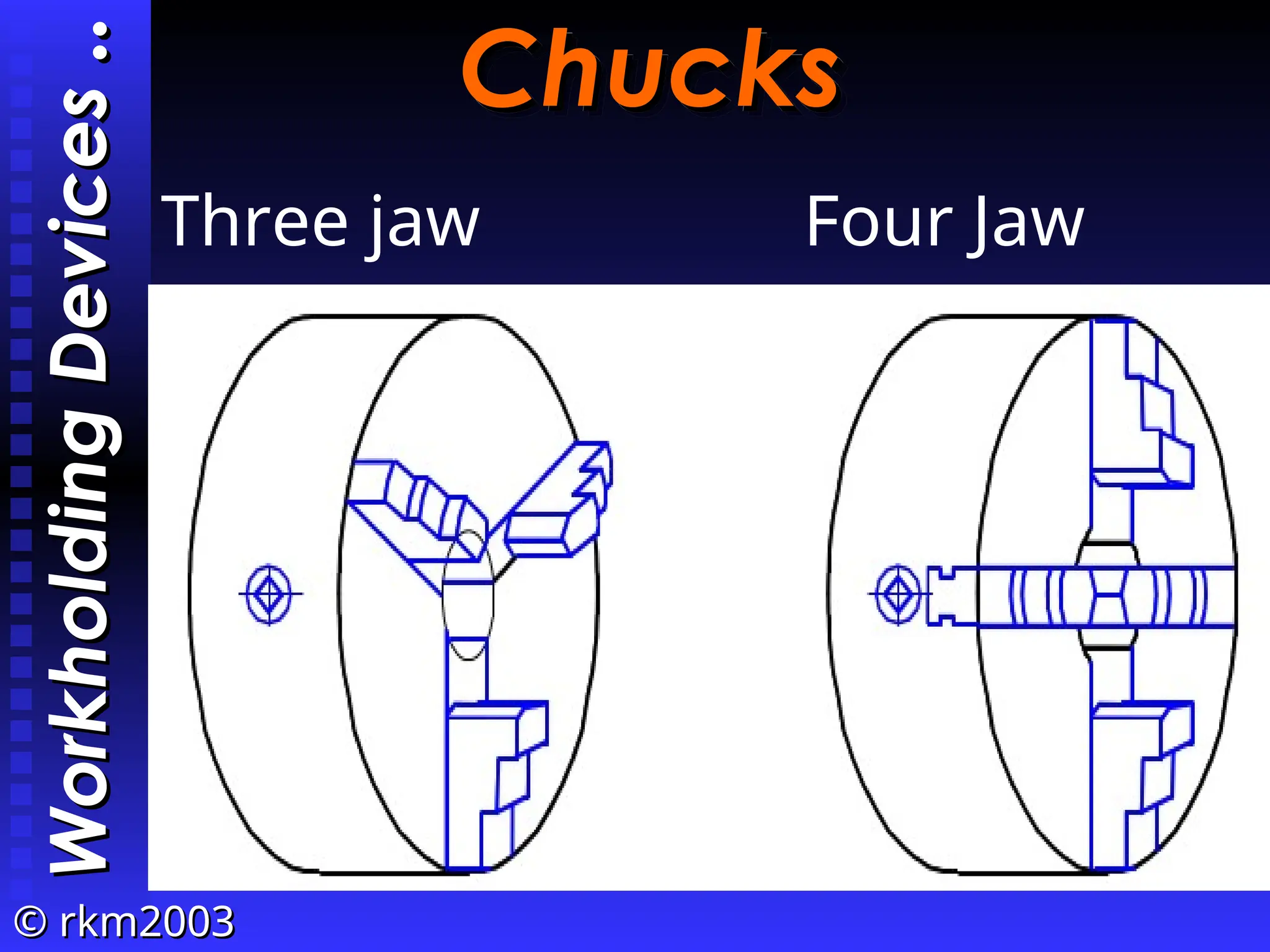
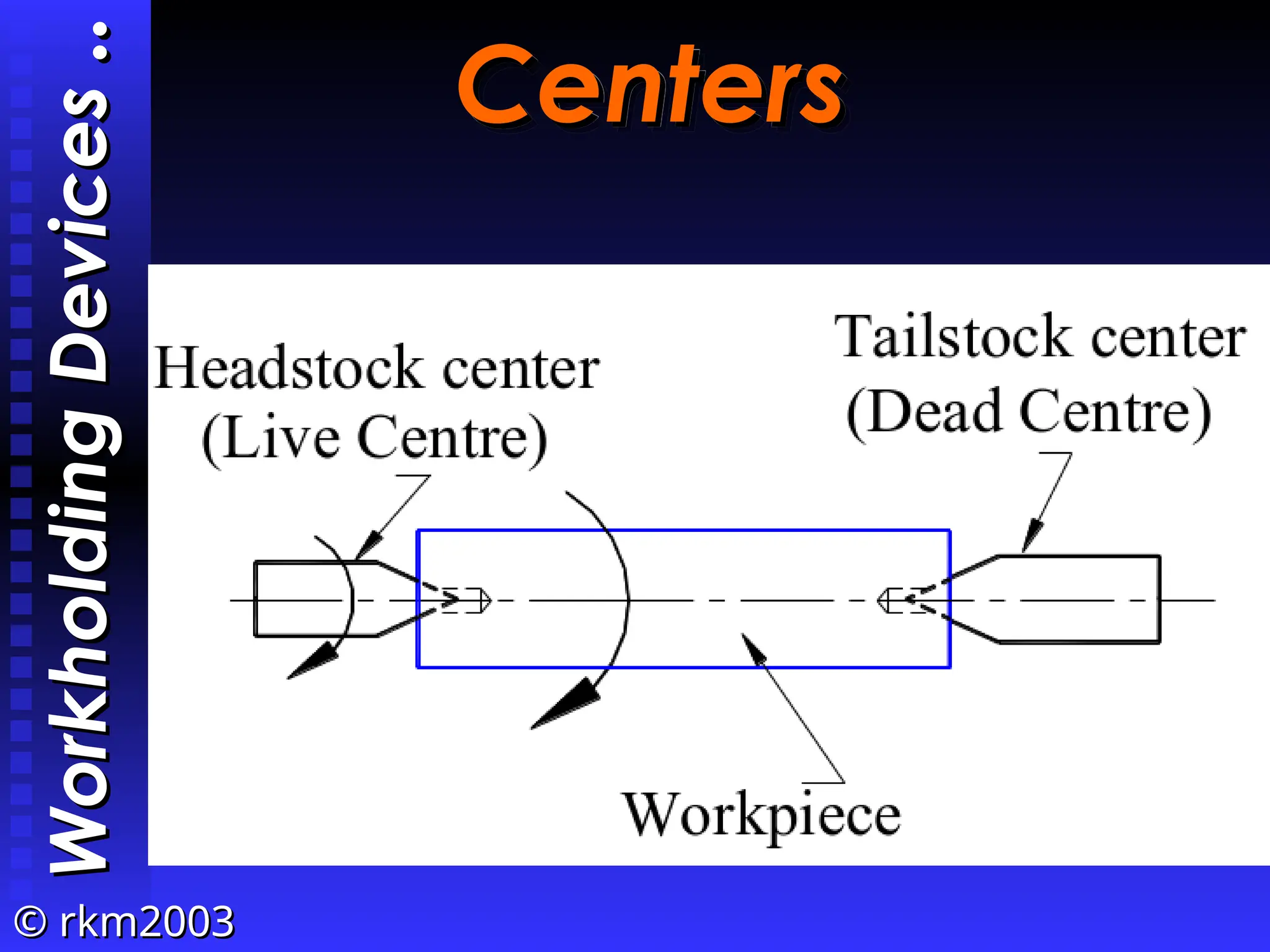
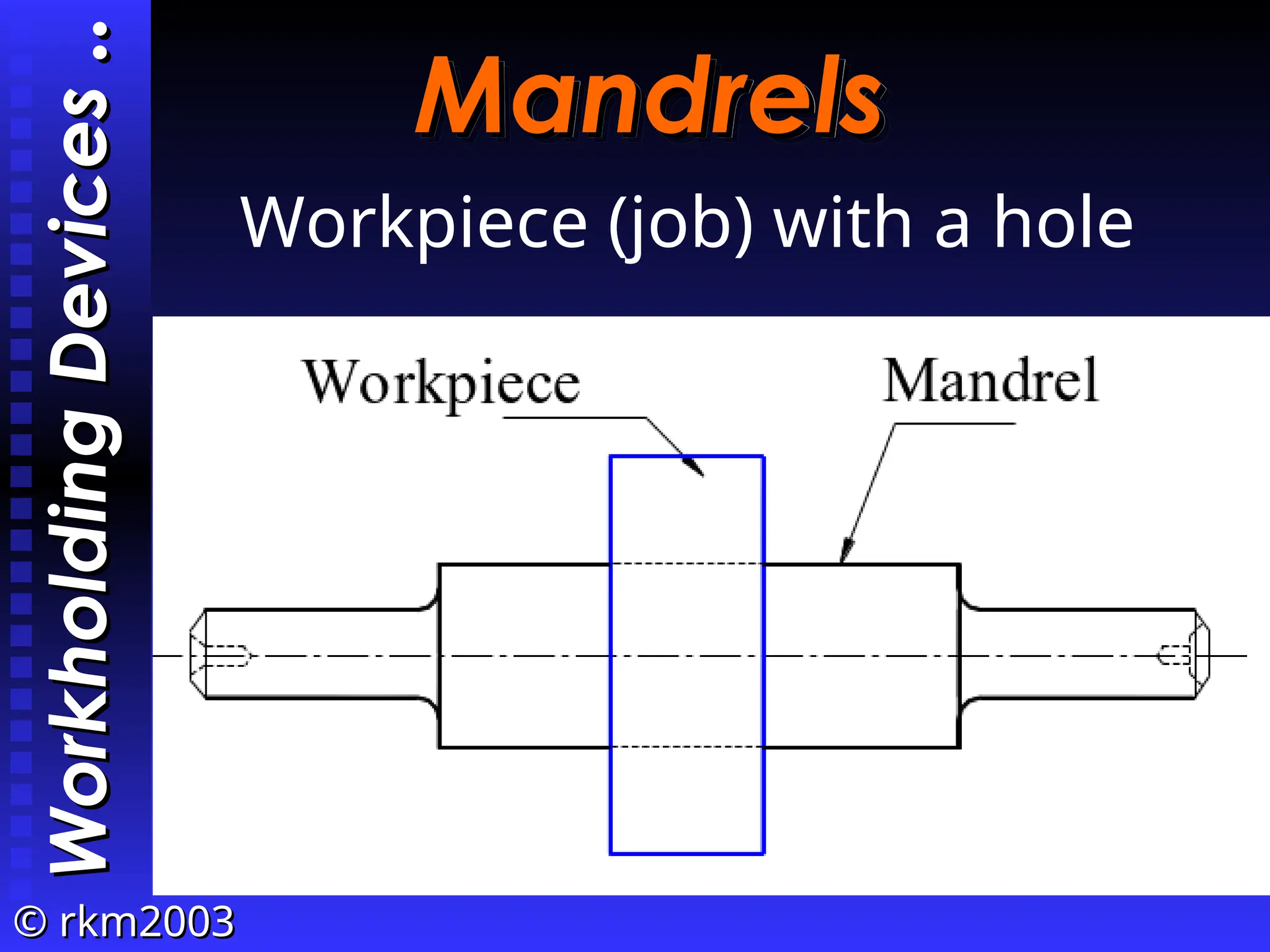
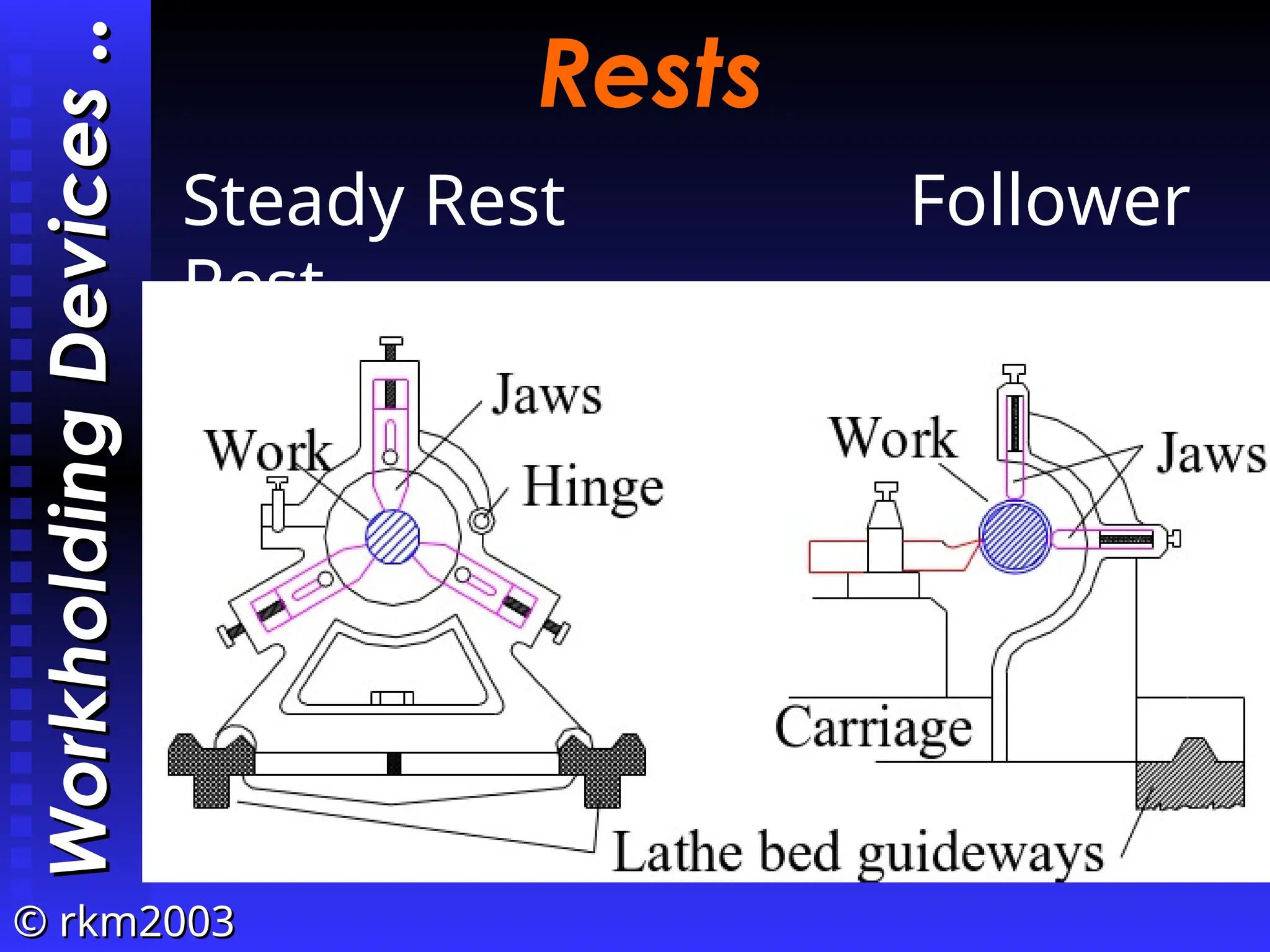
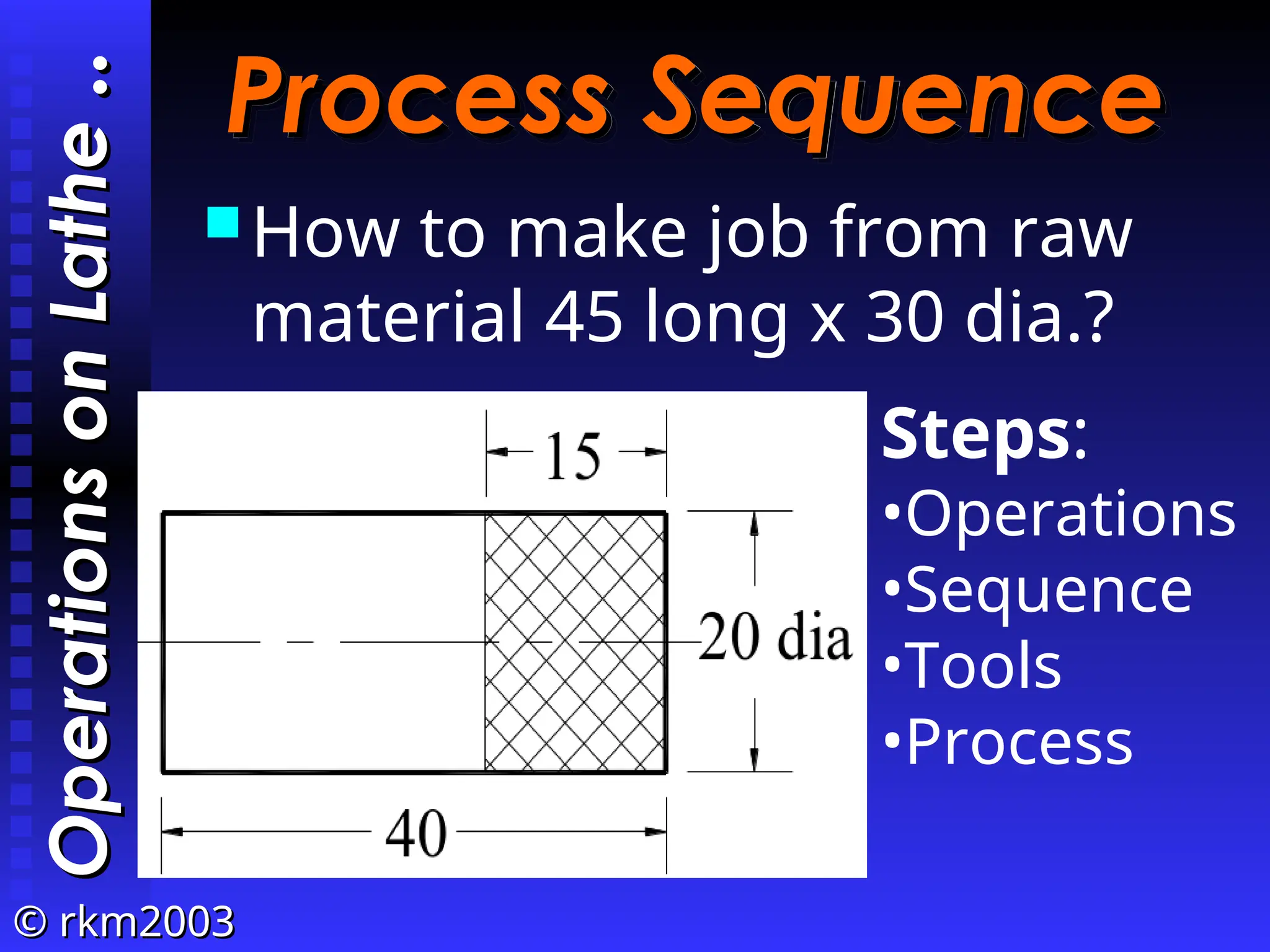
