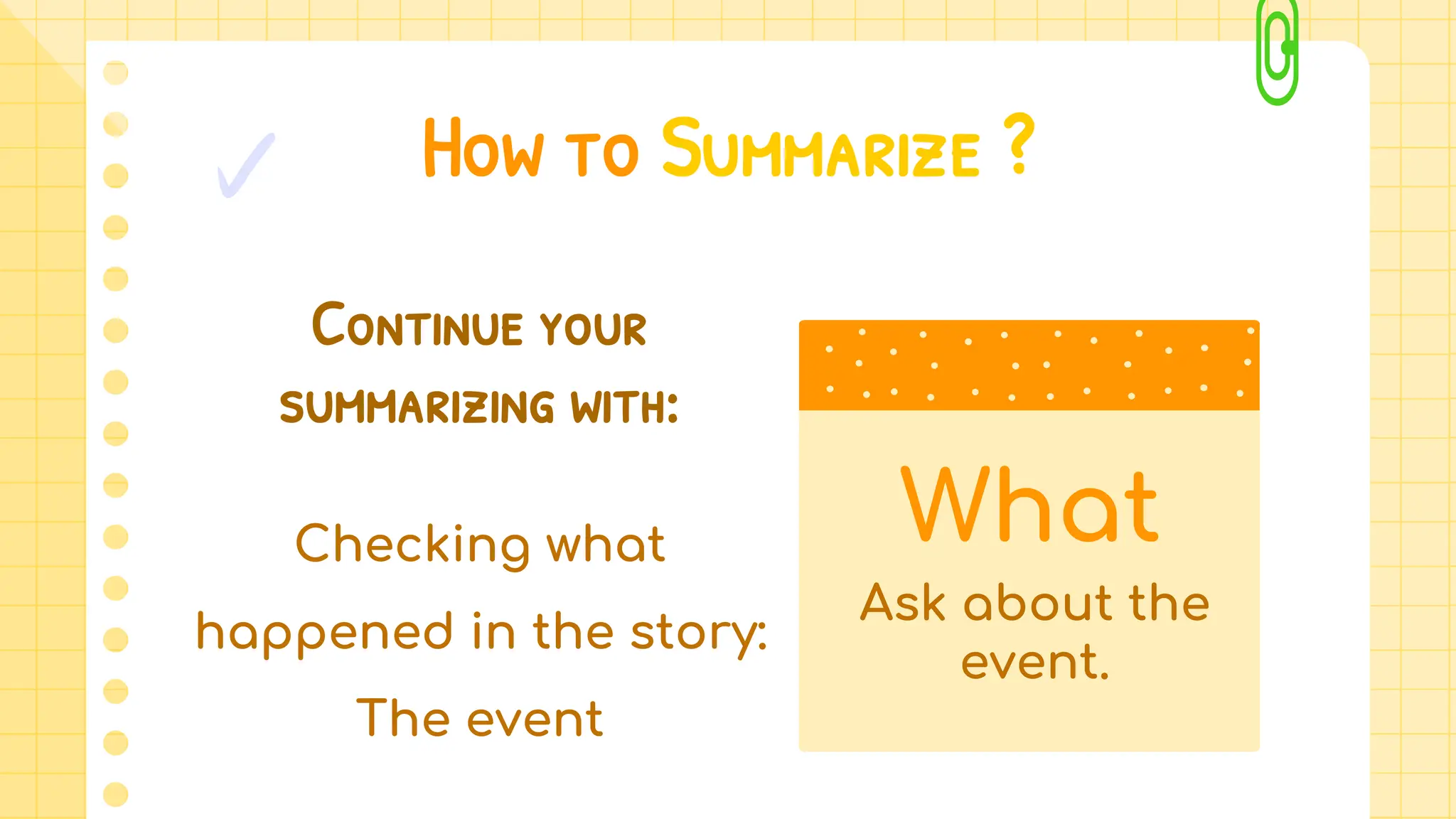
The document provides a guide on how to summarize texts effectively by using the 5 Ws (who, what, when, where, why). It includes examples, practice exercises, and emphasizes the importance of creating concise summaries that capture central ideas without personal opinions. The content is structured to help students learn the steps necessary for summarizing various topics like animals, places, and processes.