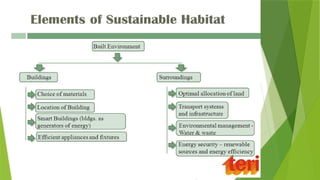
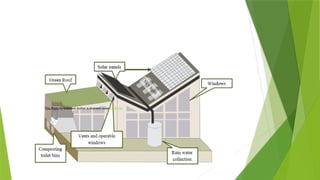
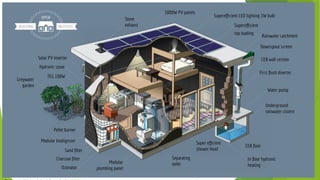
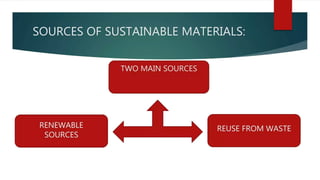
The document discusses sustainable building methods, highlighting straw bale construction and its growing popularity due to affordability and eco-friendliness. It emphasizes the importance of using renewable materials like cork, which enhances air quality and reduces environmental impact. The principles of sustainability in architecture are outlined, focusing on resource economy, life cycle design, and harmony between humans and nature throughout the building process.