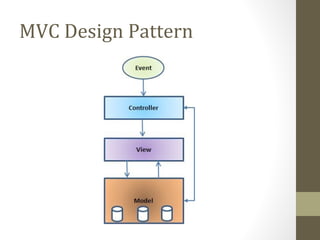
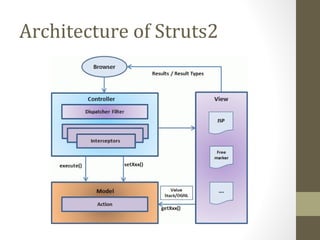
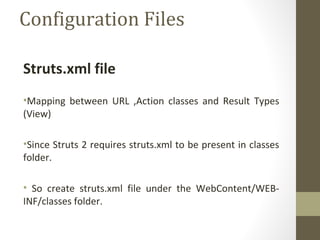
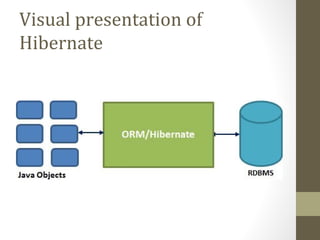
The document provides an agenda for a Struts 2 workshop over two days. Day 1 will cover understanding Struts 2 architecture and features, environment setup, and configuration. Attendees will learn about MVC design patterns, request lifecycle, interceptors, and results. They will also have a practical lab on Struts 2 applications and an introduction to Hibernate. Day 2 will involve further practical labs.