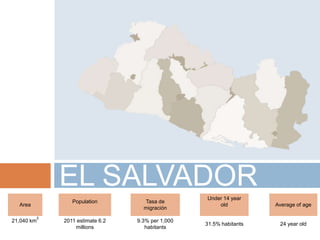
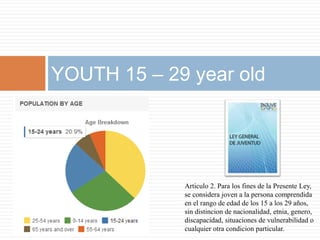
1) Youth in El Salvador, defined as ages 15-29, make up 31.5% of the population. Internet usage in El Salvador is low at 12.25% below the global average.
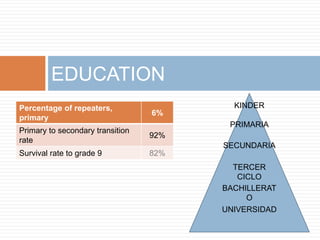
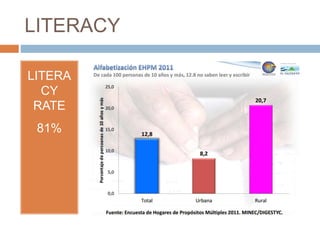
2) Education outcomes are poor, with only 81% literacy and high dropout rates, especially impacting rural youth. Poverty is a major barrier to education.
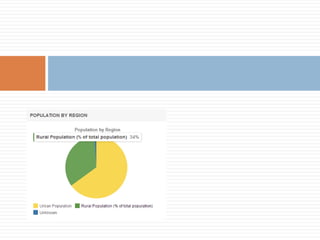
3) There are few employment opportunities for youth beyond low-paying informal work or agriculture. Rural youth struggle with work-school balance more than urban youth.