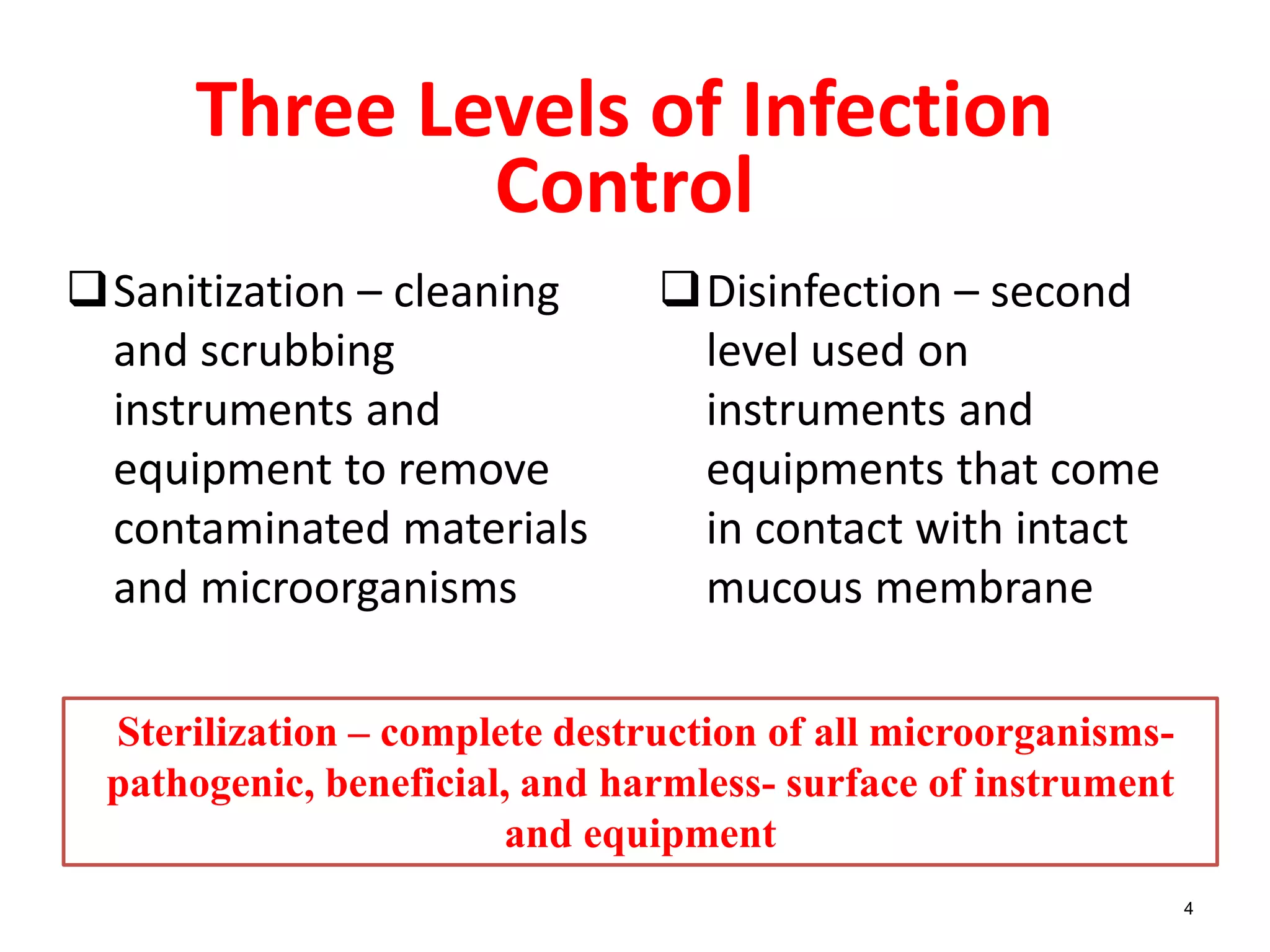
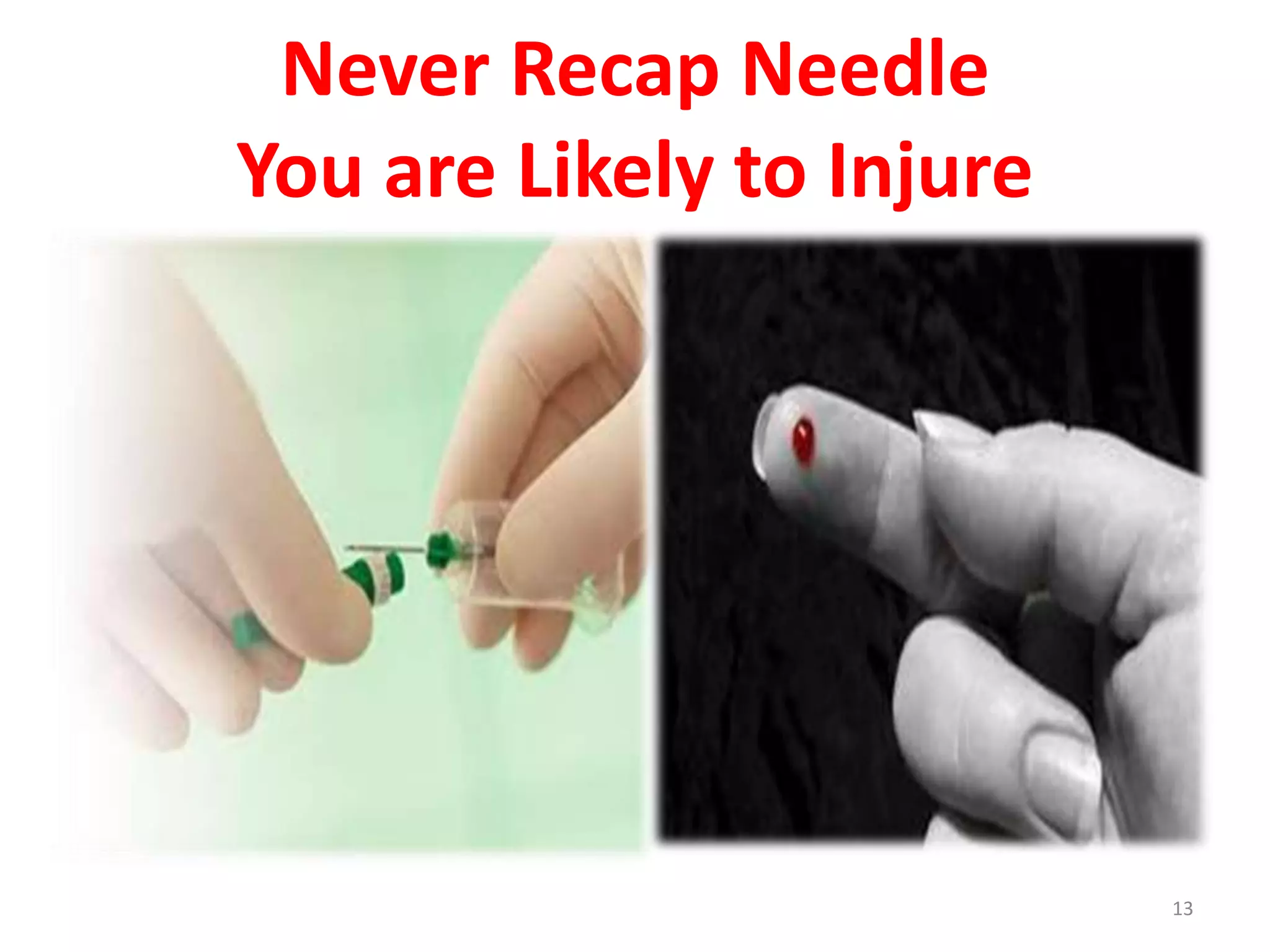
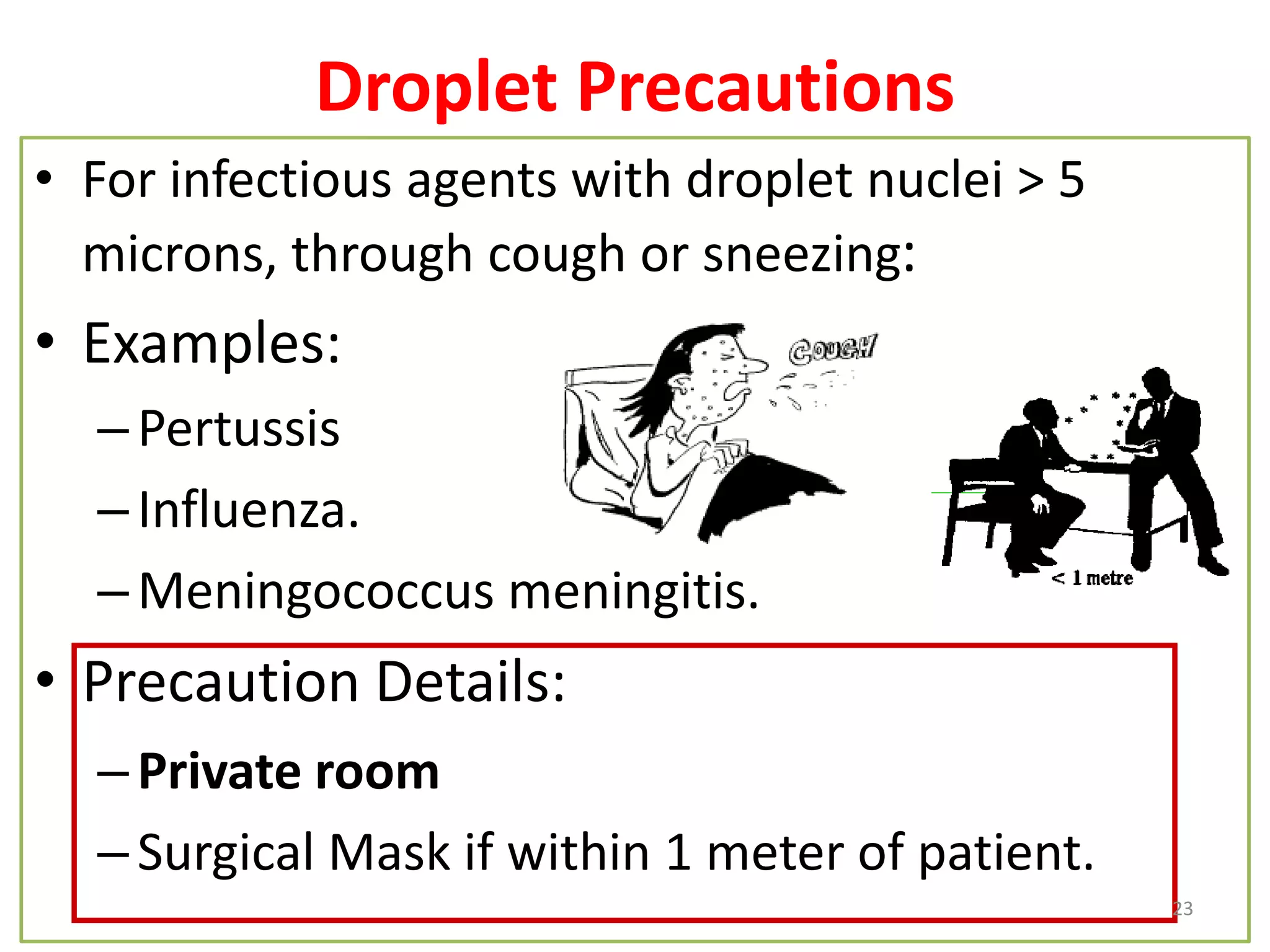
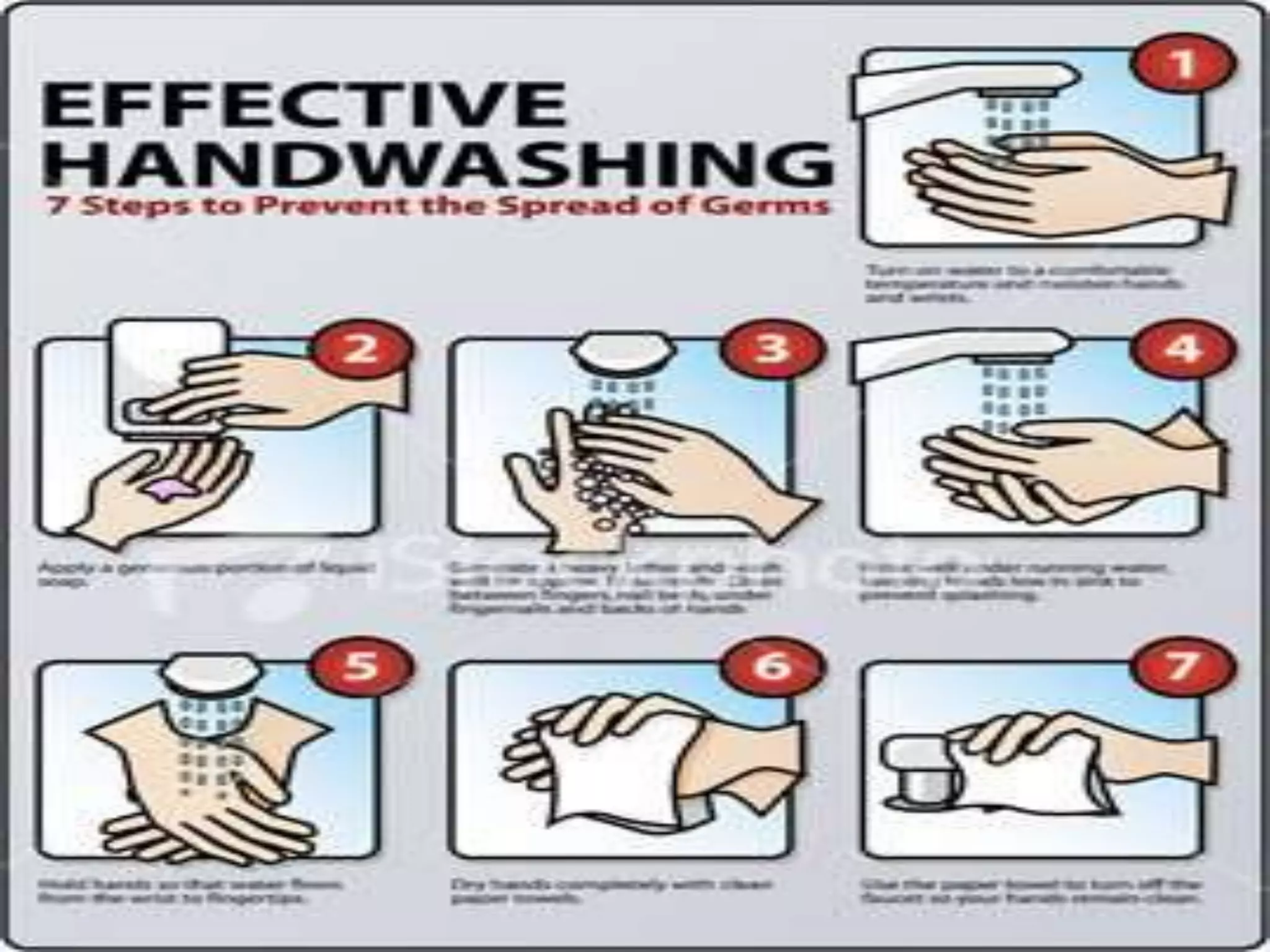
