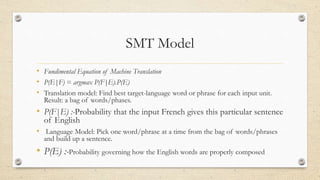
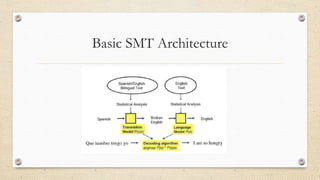
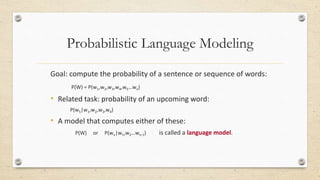
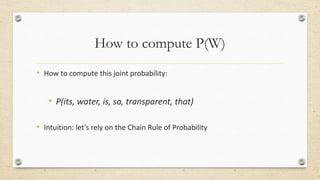
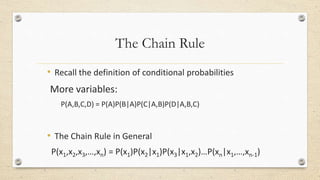
This document discusses statistical machine translation (SMT). It provides an overview of key concepts in SMT including word and sentence alignment, probability, language models, and translation models. The fundamental equation of SMT is presented as using a translation model to find the best target language words for the input and a language model to build up a sentence from those words. Basic SMT architecture and the Bayes' theorem and chain rule for calculating probabilities are also covered.