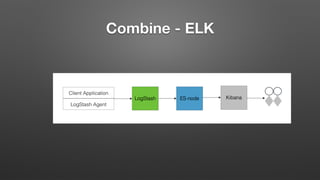
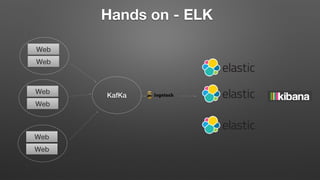
This document discusses Real Time Log Analytics using the ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) stack. It provides an overview of each component, including Elasticsearch for indexing and searching logs, Logstash for collecting, parsing, and enriching logs, and Kibana for visualizing and analyzing logs. It describes common use cases for log analytics like issue debugging and security analysis. It also covers challenges like non-consistent log formats and decentralized logs. The document includes examples of log entries from different systems and how ELK addresses issues like scalability and making logs easily searchable and reportable.




![Non-consistent log format
TOMCAT LOGS
A typical tomcat server startup log entry will look like this:
May 24, 2015 3:56:26 PM org.apache.catalina.startup.HostConfig deployWAR
INFO: Deployment of web application archive softapache-tomcat-7.0.62webappssample.war has
finished in 253 ms
APACHE ACCESS LOGS – COMBINED LOG FORMAT
A typical Apache access log entry will look like this:
127.0.0.1 - - [24/May/2015:15:54:59 +0530] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 200 21630
IIS LOGS
A typical IIS log entry will look like this:
2012-05-02 17:42:15 172.24.255.255 - 172.20.255.255 80 GET /images/favicon.ico - 200 Mozilla/
4.0+(compatible;MSIE+5.5;+Windows+2000+Server)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/technology-behind-real-time-log-analytics1-160528095346/85/Technology-behind-real-time-log-analytics-6-320.jpg)