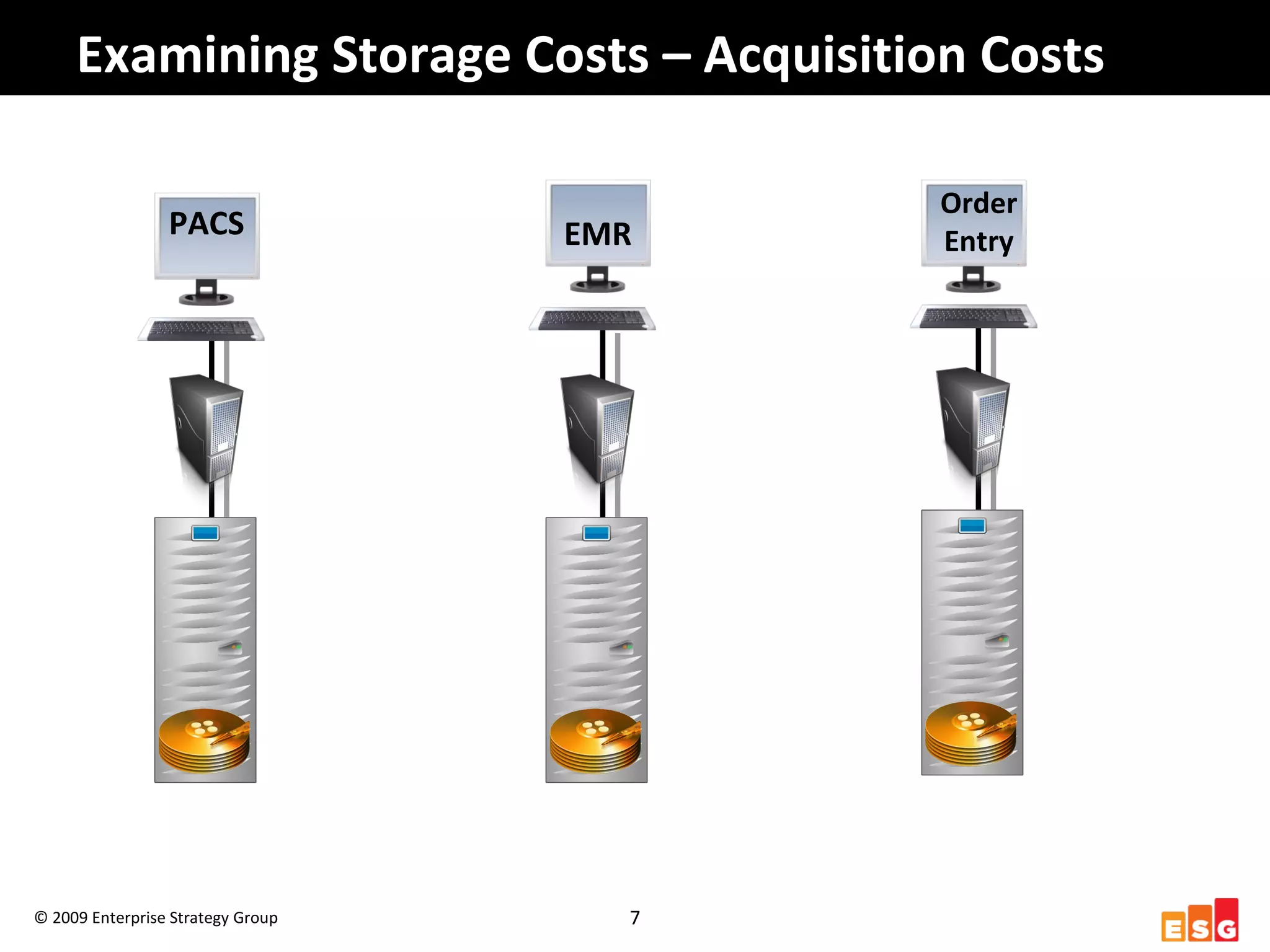
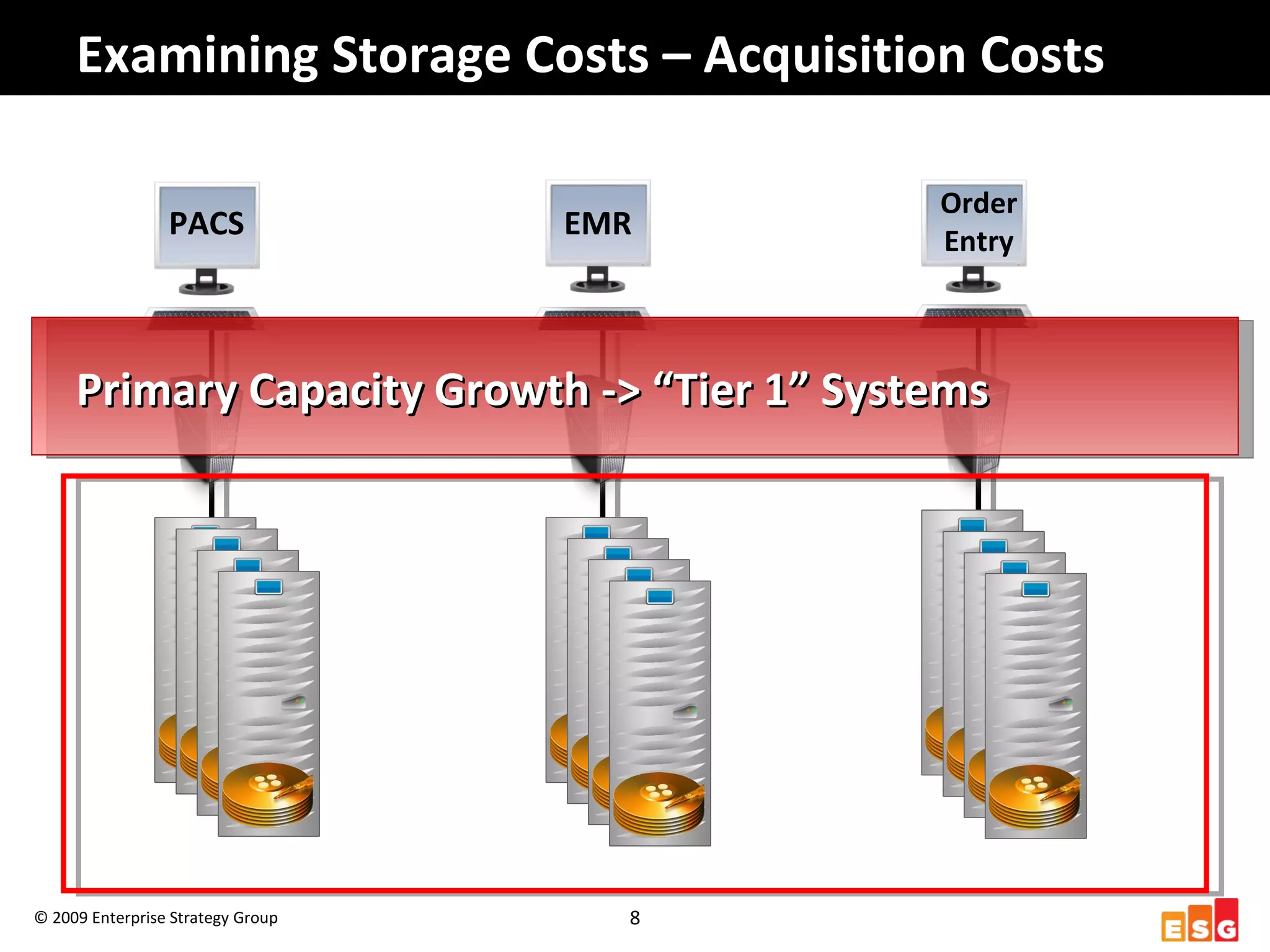
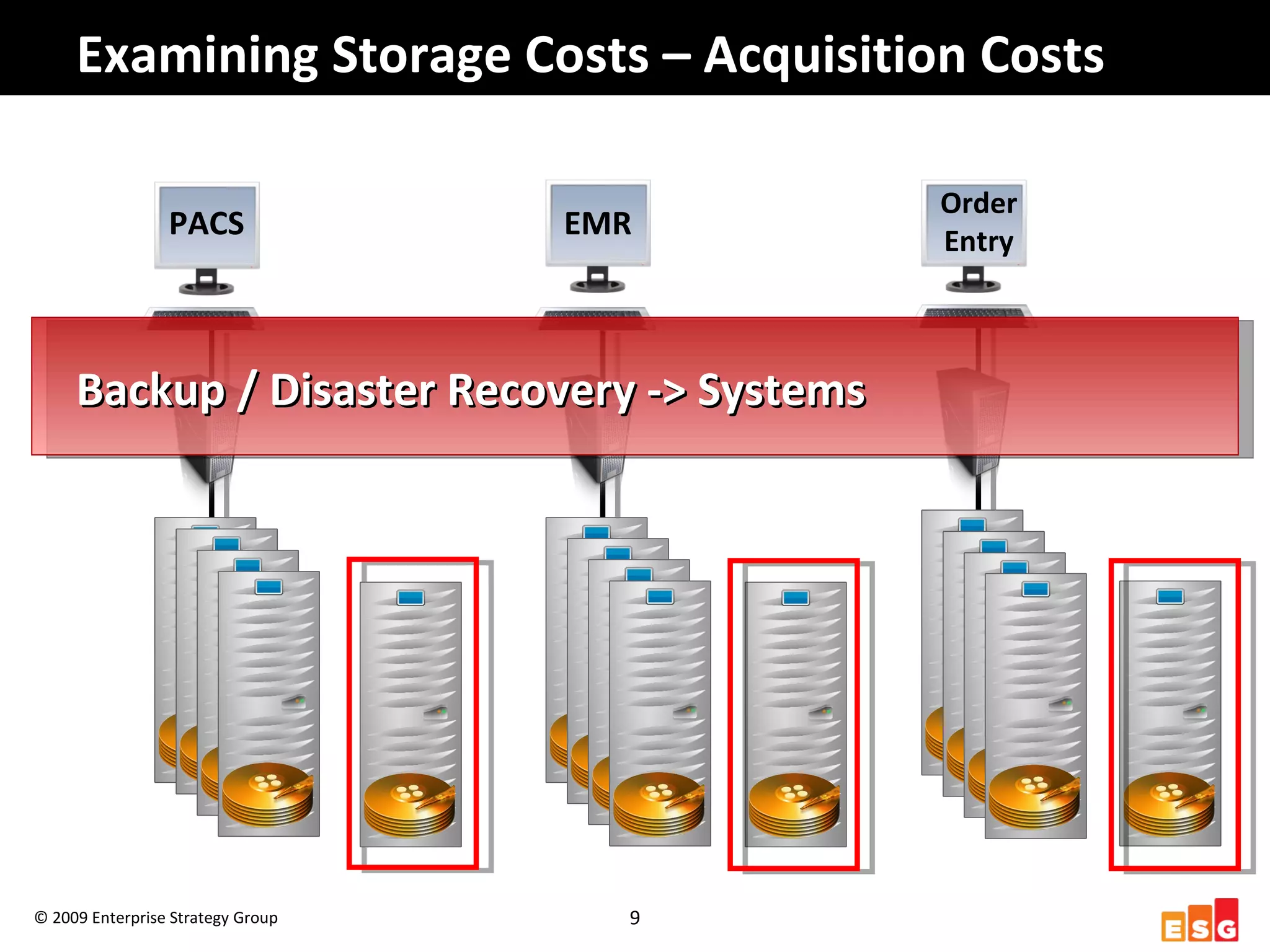
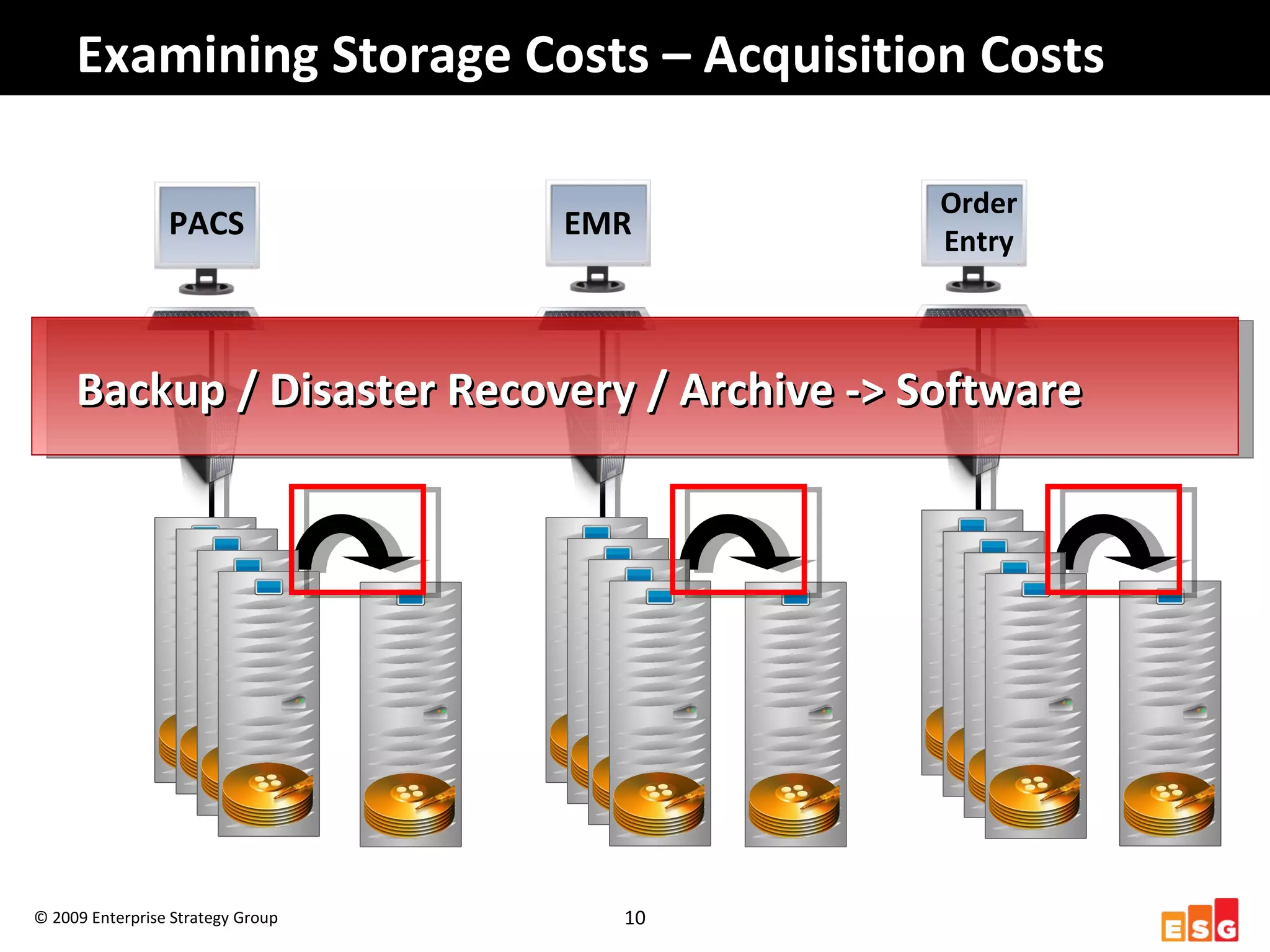
