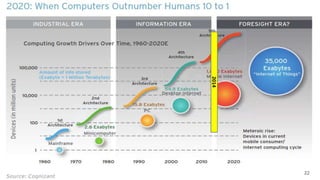
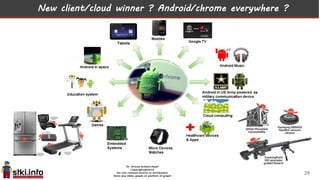
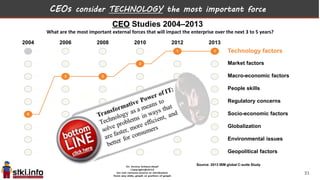
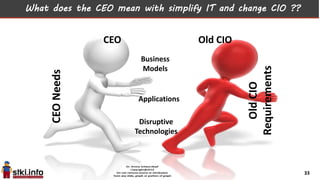
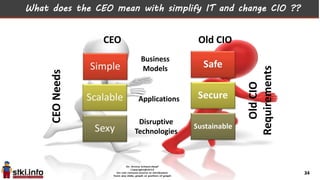
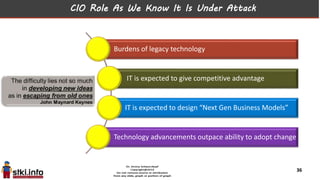
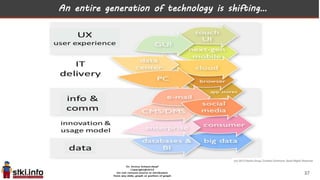
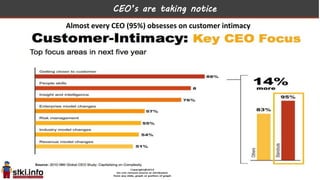
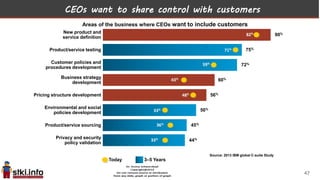
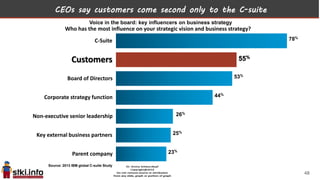
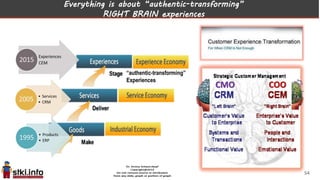
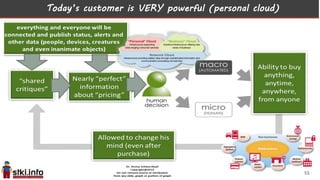
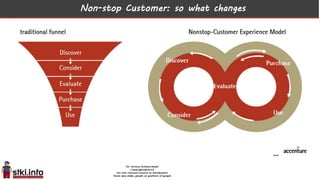
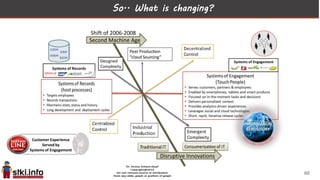
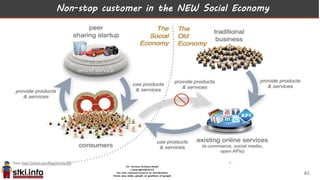
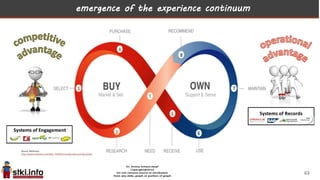
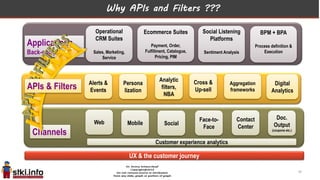
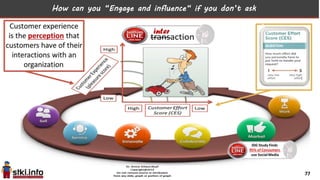
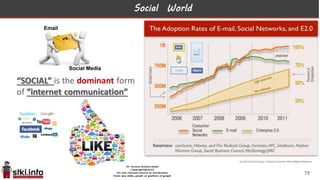
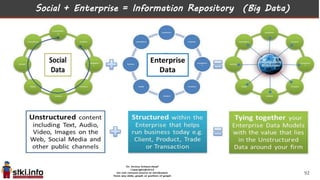
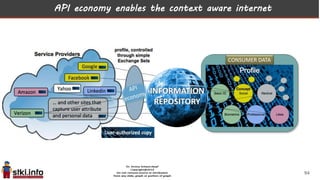
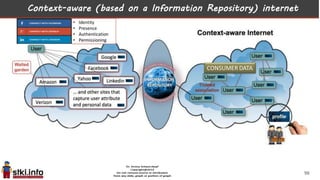
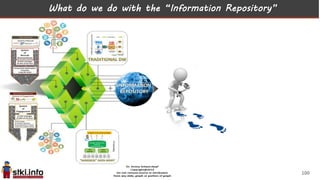
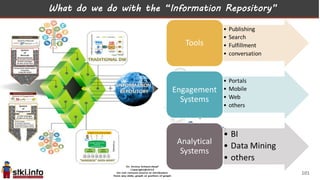
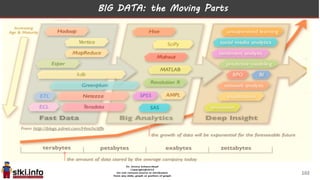
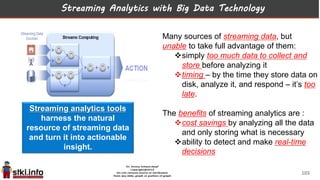
