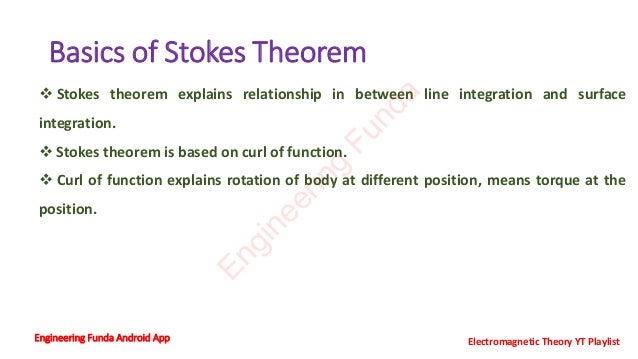
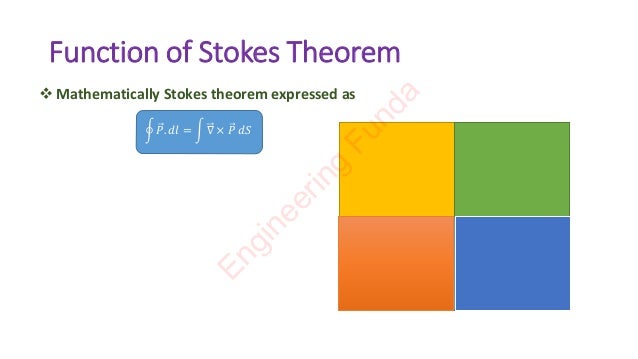
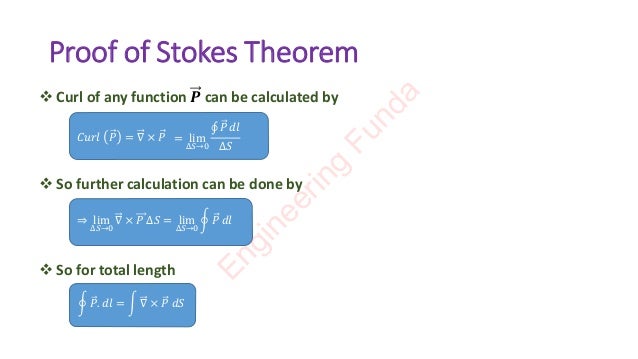
Stokes theorem explains the relationship between line integration and surface integration. It is based on the curl of a function, which describes the rotation of a body at different positions or torque. Stokes theorem mathematically equates the line integral of a vector field P around a closed curve C to the surface integral of the curl of P over any surface S bounded by C. It has various applications in fields like fluid mechanics, electromagnetics, and aerodynamics to understand the flow of fields.