The document provides an overview of lathe operations, detailing machine components, types of lathes, workholding devices, cutting conditions, and various turning operations such as turning, facing, knurling, and grooving. It includes the definitions of key concepts such as cutting speed, feed rate, and material removal rate, along with examples illustrating machining time calculations. Overall, it serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding lathe operation and its various applications.











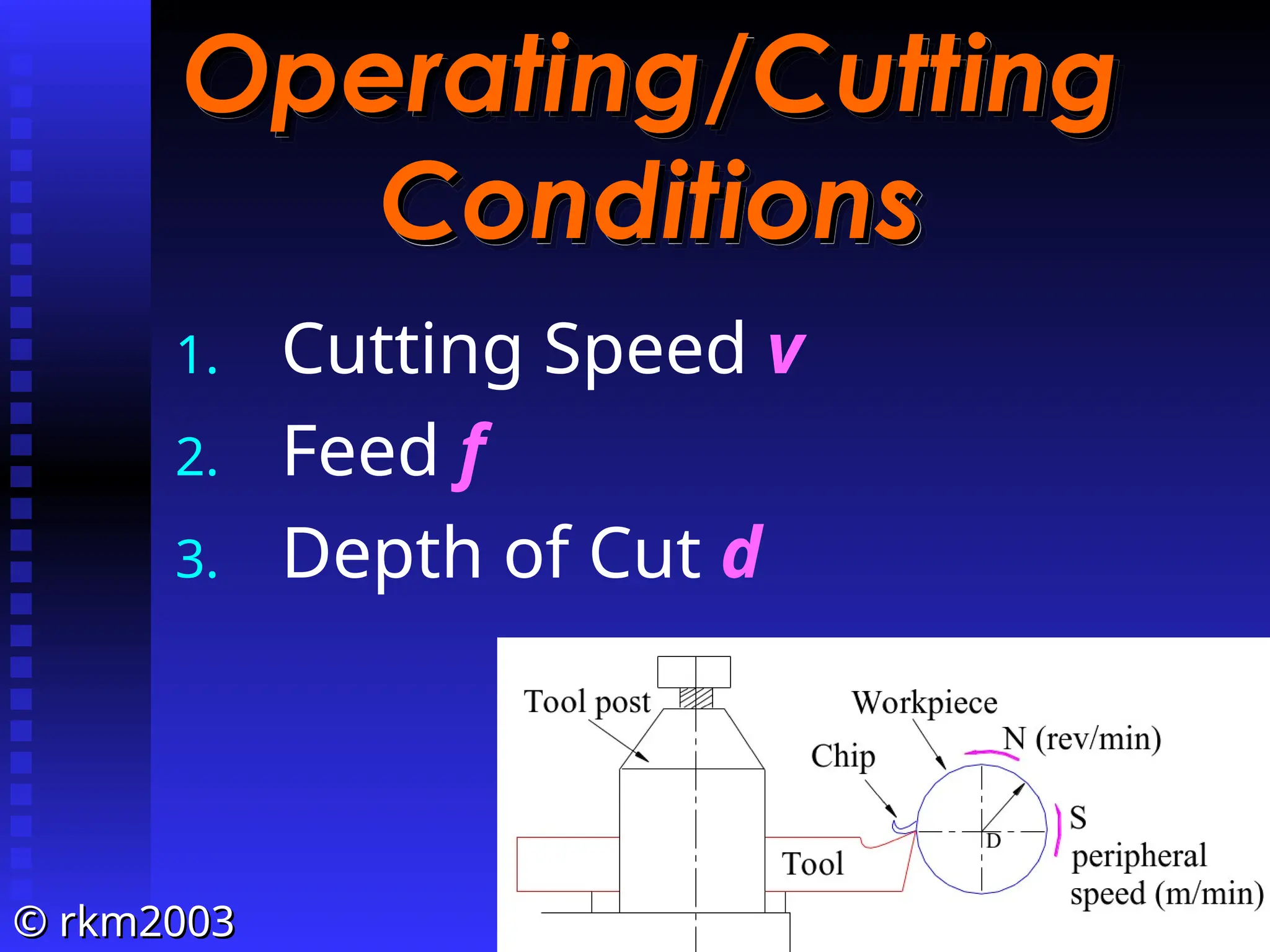
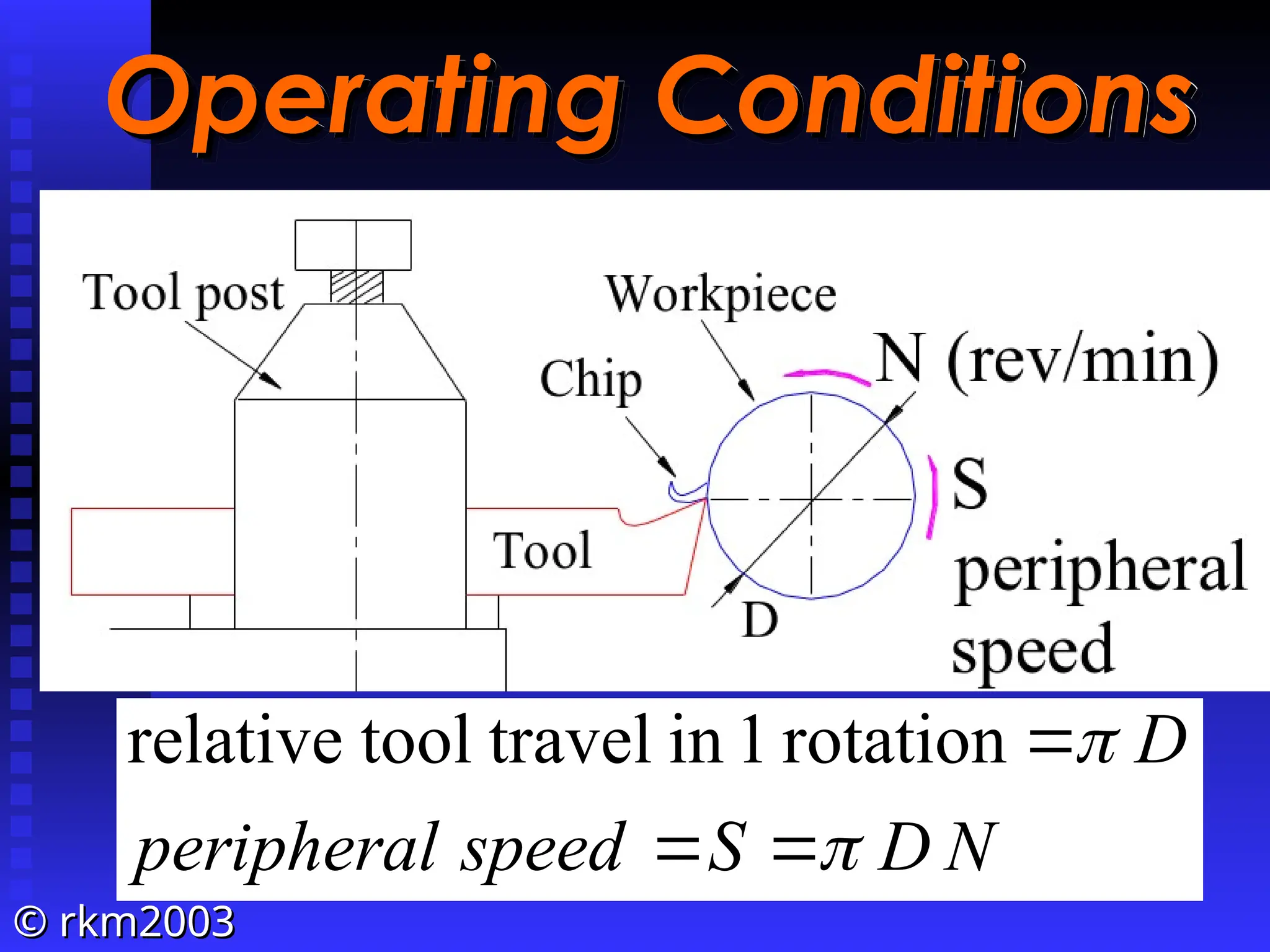
