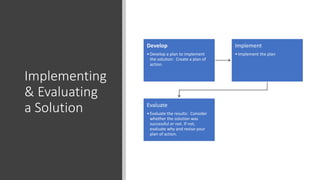
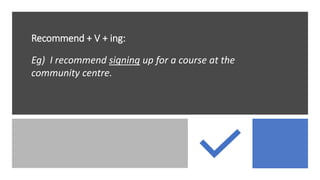
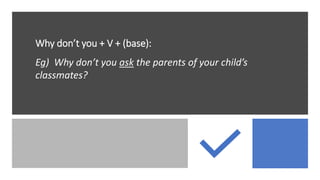
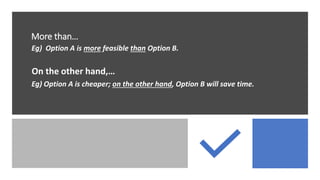
The document outlines steps for problem solving including identifying the problem, examining possible solution options, choosing the best solution based on pros and cons, developing a plan to implement the solution, implementing the plan, and evaluating the results. It also provides language for advising others and comparing/contrasting options such as suggesting, recommending, using adverbs of condition, and discussing similarities and differences.