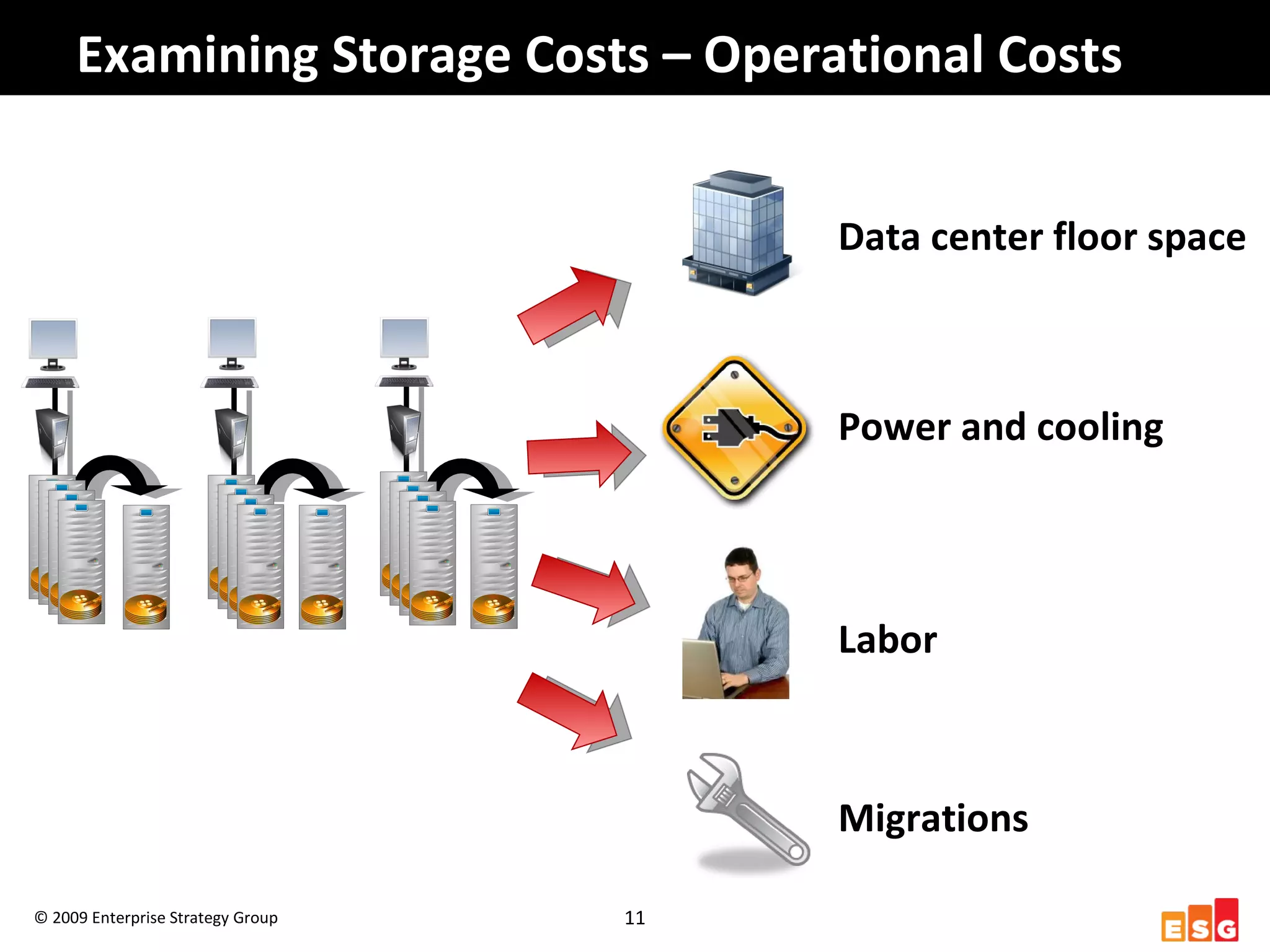
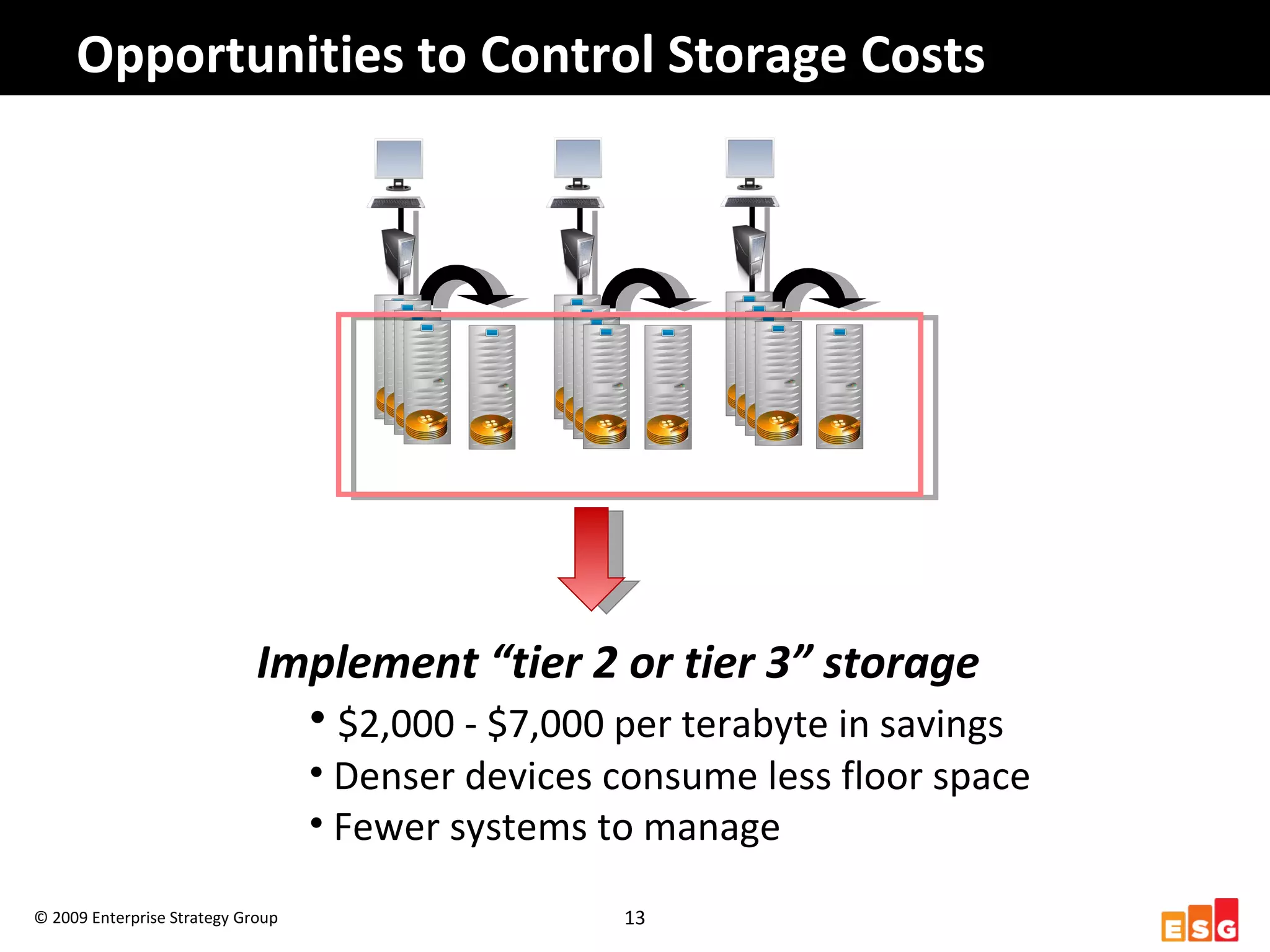
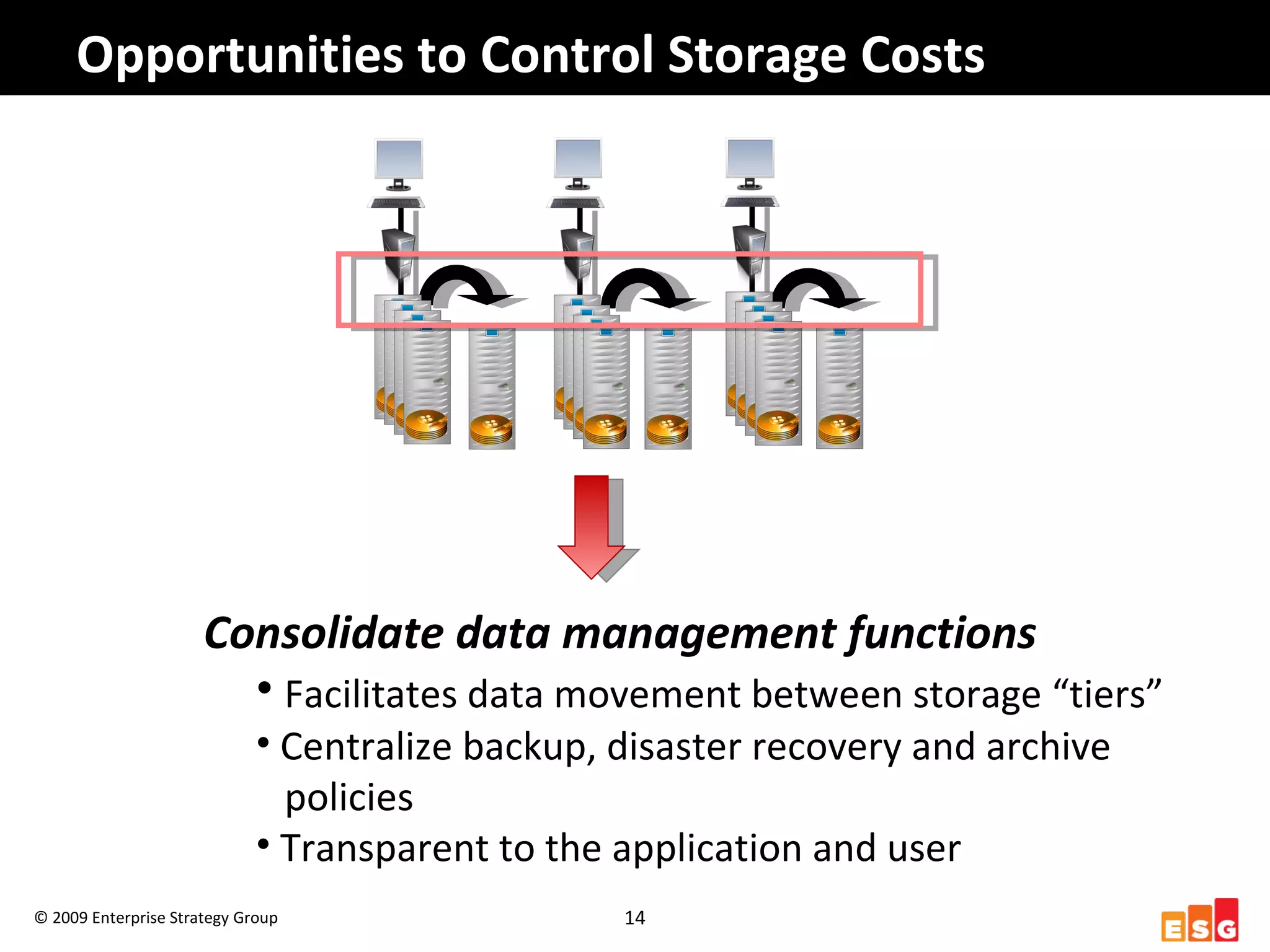
