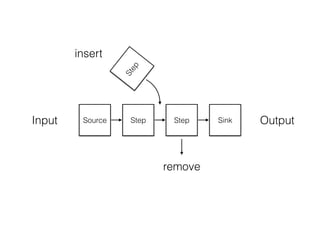
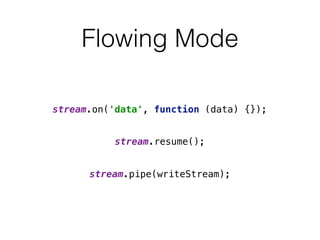
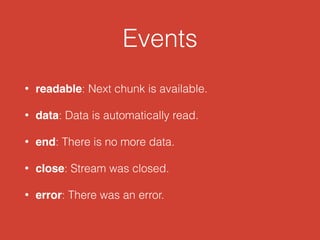
Streams allow connecting programs like connecting garden hoses. They provide a way to pipe input through multiple steps to an output. There are different types of streams like readable, writable, duplex, and transform streams. Common uses of streams in Node.js include http, fs, child processes, tcp, and zlib. Streams are event emitters that can be used to process data incrementally instead of all at once.





![Streams are EventEmitters
EventEmitter
Callbacks
Event
on(‘event’, callback)emit(‘event’ [, arg1][, arg2])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streams-151026152822-lva1-app6891/85/Streams-in-Node-js-7-320.jpg)









![Erros in ReadStreams
var rs = require('fs')
.createReadStream('nonExistant.txt');
rs.on('error', function (e) {
console.log('ERROR', e);
});
ERROR { [Error: ENOENT: no such file or directory, open 'nonExistant.txt']
errno: -2,
code: 'ENOENT',
syscall: 'open',
path: 'nonExistant.txt' }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streams-151026152822-lva1-app6891/85/Streams-in-Node-js-17-320.jpg)

























![Gulpvar gulp = require('gulp');
var babel = require('gulp-babel');
var concat = require('gulp-concat');
var uglify = require('gulp-uglify');
var rename = require('gulp-rename');
gulp.task('scripts', function() {
return gulp.src('js/*.js')
.pipe(concat('all.js'))
.pipe(gulp.dest('dist'))
.pipe(babel())
.pipe(rename('all.min.js'))
.pipe(uglify())
.pipe(gulp.dest('dist'));
});
gulp.task('default', ['scripts']);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streams-151026152822-lva1-app6891/85/Streams-in-Node-js-46-320.jpg)
![Gulp
$ gulp
[16:09:10] Using gulpfile /srv/basti/gulpfile.js
[16:09:10] Starting 'scripts'...
[16:09:10] Finished 'scripts' after 178 ms
[16:09:10] Starting 'default'...
[16:09:10] Finished 'default' after 13 μs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streams-151026152822-lva1-app6891/85/Streams-in-Node-js-47-320.jpg)