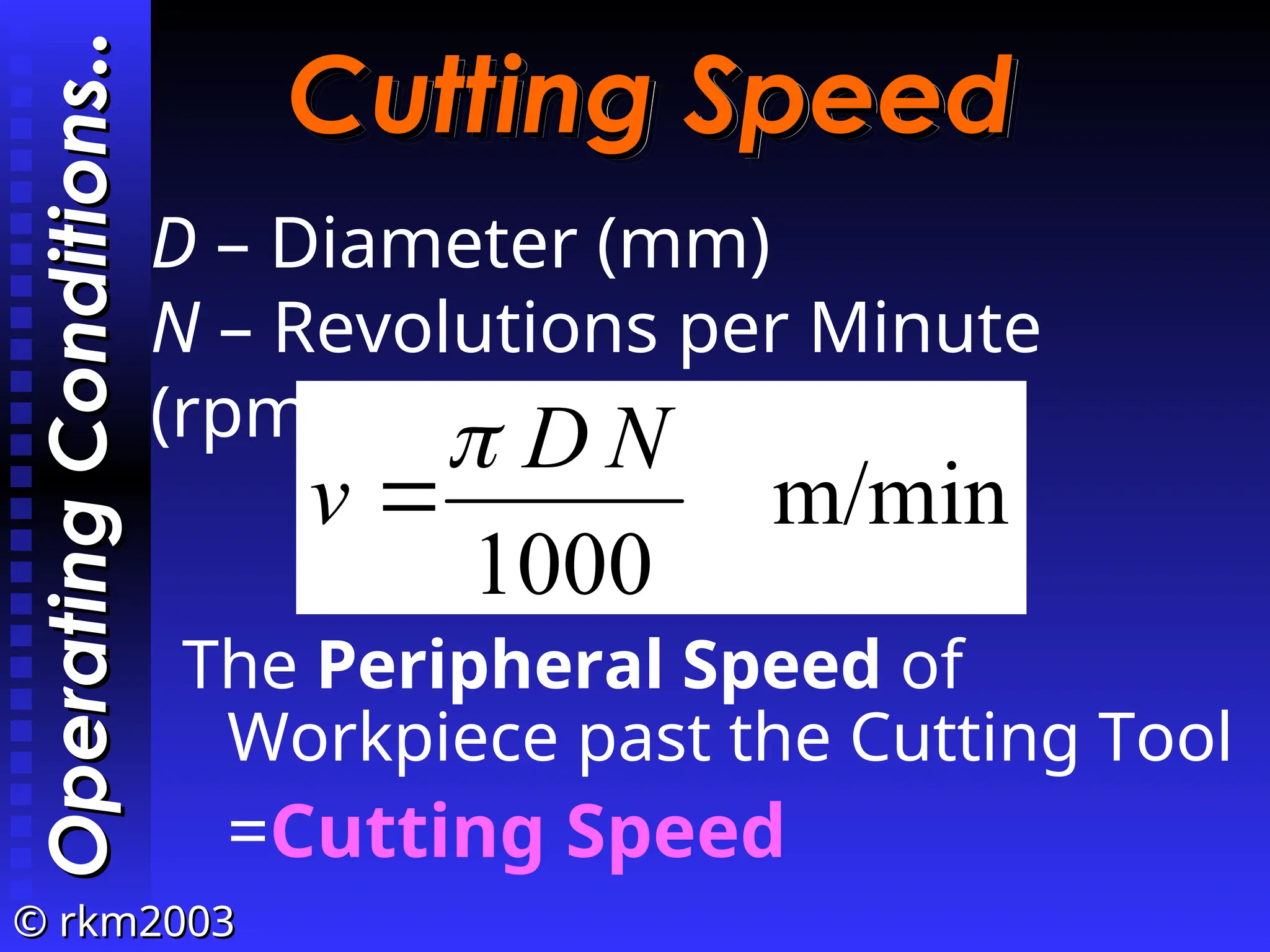
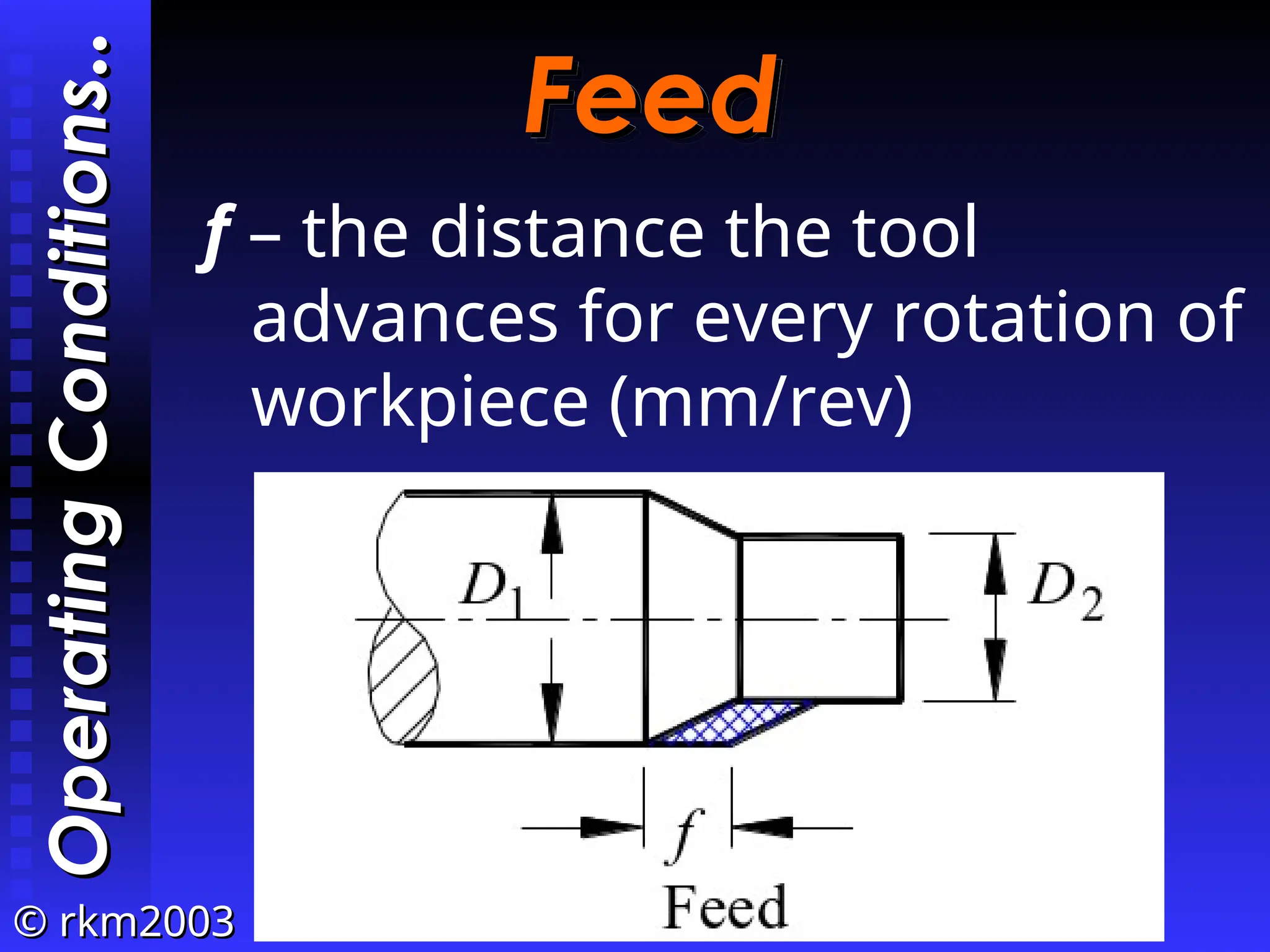
































![©
© rkm2003
rkm2003
Example
Example
Time for Turning:
Total length of tool travel = job length + length of
approach and overtravel
L = 170 + 5 = 175 mm
Required depth to be cut = (60 – 50)/2 = 5 mm
Since maximum depth of cut is 2 mm, 5 mm cannot
be cut in one pass. Therefore, we calculate number
of cuts or passes required.
Number of cuts required = 5/2 = 2.5 or 3 (since cuts
cannot be a fraction)
Machining time for one cut = L / (fN)
Total turning time = [L / (fN)] Number of cuts
= [175/(0.3440)] 3= 3.97
min.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-lathe-250116014716-687ded07/75/teori-mesin-bubut-dalam-teknik-permesinan-61-2048.jpg)












