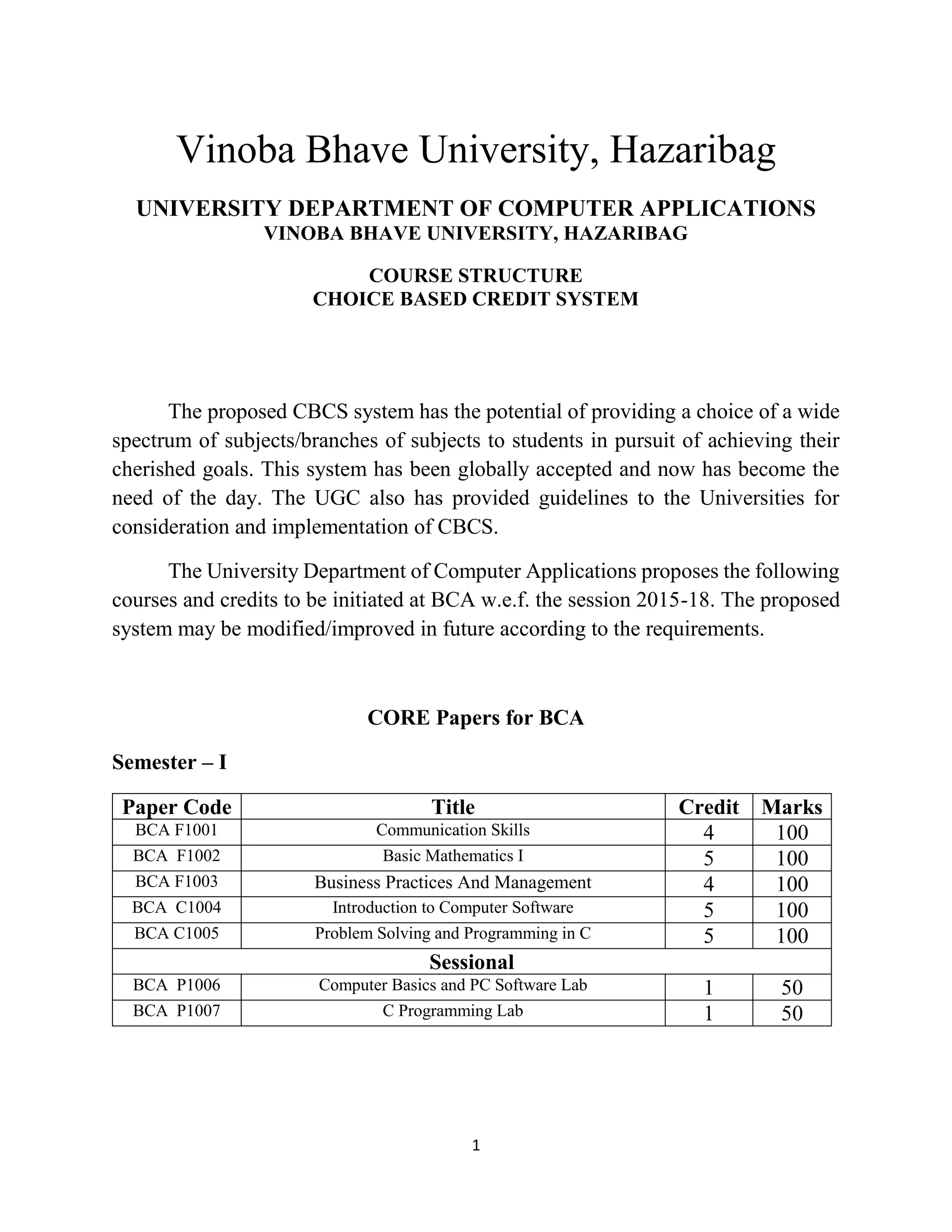
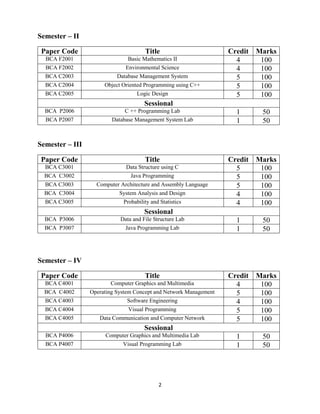
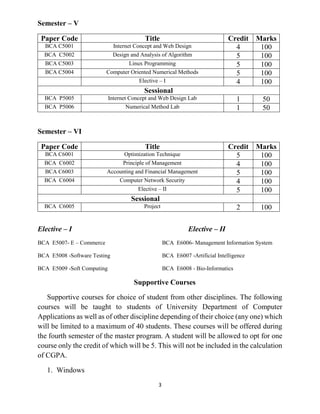
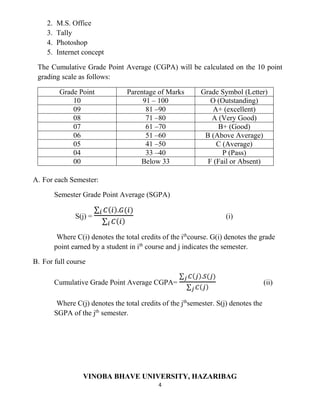
The document outlines the course structure and regulations for the Bachelor of Computer Applications (BCA) program offered by Vinoba Bhave University, Hazaribag, Jharkhand, India. It details the 6 semester program with core and elective papers in each semester totaling 150 credits. The courses cover topics like programming, databases, operating systems, computer graphics, algorithms, and management subjects. Academic performance is evaluated using a 10 point grading scale and grade point average system. Practical training and a final project in the 6th semester are also part of the program.