The document outlines a framework for building swift microservices, detailing the architecture, tools for code quality, and the integration with AWS services like DynamoDB. It emphasizes the use of Swift for its developer-friendly features and discusses the implementation of coding protocols for serialization and database operations. Additionally, it describes functionalities such as automatic credential rotation and health checks for container management, along with examples of data models and operations.












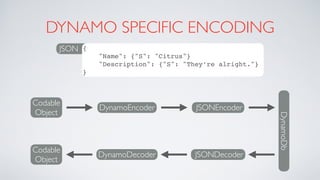


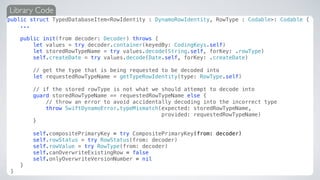
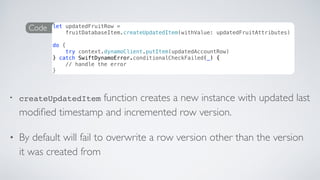

![AGAIN PROTOCOLSTOTHE RESCUE
• Similar toTypedDatabaseItem but returns a row type of Codable, de-
serialized according to the type specified in the data row
Library Code public protocol PossibleItemTypes {
static var types: [Codable.Type] { get }
}
public struct PolymorphicDatabaseItem<RowIdentity : DynamoRowIdentity,
PossibleTypes : PossibleItemTypes> : Decodable {
...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scw3-180224052508/85/Swift-Micro-services-and-AWS-Technologies-19-320.jpg)
