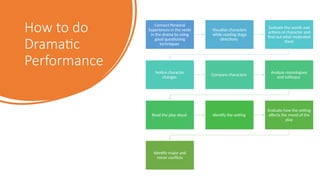
The document provides an overview of prose, including its types such as descriptive, narrative, and expository prose, as well as various sub-genres like allegory, fables, and myths. It also outlines different types of essays and prose forms, alongside strategies and objectives for teaching prose, which aim to enhance reading and comprehension skills. Additionally, it discusses methods for dramatic performance in teaching literature.