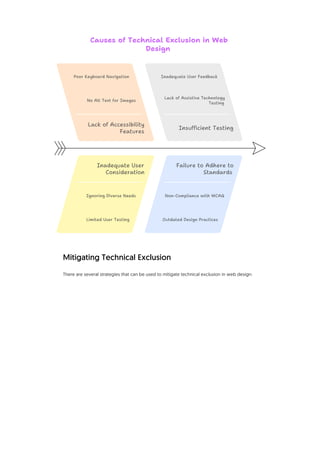
CheapWebDesign strives to deliver reliable website services and assist with most technical inquiries—but some issues fall outside the scope of their support. Here's a closer look at what is excluded from support services according to their Technical Exclusion policy: