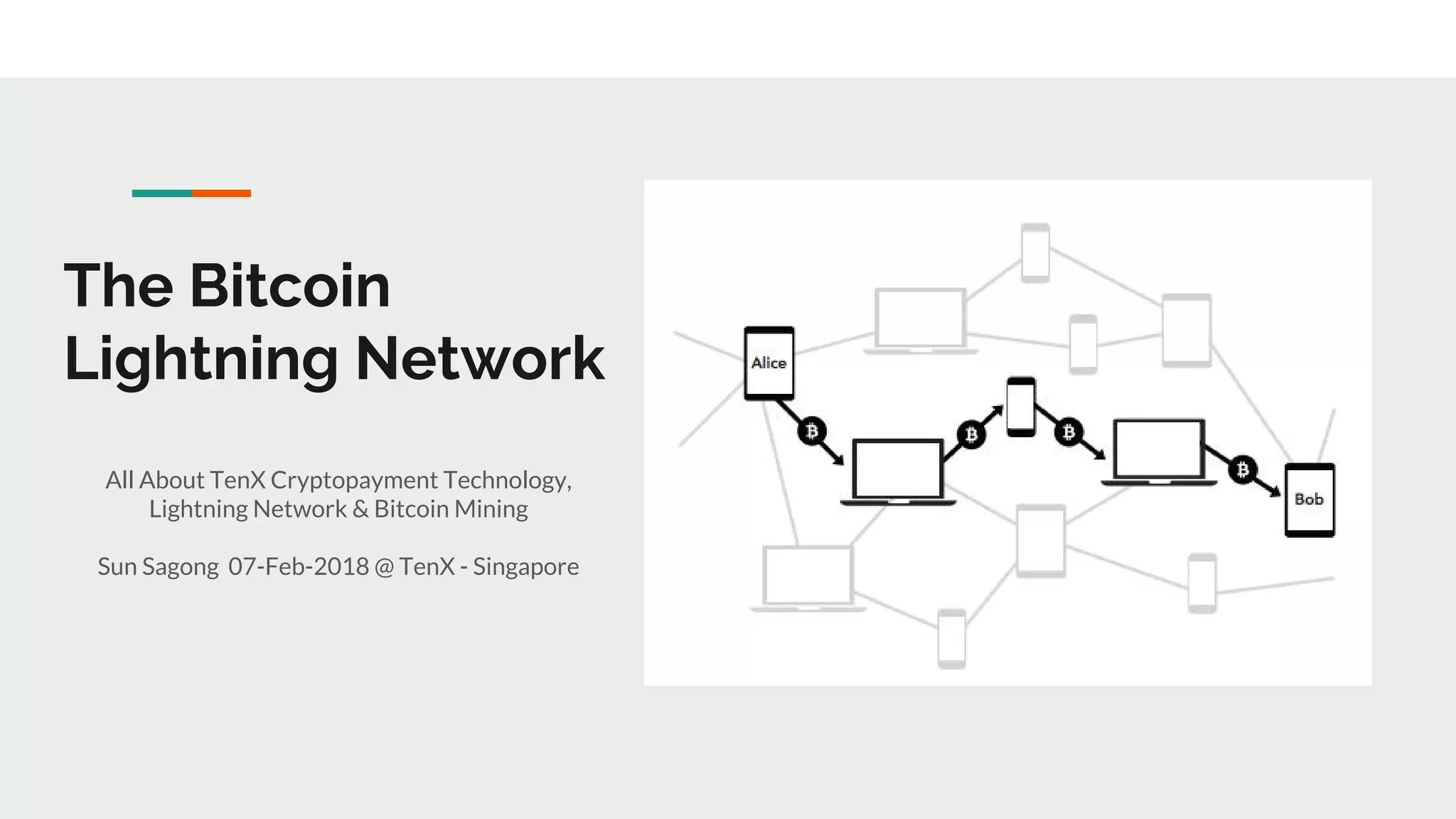
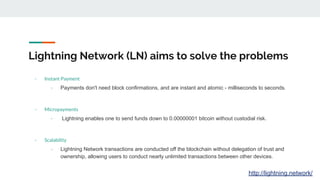
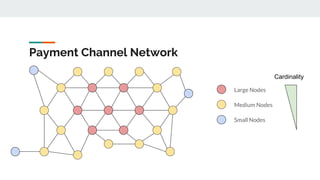
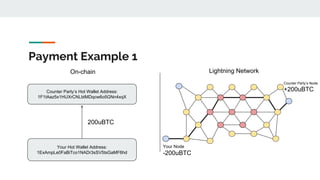
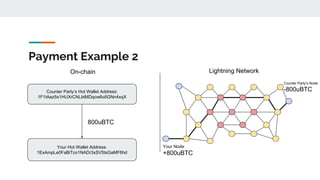
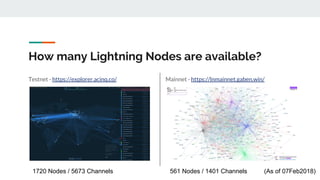
The Lightning Network aims to solve Bitcoin's problems of slow payments, high transaction costs, and poor scalability. It allows for instant, very low-cost payments between nodes by conducting transactions off-blockchain through payment channels. There are currently three main implementations of Lightning that have achieved compatibility. The network functions as a layer on top of Bitcoin through defined BOLT protocols, forming a decentralized network of payment channels between nodes.