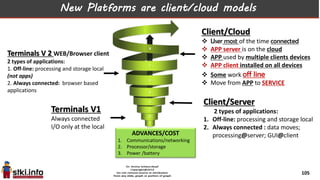
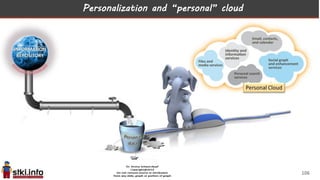
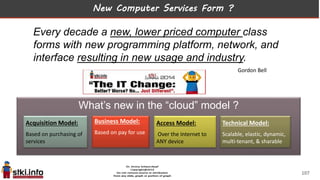
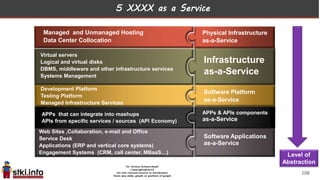
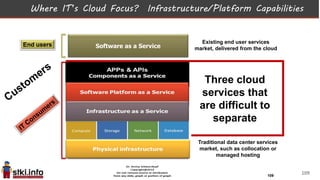
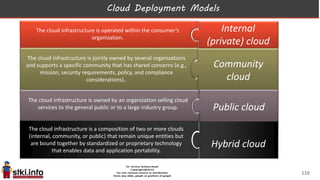
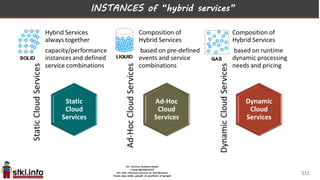
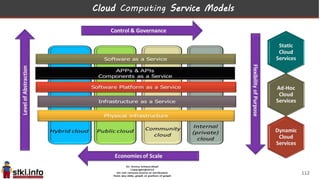
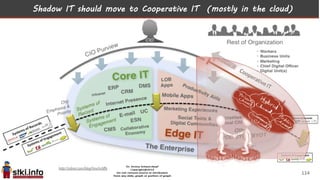
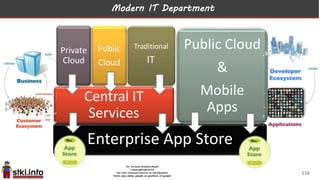
This document discusses trends in information technology and the changing role of the CIO. It notes that CIOs must now focus on both engaging customers through digital experiences as well as maintaining backend systems. There is a divide between traditional IT operations and new "engagement systems" focused on personalization, mobility, social media, and analytics. The role of the CIO is shifting from a focus on transactions to driving differentiation and innovation through customer-centric digital strategies. Mobility and creating engaging digital experiences for customers on any device are also discussed as top priorities.