Embed presentation



















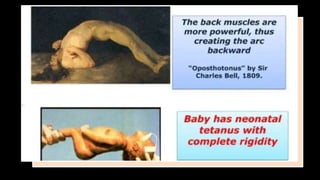














Tetanus is caused by Clostridium tetani, a bacteria commonly found in soil and the intestines of humans and animals. The bacteria produces a toxin called tetanospasmin that affects the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord, causing painful muscle rigidity and convulsions. Symptoms include lockjaw (trismus), risus sardonicus (contraction of facial muscles), and board-like abdominal rigidity. Management of tetanus involves neutralizing the toxin with tetanus antitoxin, debriding wounds to prevent further toxin production, antibiotics to prevent secondary infections, muscle relaxants to control spasms, and maintaining hydration, nutrition, and a quiet environment for


































