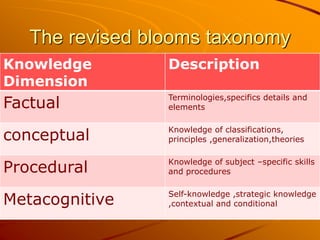
This document provides information on test construction. It discusses the key steps in constructing a valid test, which include formulating test objectives based on cognitive learning objectives and creating a table of specifications. It also discusses writing test items, with a focus on constructing high-quality multiple choice items. Guidelines are provided for writing clear stems, plausible distractors, and avoiding common issues. The document emphasizes writing items that measure intended cognitive skills based on a taxonomy, such as Bloom's. It also notes the importance of validating items and checking that test construction guidelines were followed.