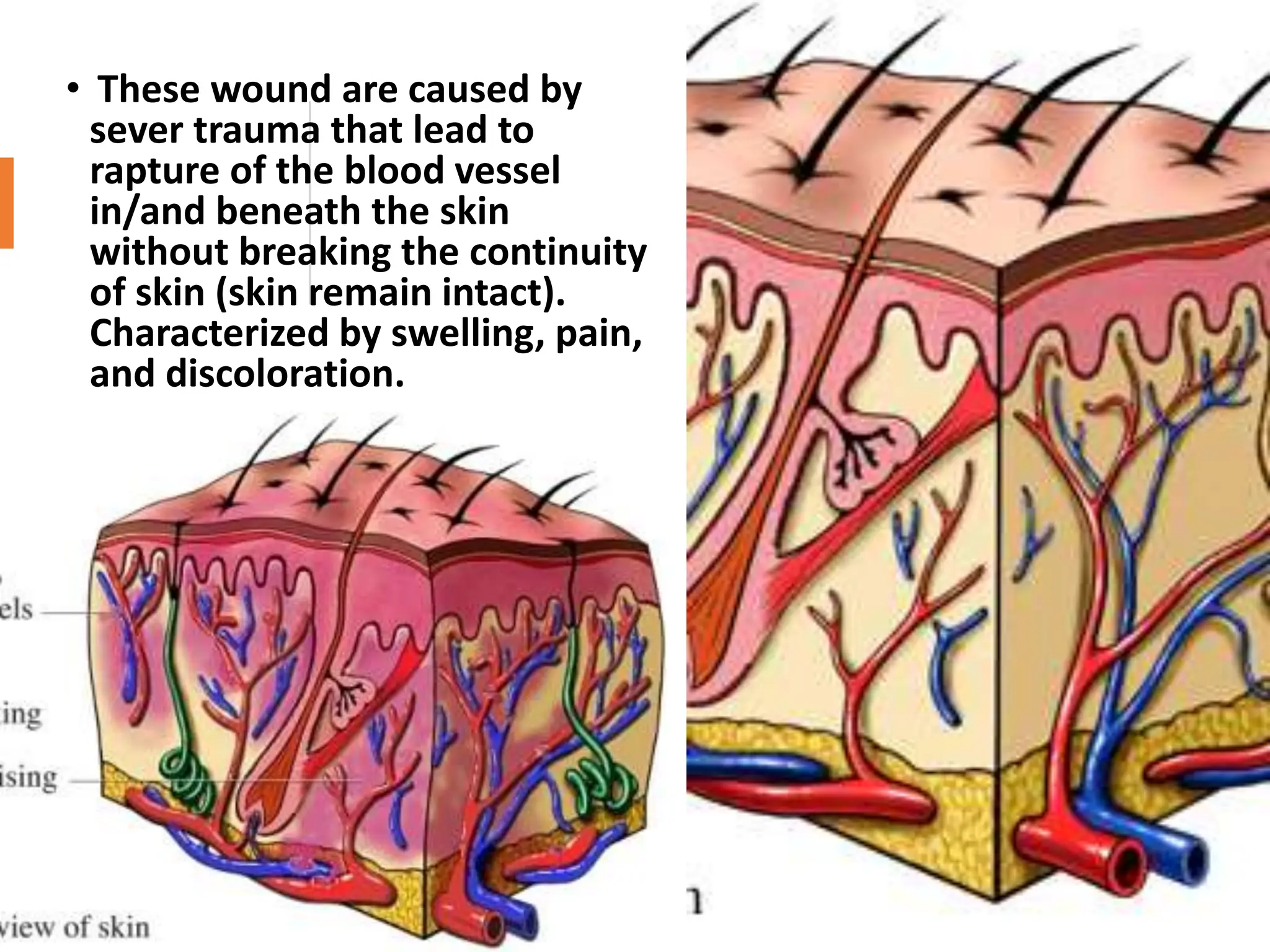
Subcutaneous wounds, such as bruises and muscle contusions, result from severe trauma causing blood vessel rupture beneath the skin while keeping the skin intact. These are categorized into three severity levels, ranging from minor ruptures causing mild symptoms to major ruptures leading to massive swelling and severe pain. Treatment varies by severity, including cold applications for first-degree contusions, aspiration for second-degree, and hot applications along with removal of necrotic tissue for third-degree contusions.