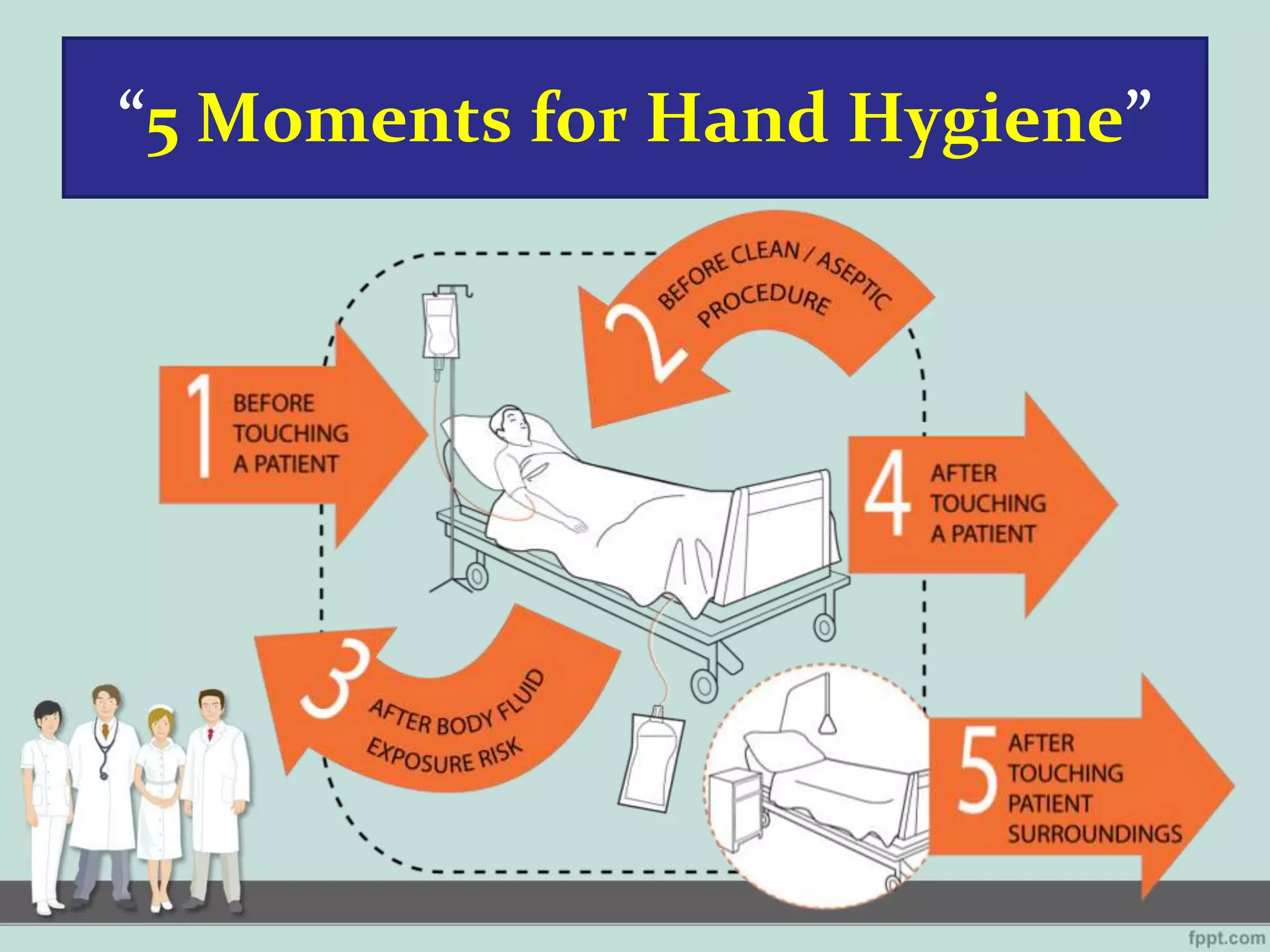
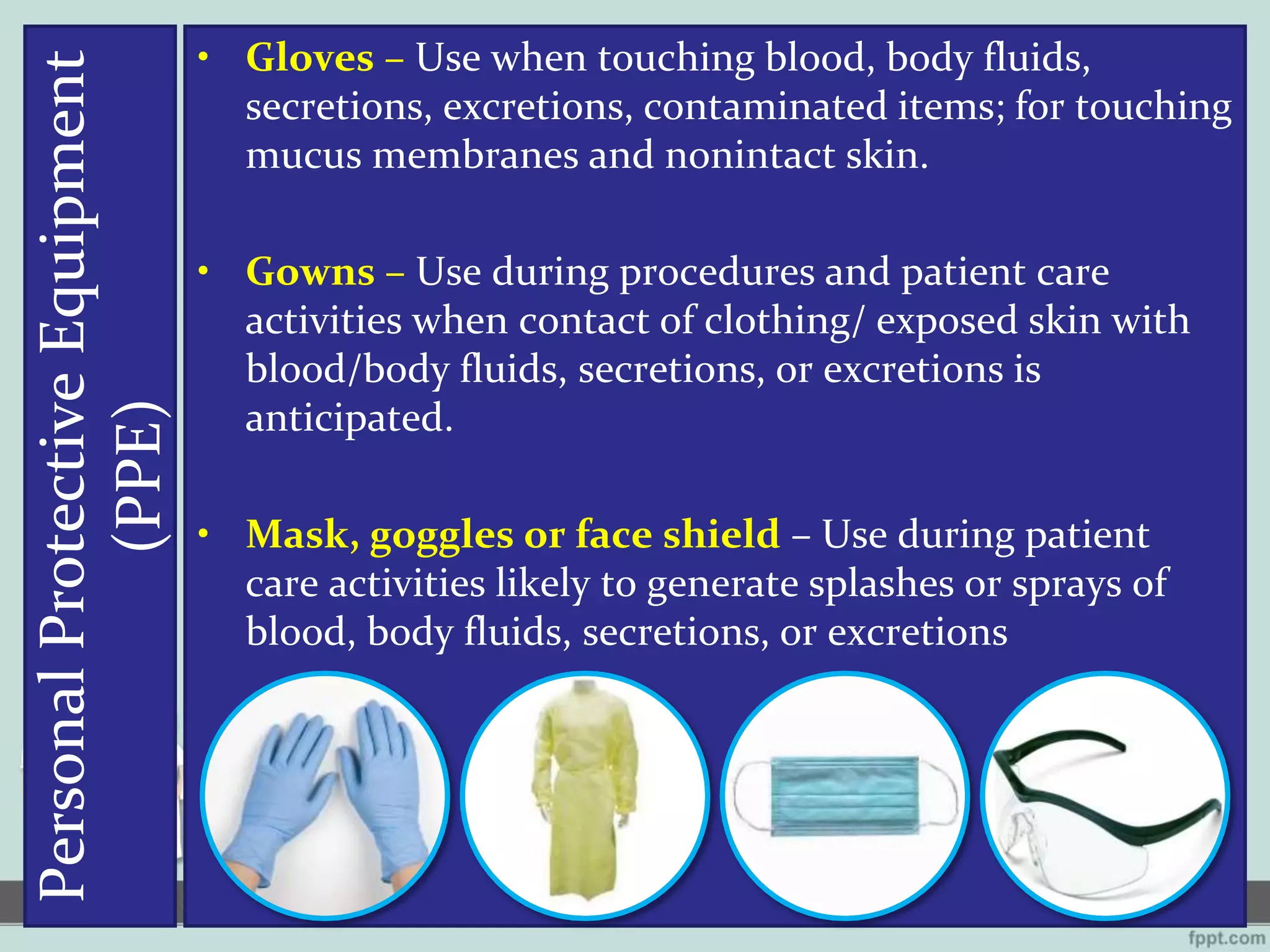
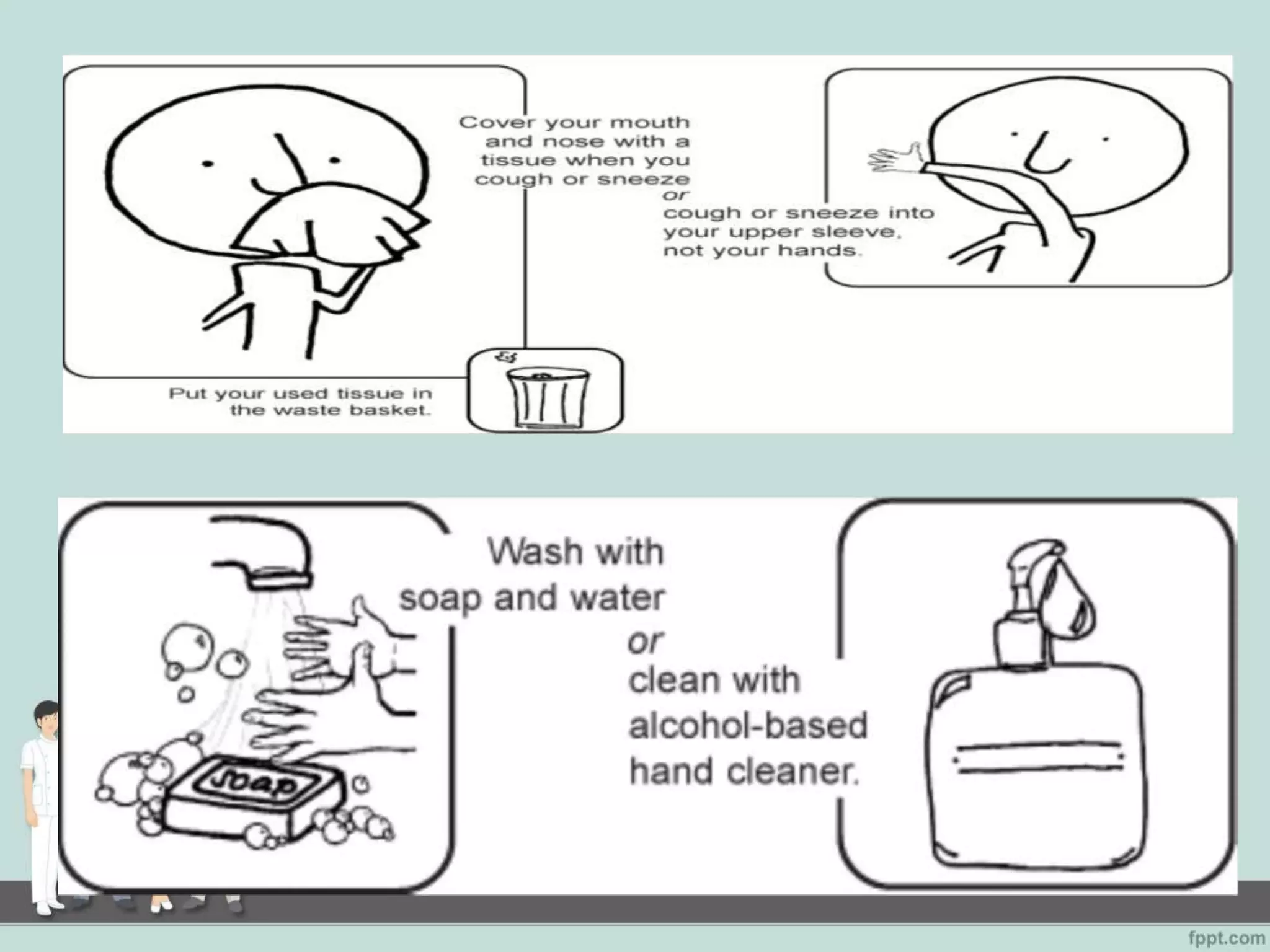
This document outlines standard precautions for infection control, including proper hand hygiene techniques, use of personal protective equipment like gloves and gowns, safe injection practices, and protocols for cleaning patient equipment and transport. It emphasizes applying these practices to all patient care to prevent transmission of pathogens through contact with blood, body fluids, secretions, or contaminated surfaces or equipment.