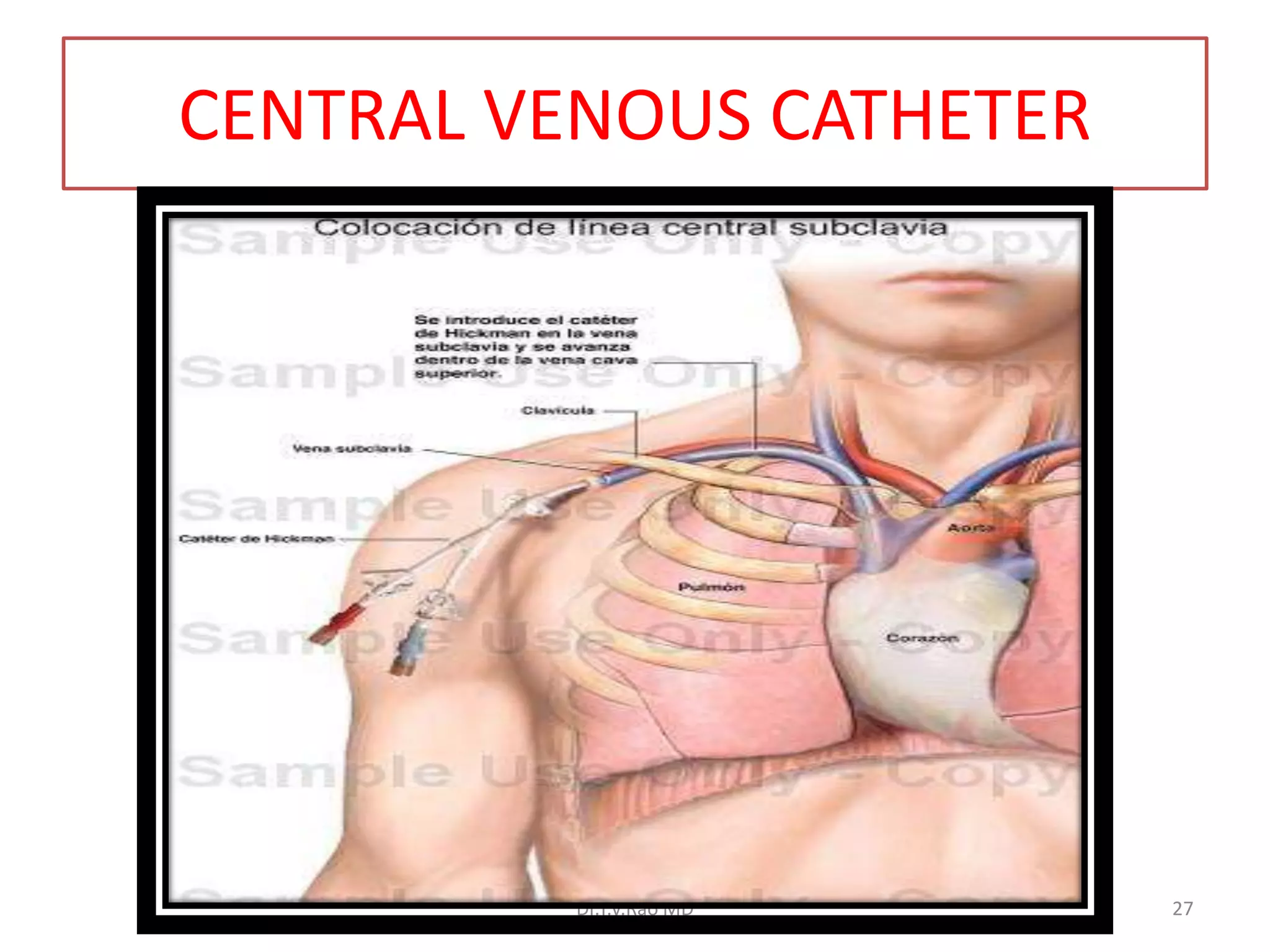
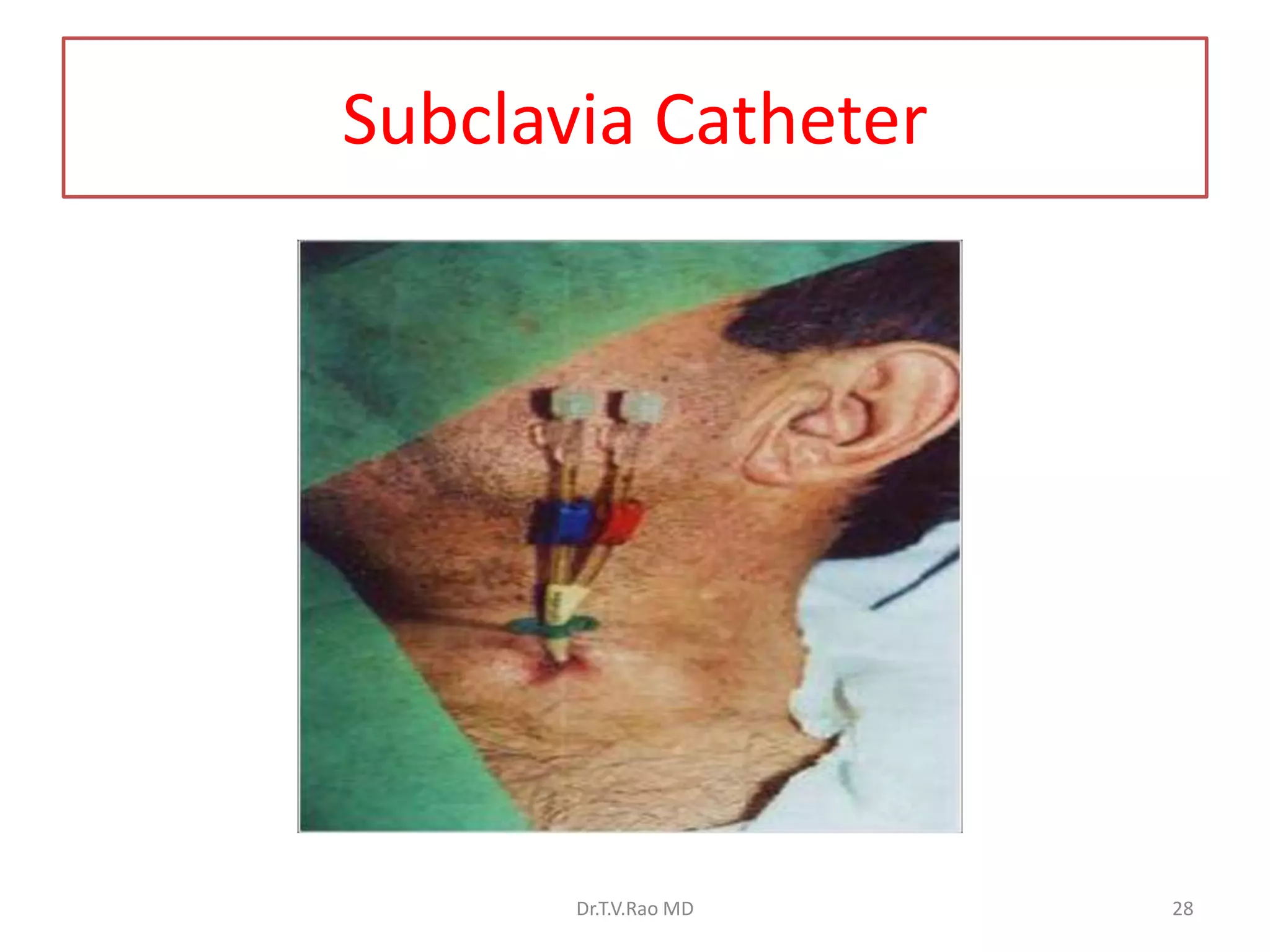
This document provides information on basic infection prevention practices for healthcare workers. It discusses three levels of infection control: sanitization, disinfection, and sterilization. It outlines proper sanitization methods including collecting, cleaning and drying instruments. Disinfection techniques are described for items that contact intact mucous membranes. The importance of hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment, and safe handling of needles and sharps waste is emphasized. Transmission-based precautions for droplet infections are also reviewed. The goal is to educate nursing staff on infection control programs to prevent spread of disease.