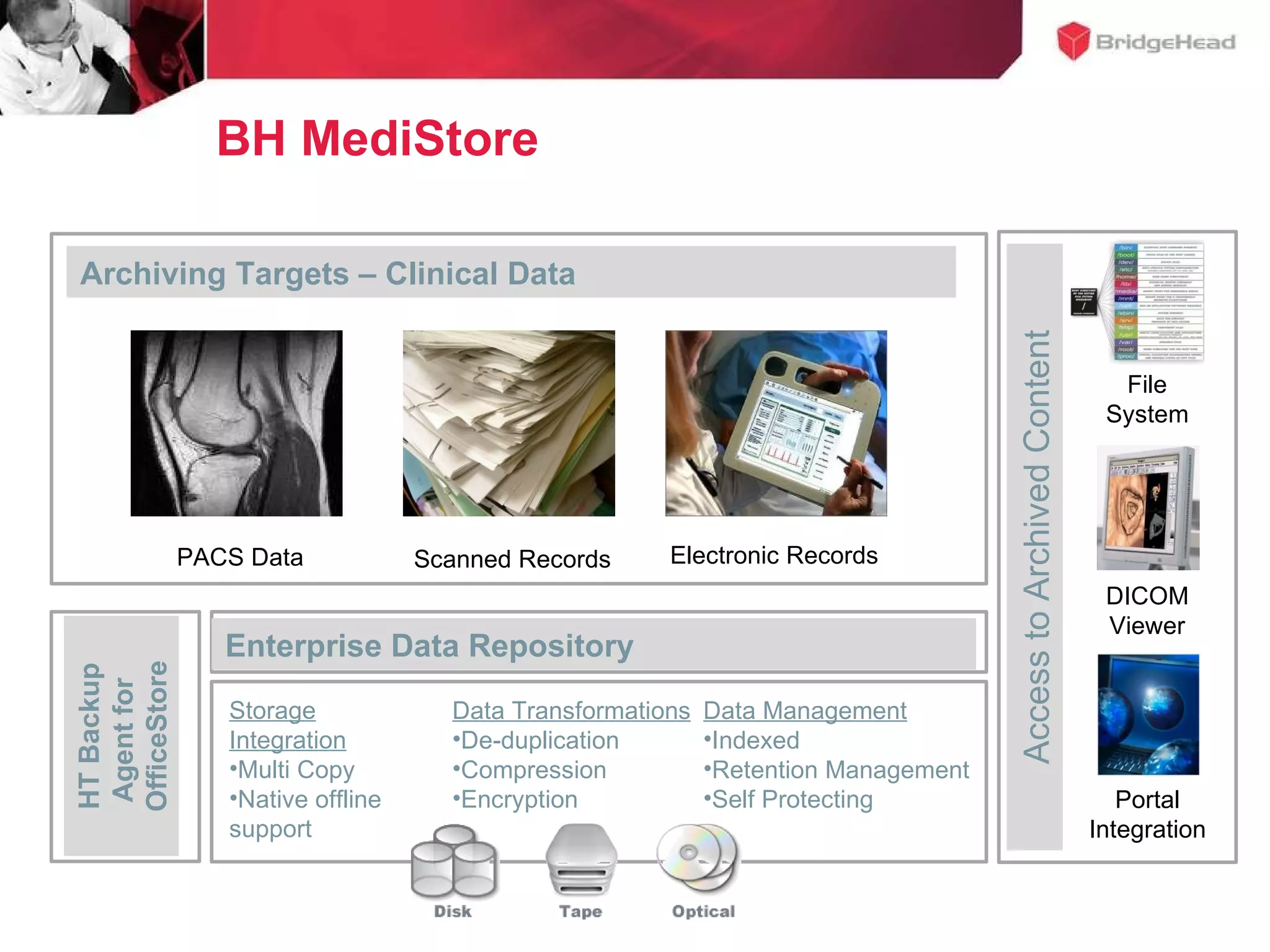
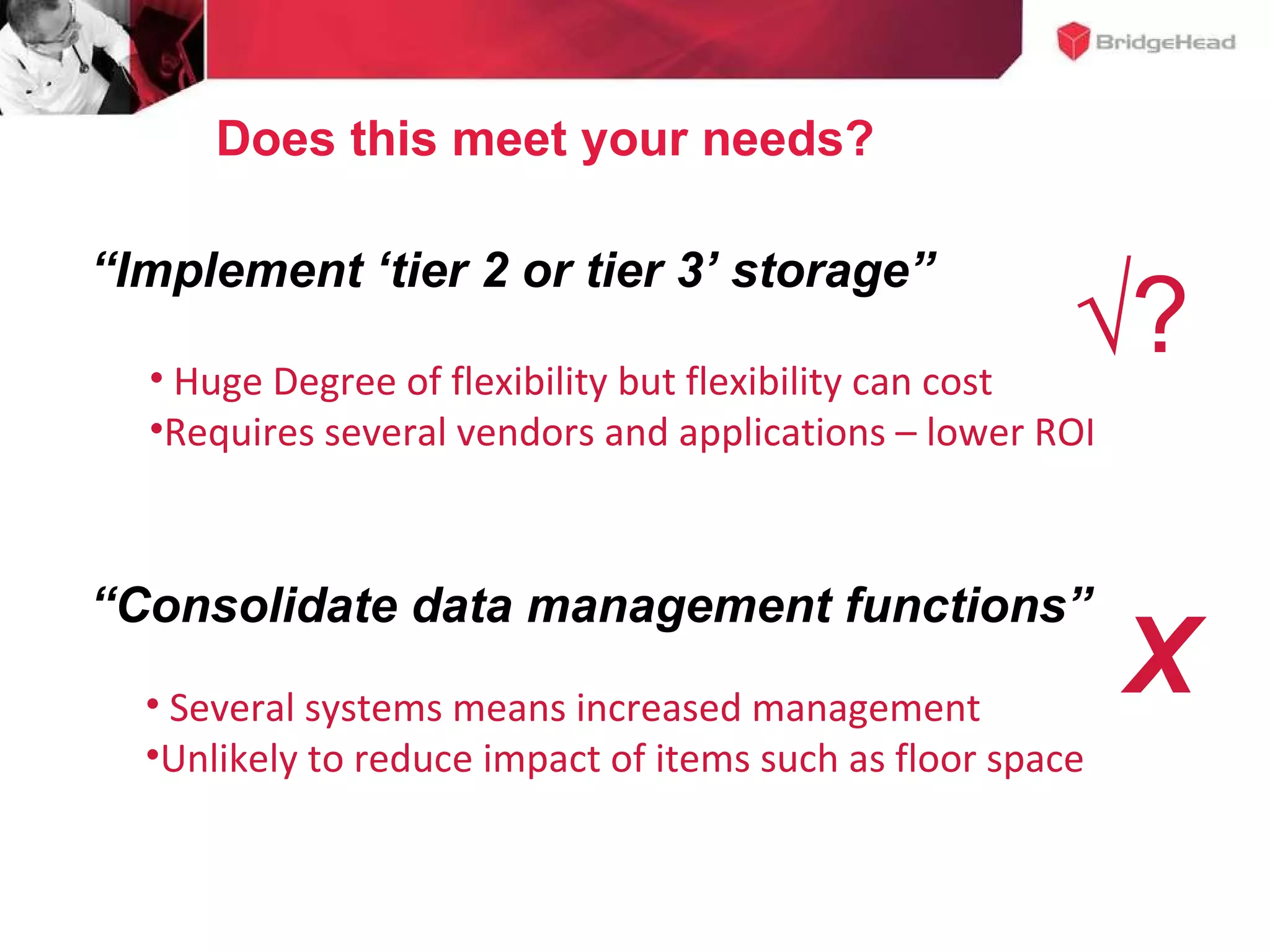
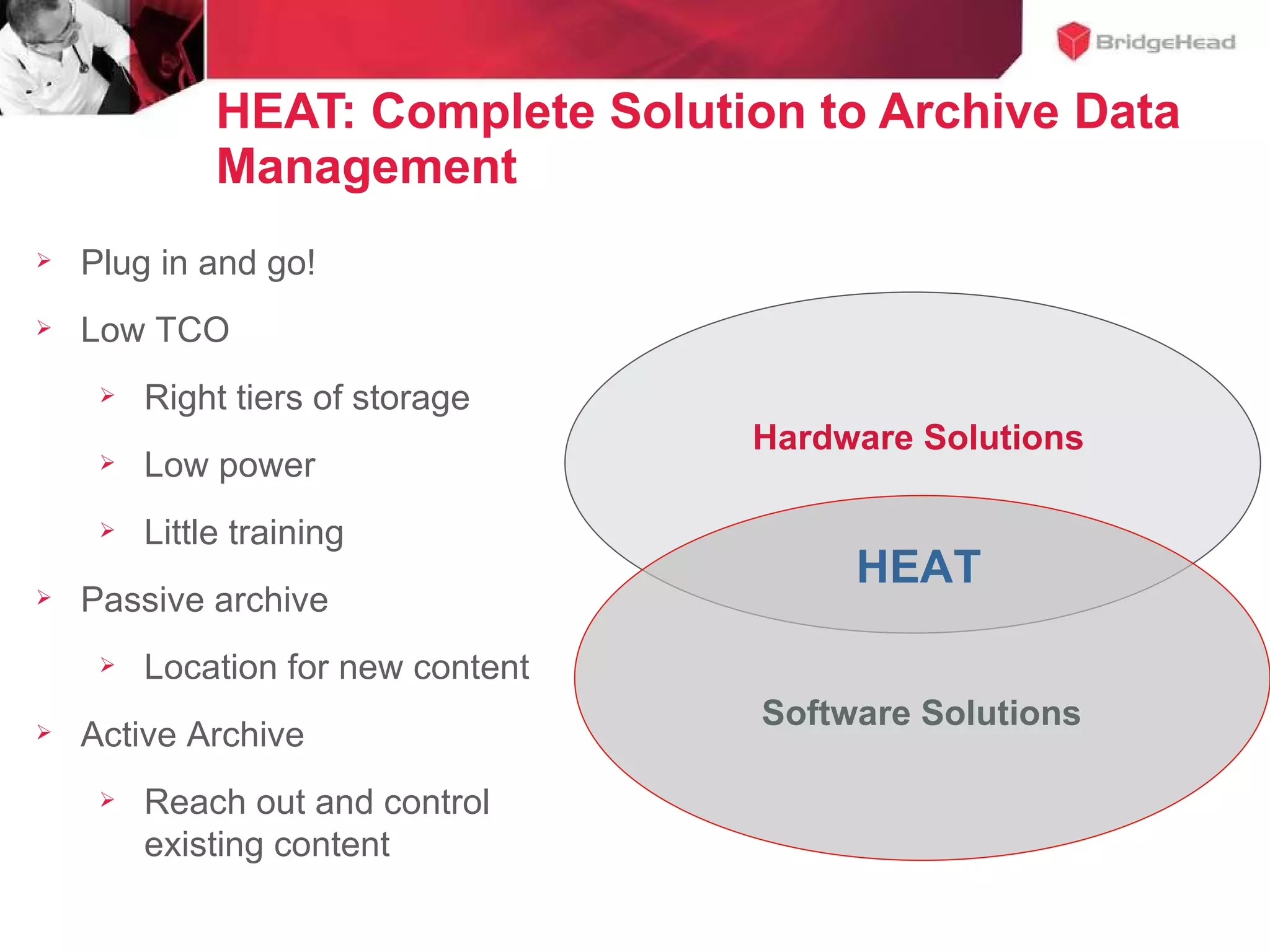
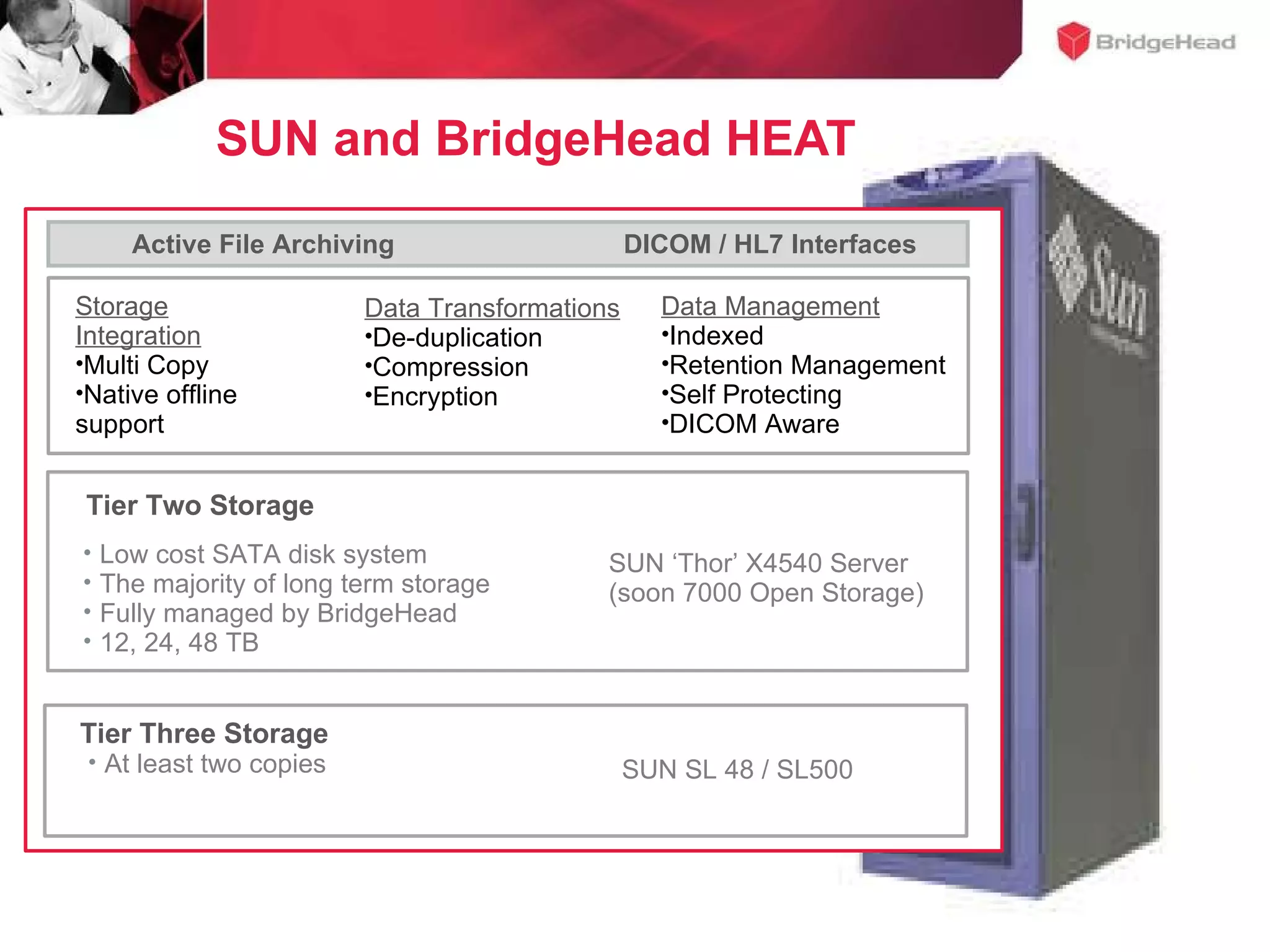
The document discusses challenges in managing healthcare data to balance storage costs with compliance and access requirements. It notes that increased use of electronic medical records and imaging systems has led to exponential growth in healthcare data. This data must be stored and managed for long periods as required by regulations while controlling rising storage costs. The presented solution proposes implementing tiered storage with lower-cost systems to reduce storage expenses while also consolidating data management functions into a single archiving appliance to decrease management overhead and floor space usage. This integrated approach aims to help healthcare organizations meet data retention mandates cost-effectively.