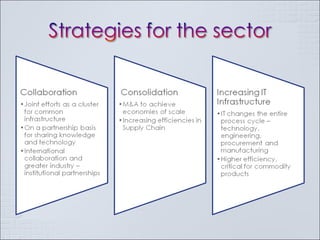
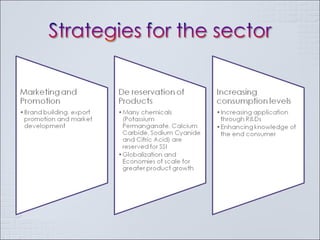
The Indian chemical industry generated USD 42 billion in revenue in fiscal year 2009, growing 11.5% in 2009-2010. It is the third largest chemical industry in Asia, yet only accounts for 2% of the global chemical industry. The industry consumes 1/3 of its production and contributes 13% to exports, 13% to industrial output, 7% to GDP, and 20% to tax revenues. The industry is cyclical and driven by demand from customer segments, but players often add new capacity at the end of growth phases, leading to excess capacity when business cycles decline. Petrochemicals such as olefins and aromatics make up over 60% of the basic chemical industry by revenue. Companies must pursue strategies